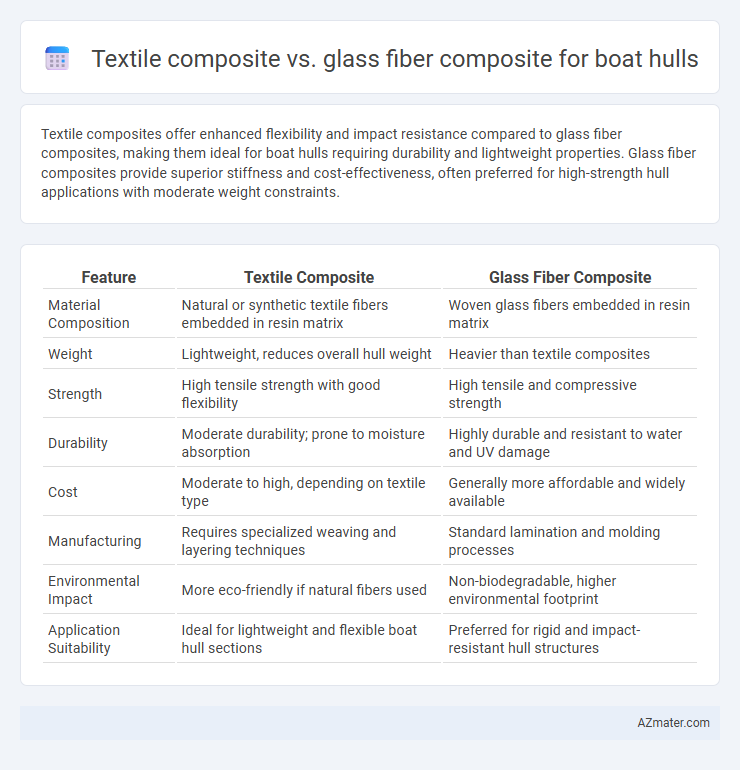
Textile composites offer enhanced flexibility and impact resistance compared to glass fiber composites, making them ideal for boat hulls requiring durability and lightweight properties. Glass fiber composites provide superior stiffness and cost-effectiveness, often preferred for high-strength hull applications with moderate weight constraints.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Textile Composite | Glass Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural or synthetic textile fibers embedded in resin matrix | Woven glass fibers embedded in resin matrix |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces overall hull weight | Heavier than textile composites |
| Strength | High tensile strength with good flexibility | High tensile and compressive strength |
| Durability | Moderate durability; prone to moisture absorption | Highly durable and resistant to water and UV damage |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on textile type | Generally more affordable and widely available |
| Manufacturing | Requires specialized weaving and layering techniques | Standard lamination and molding processes |
| Environmental Impact | More eco-friendly if natural fibers used | Non-biodegradable, higher environmental footprint |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for lightweight and flexible boat hull sections | Preferred for rigid and impact-resistant hull structures |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Textile composites and glass fiber composites are prominent materials in boat hull construction due to their strength-to-weight ratios and durability. Textile composites offer enhanced flexibility and impact resistance through woven fibers such as carbon or aramid, while glass fiber composites provide cost-effective stiffness and corrosion resistance using E-glass fibers. Selecting the appropriate material involves evaluating mechanical properties, environmental exposure, and weight constraints critical for marine performance and safety.
Overview of Textile Composites
Textile composites for boat hulls consist of woven or non-woven fibers such as carbon, aramid, or hybrid blends embedded in a resin matrix, offering enhanced flexibility and impact resistance compared to traditional glass fiber composites. These composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratios, improved fatigue resistance, and better vibration dampening, making them ideal for high-performance marine applications. Innovations in textile architecture and resin infusion techniques allow for tailored mechanical properties and design versatility, boosting overall hull durability and efficiency.
Glass Fiber Composites Explained
Glass fiber composites are widely used for boat hulls due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness compared to textile composites. These composites consist of glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, providing excellent durability and impact resistance essential for marine environments. Their versatility and ease of fabrication make glass fiber composites the preferred choice for lightweight, robust, and affordable boat hull construction.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Textile composites exhibit superior impact resistance and flexibility compared to glass fiber composites, making them ideal for absorbing dynamic loads on boat hulls. Glass fiber composites offer higher tensile strength and stiffness, providing excellent structural rigidity essential for hull durability and performance. The balance between the enhanced toughness of textile composites and the strength of glass fibers determines the optimal choice for specific marine applications.
Weight and Performance Analysis
Textile composites exhibit superior weight reduction compared to glass fiber composites, significantly enhancing boat hull speed and fuel efficiency. Glass fiber composites, while heavier, offer high tensile strength and impact resistance, improving hull durability in harsh marine environments. The choice between these materials hinges on balancing lightweight performance benefits of textile composites against the robustness and cost-effectiveness of glass fiber composites for optimal boat hull design.
Durability and Lifespan Differences
Textile composites, often utilizing carbon or aramid fibers, offer superior tensile strength and resistance to fatigue compared to glass fiber composites, enhancing the overall durability of boat hulls in demanding marine environments. Glass fiber composites, while more cost-effective and easier to manufacture, tend to exhibit lower impact resistance and a shorter lifespan due to susceptibility to water ingress and UV degradation. The advanced resin systems used with textile composites further extend hull lifespan by minimizing matrix cracking and delamination under cyclic stresses.
Cost Efficiency and Affordability
Textile composites generally offer greater cost efficiency for boat hull construction due to lower raw material costs and simpler manufacturing processes compared to glass fiber composites. Glass fiber composites, while more expensive, provide superior strength-to-weight ratios and durability, which can reduce long-term maintenance expenses. For budget-conscious projects, textile composites present a more affordable option without significant compromises in performance for small to mid-sized watercraft.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Textile composites for boat hulls typically use natural fibers such as flax or hemp, which offer biodegradability and lower carbon footprints compared to glass fiber composites made from energy-intensive glass manufacturing. Glass fiber composites generate significant CO2 emissions during production and are challenging to recycle, contributing to landfill waste and environmental pollution. The adoption of natural fiber textile composites promotes sustainability through renewable resources, reduced energy consumption, and potential for compostability at end-of-life.
Maintenance Requirements and Repairability
Textile composites for boat hulls generally offer enhanced flexibility and easier localized repairs compared to glass fiber composites, which tend to be more rigid and require specialized tools for maintenance. Glass fiber composites boast higher durability and resistance to environmental factors, yet their repair process often involves extensive sanding, layering, and curing to restore structural integrity. Maintenance of textile composites often involves routine inspection and minor patching, whereas glass fiber composites demand more labor-intensive procedures to address cracks or delamination effectively.
Choosing the Right Composite for Boat Hulls
Textile composites offer enhanced flexibility and impact resistance, making them ideal for boat hulls exposed to dynamic marine environments. Glass fiber composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratios and excellent stiffness, ensuring durability and structural integrity in larger vessels. Selecting the right composite depends on balancing performance requirements, cost considerations, and specific application demands in marine construction.
Infographic: Textile composite vs Glass fiber composite for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com