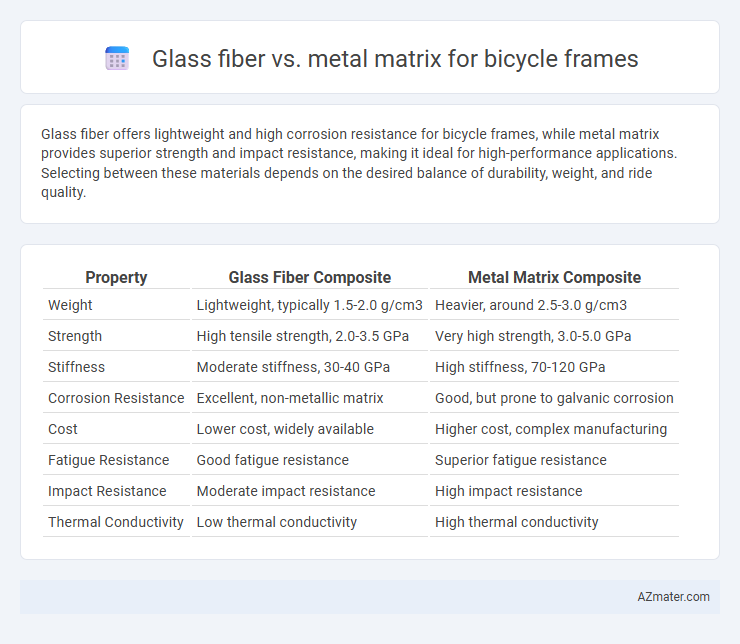
Glass fiber offers lightweight and high corrosion resistance for bicycle frames, while metal matrix provides superior strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Selecting between these materials depends on the desired balance of durability, weight, and ride quality.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber Composite | Metal Matrix Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight, typically 1.5-2.0 g/cm3 | Heavier, around 2.5-3.0 g/cm3 |
| Strength | High tensile strength, 2.0-3.5 GPa | Very high strength, 3.0-5.0 GPa |
| Stiffness | Moderate stiffness, 30-40 GPa | High stiffness, 70-120 GPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, non-metallic matrix | Good, but prone to galvanic corrosion |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, complex manufacturing |
| Fatigue Resistance | Good fatigue resistance | Superior fatigue resistance |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate impact resistance | High impact resistance |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low thermal conductivity | High thermal conductivity |
Introduction to Bicycle Frame Materials
Glass fiber and metal matrix composites represent two advanced materials used in bicycle frame construction, each offering distinct mechanical properties and performance benefits. Glass fiber provides excellent tensile strength, lightweight characteristics, and vibration damping, making it suitable for comfort-oriented and cost-effective frames. Metal matrix composites combine lightweight metal alloys, typically aluminum or magnesium, with reinforcing fibers to achieve superior strength, stiffness, and impact resistance, favoring high-performance and durability in racing and off-road bicycles.
Overview of Glass Fiber Composites
Glass fiber composites for bicycle frames offer high tensile strength and lightweight properties, making them ideal for performance cycling. These composites consist of glass fibers embedded in a polymer resin matrix, delivering excellent corrosion resistance and vibration damping compared to metal matrix frames. The efficient load distribution and fatigue resistance of glass fiber composites contribute to enhanced ride comfort and durability in various cycling conditions.
Metal Matrix Composites Explained
Metal matrix composites (MMCs) used in bicycle frames combine metal alloys like aluminum or titanium with ceramic fibers or particles, offering superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to traditional glass fiber composites. MMCs provide enhanced stiffness, improved fatigue resistance, and better thermal conductivity, making frames more durable and responsive under high stress. Their higher cost and complex manufacturing processes are offset by performance gains prized in high-end cycling applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Glass fiber bicycle frames offer excellent tensile strength and flexibility, making them resistant to fatigue and impact damage. Metal matrix frames, particularly those reinforced with aluminum or titanium alloys, provide superior overall strength and higher resistance to deformation under heavy loads. Durability in metal matrix composites typically surpasses glass fiber due to enhanced wear resistance and improved performance in extreme environmental conditions.
Weight and Performance Analysis
Glass fiber bicycle frames typically offer lighter weight compared to metal matrix frames due to the high strength-to-weight ratio of composite materials. Metal matrix frames, often made from aluminum or titanium alloys reinforced with ceramic particles, provide superior stiffness and durability but usually result in increased frame weight. Performance analysis reveals that glass fiber frames excel in vibration damping and comfort, while metal matrix frames deliver enhanced power transfer and impact resistance, influencing the choice based on rider priorities.
Ride Quality and Comfort Factors
Glass fiber bicycle frames offer superior vibration damping due to their flexibility and resilience, resulting in a smoother, more comfortable ride on rough surfaces. Metal matrix frames, often aluminum or titanium composites, provide increased stiffness and strength but can transmit more road vibrations, potentially reducing comfort during long rides. Riders prioritizing ride quality and shock absorption typically favor glass fiber, while those seeking enhanced power transfer and frame rigidity might prefer metal matrix options despite minor comfort trade-offs.
Cost and Accessibility
Glass fiber bicycle frames typically offer lower manufacturing costs due to inexpensive raw materials and simpler production processes, making them more accessible to a broader range of consumers. Metal matrix frames, often made from aluminum or titanium composites, incur higher costs because of advanced fabrication techniques and specialized materials, limiting accessibility to premium market segments. The affordability of glass fiber frames encourages widespread use among casual riders, while metal matrix frames target enthusiasts seeking performance despite the increased expense.
Repairability and Maintenance
Glass fiber bicycle frames offer superior corrosion resistance and ease of patch repairs using epoxy resin, making maintenance straightforward and cost-effective. Metal matrix frames, often aluminum or titanium composites, require specialized equipment for welding or machining during repairs, which can increase downtime and repair costs. Regular inspections for microcracks are crucial for both materials, but glass fiber frames allow for simpler on-site fixes compared to metal matrix alternatives.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Glass fiber bicycle frames offer lower environmental impact due to their lightweight nature and energy-efficient production processes, which result in reduced carbon emissions compared to metal matrix frames. Metal matrix composites, often incorporating aluminum or titanium, involve energy-intensive extraction and processing, contributing to higher greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. Recycling challenges exist for both materials, but glass fiber composites can be more difficult to recycle effectively, while metal matrix frames benefit from established metal recycling infrastructure, impacting overall sustainability profiles.
Which Material is Best for Your Riding Style?
Glass fiber composite offers excellent vibration damping and lightweight properties ideal for endurance riders seeking comfort on long distances. Metal matrix composites provide superior stiffness and impact resistance, making them suitable for aggressive riders who prioritize power transfer and durability in demanding terrains. Choosing the best material depends on your riding style: opt for glass fiber if smoothness and weight savings are top priorities, or metal matrix for responsiveness and rugged performance.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Metal matrix for Bicycle frame
 azmater.com
azmater.com