Green composites, made from natural fibers and biodegradable resins, offer superior environmental benefits and sustainability compared to traditional polymer composites, which rely on synthetic materials. In construction panels, green composites provide enhanced eco-friendliness, lower carbon footprint, and comparable mechanical strength, making them a preferred choice for sustainable building solutions.
Table of Comparison
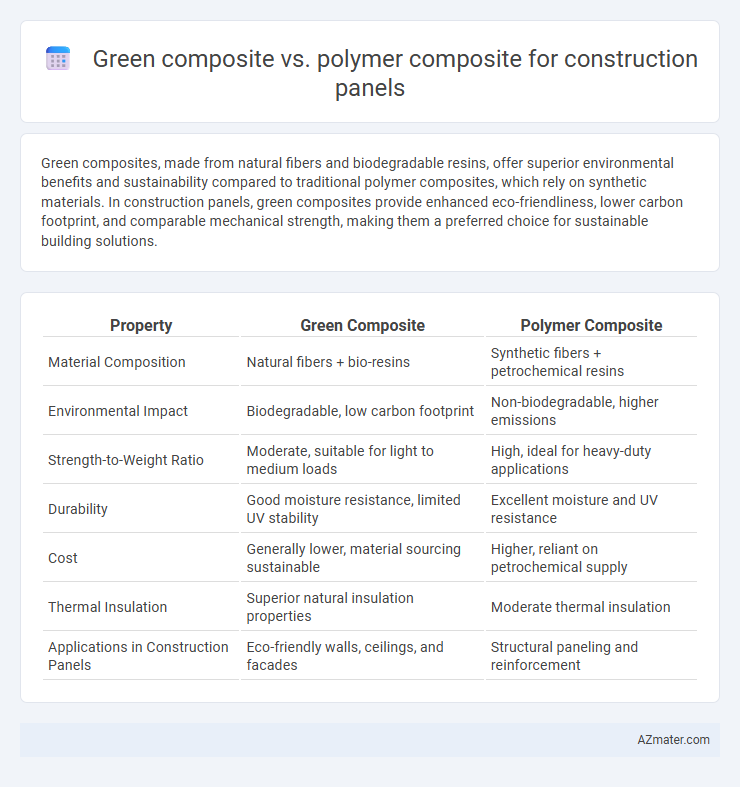
| Property | Green Composite | Polymer Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers + bio-resins | Synthetic fibers + petrochemical resins |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher emissions |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Moderate, suitable for light to medium loads | High, ideal for heavy-duty applications |
| Durability | Good moisture resistance, limited UV stability | Excellent moisture and UV resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower, material sourcing sustainable | Higher, reliant on petrochemical supply |
| Thermal Insulation | Superior natural insulation properties | Moderate thermal insulation |
| Applications in Construction Panels | Eco-friendly walls, ceilings, and facades | Structural paneling and reinforcement |
Introduction to Construction Panels
Construction panels serve as essential components in building structures, offering support, insulation, and durability. Green composites, made from natural fibers and biodegradable resins, provide eco-friendly alternatives with reduced environmental impact and enhanced sustainability. Polymer composites, composed of synthetic fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, deliver high strength and moisture resistance but often lack the biodegradability found in green composites.
Overview of Green Composites
Green composites for construction panels incorporate natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute combined with biodegradable resins, offering enhanced sustainability and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional polymer composites. These composites provide excellent thermal insulation, moisture resistance, and mechanical strength while significantly lowering carbon footprint through renewable materials and lower energy consumption during production. The integration of green composites supports circular economy principles by enabling recyclability and biodegradability, making them increasingly viable for eco-friendly construction applications.
Overview of Polymer Composites
Polymer composites for construction panels consist of a polymer matrix reinforced with fibers such as glass, carbon, or aramid, offering high strength-to-weight ratios and durability. These composites provide excellent resistance to corrosion, weathering, and chemical exposure, making them suitable for harsh environmental conditions in construction applications. The versatility and ease of fabrication of polymer composites allow for customizable mechanical properties and design flexibility compared to traditional materials.
Material Composition and Sourcing
Green composites for construction panels primarily use natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute combined with bio-based resins derived from renewable resources, ensuring reduced environmental impact and enhanced sustainability. Polymer composites typically consist of synthetic fibers like glass or carbon reinforced with petroleum-based resins, which offer high mechanical strength but rely heavily on non-renewable raw materials. Material sourcing for green composites emphasizes local and biodegradable inputs, minimizing carbon footprint and waste, whereas polymer composites depend on global petrochemical supply chains with higher energy consumption and ecological concerns.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Green composites, typically composed of natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute combined with bio-based resins, exhibit lower density and higher specific strength compared to conventional polymer composites, making them advantageous for lightweight construction panels. Polymer composites, often reinforced with synthetic fibers like glass or carbon, demonstrate superior tensile strength, stiffness, and impact resistance, which enhances durability and load-bearing capacity in structural applications. The mechanical performance of green composites is improving with advancements in fiber treatment and resin formulations, narrowing the gap with polymer composites while offering enhanced sustainability and environmental benefits.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Green composites, made from natural fibers and bio-based resins, significantly reduce carbon footprint and minimize toxic emissions compared to traditional polymer composites derived from petroleum. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) studies highlight green composites' superior biodegradability and lower energy consumption during production, contributing to sustainable construction practices. Incorporating green composites in construction panels enhances environmental performance by reducing waste generation and reliance on non-renewable resources.
Durability and Lifespan
Green composites, made from natural fibers and bio-based resins, offer enhanced environmental benefits but generally have lower durability and shorter lifespan compared to polymer composites in construction panels. Polymer composites, such as fiberglass-reinforced polymers, provide superior resistance to moisture, UV radiation, and mechanical stress, resulting in longer-lasting performance. The degradation rate of green composites is typically higher due to organic fiber susceptibility, making polymer composites more suitable for applications requiring extended durability and longevity.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Green composites typically exhibit lower raw material costs compared to polymer composites, as they utilize natural fibers like hemp or flax instead of synthetic reinforcements. Manufacturing processes of green composites often demand less energy, reducing overall production expenses and enhancing economic feasibility for large-scale construction panels. Although polymer composites can provide superior mechanical strength, their higher material and processing costs usually result in elevated capital investment and longer payback periods in construction applications.
Applications in Construction Industry
Green composites, made from natural fibers like hemp or flax combined with biodegradable resins, offer sustainable solutions for construction panels by enhancing insulation and reducing environmental impact. Polymer composites, often reinforced with glass or carbon fibers, provide superior mechanical strength and durability, making them ideal for structural applications requiring high load-bearing capacity. In the construction industry, green composites are preferred for eco-friendly interior panels and acoustic insulation, whereas polymer composites are widely used in exterior cladding and load-bearing wall panels due to their robustness and weather resistance.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Green composites in construction panels are increasingly favored due to their biodegradability, reduced carbon footprint, and utilization of renewable natural fibers like hemp and flax, enhancing sustainability. Innovations in polymer composites emphasize improving recyclability and integrating nanomaterials such as graphene to boost mechanical strength and thermal insulation. Future prospects highlight hybrid composites combining green fibers with advanced polymers to achieve optimal durability, cost-effectiveness, and environmental resilience in building applications.
Infographic: Green composite vs Polymer composite for Construction panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com