Wood plastic composite flooring offers superior moisture resistance and durability compared to oriented strand board, which is more prone to water damage and warping. Oriented strand board is cost-effective and provides structural strength but lacks the long-term resilience of wood plastic flooring materials.
Table of Comparison
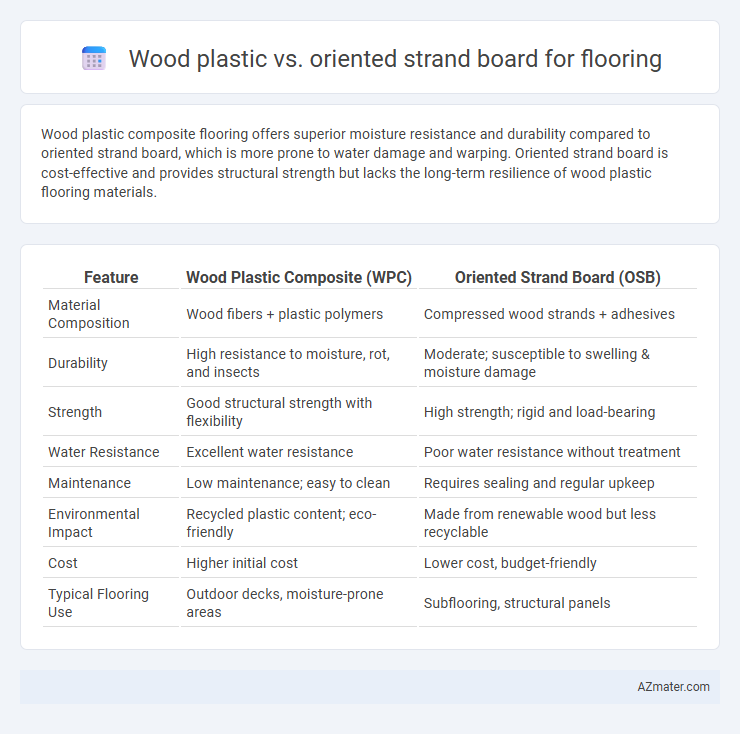
| Feature | Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) | Oriented Strand Board (OSB) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood fibers + plastic polymers | Compressed wood strands + adhesives |
| Durability | High resistance to moisture, rot, and insects | Moderate; susceptible to swelling & moisture damage |
| Strength | Good structural strength with flexibility | High strength; rigid and load-bearing |
| Water Resistance | Excellent water resistance | Poor water resistance without treatment |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; easy to clean | Requires sealing and regular upkeep |
| Environmental Impact | Recycled plastic content; eco-friendly | Made from renewable wood but less recyclable |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly |
| Typical Flooring Use | Outdoor decks, moisture-prone areas | Subflooring, structural panels |
Introduction to Wood Plastic and Oriented Strand Board
Wood plastic composite (WPC) is a durable material made from a blend of wood fibers and thermoplastics, offering enhanced moisture resistance and low maintenance ideal for flooring applications. Oriented strand board (OSB) consists of compressed wood strands arranged in layers, providing structural strength and cost-effectiveness commonly used as subflooring. Both materials serve distinct flooring purposes, with WPC excelling in moisture-prone environments and OSB preferred for foundational support.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Wood plastic composites (WPC) are made by combining wood fibers or sawdust with thermoplastic polymers through an extrusion or molding process, resulting in a durable, moisture-resistant material ideal for flooring. Oriented strand board (OSB) consists of large, thin wood strands layered in specific orientations and bonded with waterproof adhesives under heat and pressure, producing a strong structural panel commonly used as a subfloor. The manufacturing of WPC involves blending recycled plastics with wood fibers, enhancing durability and water resistance, whereas OSB relies on wood strand alignment and resin curing to achieve strength and load-bearing capacity.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Wood plastic composites (WPC) offer superior moisture resistance and dimensional stability compared to Oriented Strand Board (OSB), making WPC more durable in humid or wet environments. OSB has high structural strength due to its layered wood strands bonded with resin, but it is prone to swelling and delamination when exposed to prolonged moisture. For flooring applications requiring long-term strength and resistance to environmental damage, wood plastic composites provide enhanced durability and maintenance benefits over OSB.
Moisture and Water Resistance
Wood plastic composites (WPC) offer superior moisture and water resistance compared to Oriented Strand Board (OSB), making WPC a more durable option for flooring in wet or humid environments. OSB tends to absorb water, leading to swelling, warping, and eventual structural degradation, whereas WPC's synthetic components provide enhanced water repellency and dimensional stability. This moisture resistance significantly reduces the risk of mold and mildew growth, extending the flooring's lifespan and maintaining structural integrity.
Installation Methods and Ease
Wood plastic composite (WPC) flooring features click-lock installation systems that enable quick, tool-free assembly, making it highly user-friendly for DIY projects. Oriented Strand Board (OSB), while primarily used as subflooring, requires nailing or screwing to secure it, and its surface must typically be covered with another layer for flooring purposes, adding complexity to the installation process. WPC's moisture resistance and uniform thickness contribute to easier leveling and alignment compared to OSB, which can warp or swell if exposed to moisture during installation.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Wood plastic composite (WPC) flooring generally offers a higher upfront cost compared to oriented strand board (OSB) due to its synthetic components and advanced manufacturing processes. OSB is significantly more affordable, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious construction projects and subflooring applications. Considering long-term durability and maintenance, WPC may provide better economic value through reduced repairs and enhanced lifespan, offsetting initial investment over time.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Wood plastic composite flooring utilizes recycled plastics and wood fibers, reducing landfill waste and promoting circular economy principles, while oriented strand board (OSB) is made from fast-growing, small-diameter trees that maximize wood utilization with minimal waste. Both materials offer renewable options; however, OSB has a lower embodied energy compared to wood plastic composites, which require plastic processing and have challenges with end-of-life recyclability. The choice between wood plastic and OSB flooring ultimately balances recycled content, resource renewability, and carbon footprint considerations within sustainable building practices.
Maintenance and Longevity
Wood plastic composite flooring offers superior resistance to moisture, insects, and rot, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and extended durability compared to oriented strand board (OSB). OSB flooring is susceptible to swelling and delamination when exposed to water, necessitating more frequent repairs and protective treatments to maintain structural integrity. The lifespan of wood plastic flooring can exceed 25 years with minimal upkeep, while OSB typically requires replacement or refinishing within 10-15 years due to wear and environmental damage.
Aesthetic Appearance and Design Options
Wood plastic composite flooring offers a sleek, uniform appearance with a variety of colors and textured finishes that mimic natural wood, providing versatile design options for modern interiors. Oriented strand board (OSB), with its distinctive, flaky wood strand pattern, delivers a unique rustic aesthetic that is less refined but valued in industrial or contemporary designs. Both materials allow customization, yet wood plastic composites provide more consistent visual appeal and rich design flexibility compared to the inherently patterned OSB.
Best Applications and Recommendations for Flooring
Wood plastic composites (WPC) excel in moisture resistance and durability, making them ideal for areas prone to humidity such as basements and bathrooms. Oriented strand board (OSB) offers structural strength and cost-effectiveness, best suited for subflooring and underlayment in dry, indoor environments. For flooring applications requiring longevity and low maintenance, WPC is recommended, while OSB is preferred for foundational support beneath finish flooring materials.
Infographic: Wood plastic vs Oriented strand board for Flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com