Glass fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and durability for automotive interiors compared to natural fibers. Natural fibers provide enhanced sustainability and biodegradability but typically exhibit lower mechanical performance and moisture resistance.
Table of Comparison
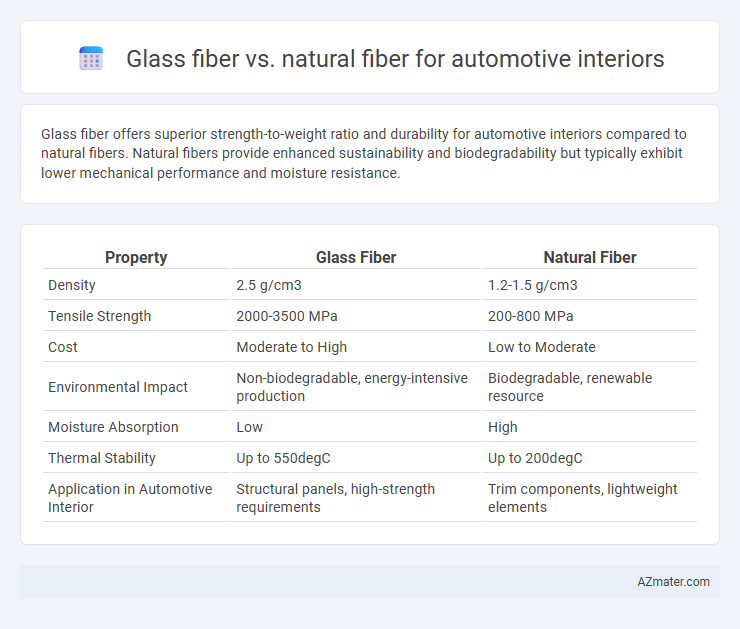
| Property | Glass Fiber | Natural Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 | 1.2-1.5 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 2000-3500 MPa | 200-800 MPa |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, energy-intensive production | Biodegradable, renewable resource |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | High |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 550degC | Up to 200degC |
| Application in Automotive Interior | Structural panels, high-strength requirements | Trim components, lightweight elements |
Introduction to Automotive Interior Materials
Glass fiber and natural fiber are pivotal materials in automotive interior design, each offering unique benefits. Glass fiber provides superior strength, durability, and heat resistance, making it ideal for structural components and panels. Natural fibers, such as hemp or flax, contribute to lightweight construction and sustainability, enhancing eco-friendly vehicle interiors while maintaining adequate mechanical performance.
Overview of Glass Fiber in Automotive Interiors
Glass fiber is widely used in automotive interiors due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent durability, and resistance to heat and moisture, making it ideal for components such as door panels, dashboards, and seat backs. Its superior mechanical properties contribute to improved safety and vehicle performance by reducing overall weight and enhancing impact resistance. Glass fiber composites also offer design flexibility and cost-effectiveness, promoting sustainability through recyclability in automotive manufacturing.
Overview of Natural Fiber in Automotive Interiors
Natural fibers such as flax, hemp, jute, and kenaf are increasingly used in automotive interiors due to their lightweight properties, biodegradability, and sustainability benefits. These fibers offer good vibration damping, thermal insulation, and sound absorption, contributing to enhanced passenger comfort and reduced vehicle weight for improved fuel efficiency. Natural fiber composites also support automakers' goals of reducing carbon footprints by replacing traditional glass fiber reinforcements with renewable, eco-friendly alternatives.
Mechanical Performance Comparison: Glass vs Natural Fiber
Glass fiber offers superior tensile strength, stiffness, and impact resistance compared to natural fibers like flax or hemp, making it ideal for high-performance automotive interior components. Natural fibers provide better vibration damping and lower density, which contributes to weight reduction and improved fuel efficiency but typically show lower mechanical durability under prolonged stress. Advances in hybrid composites combining glass and natural fibers aim to balance mechanical strength with sustainability in automotive interior applications.
Weight Reduction and Efficiency Advantages
Glass fiber composites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, enabling significant weight reduction in automotive interiors compared to traditional materials while maintaining structural integrity and safety standards. Natural fibers, such as flax or hemp, provide eco-friendly alternatives with lower density, contributing to further weight savings and potentially enhancing fuel efficiency due to reduced vehicle mass. Both materials improve energy efficiency by optimizing weight, but glass fiber excels in mechanical performance, whereas natural fibers offer sustainability benefits and vibration damping properties.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Glass fiber, widely used in automotive interiors, offers high strength and durability but has a significant environmental footprint due to energy-intensive production and non-biodegradability. Natural fibers like flax, hemp, and kenaf provide sustainable alternatives with lower carbon emissions, biodegradability, and reduced weight, which contribute to improved fuel efficiency and lower lifecycle environmental impact. The shift toward bio-based composites supports circular economy goals by enhancing recyclability and reducing reliance on petrochemical materials in automotive manufacturing.
Cost Analysis: Glass Fiber vs Natural Fiber
Glass fiber typically incurs higher upfront costs due to energy-intensive production processes and raw material expenses compared to natural fibers such as flax or hemp, which are renewable and more cost-effective. However, natural fibers may involve additional processing costs to meet automotive standards for durability and fire resistance, potentially offsetting initial savings. Considering lifecycle expenses, glass fiber offers longer durability and consistent performance, while natural fibers contribute to reduced material costs and environmental impact, influencing total cost calculations in automotive interior applications.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Glass fiber offers superior strength and a sleek, uniform appearance, enabling high-quality finishes and intricate design details in automotive interiors. Natural fibers provide unique textures and a warm, organic aesthetic that appeals to eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable design options. Design flexibility with glass fiber supports complex shapes and customization, while natural fibers excel in creating distinctive, tactile surfaces that enhance interior ambiance.
Durability and Longevity in Automotive Applications
Glass fiber offers superior durability and longevity in automotive interiors due to its high tensile strength, resistance to moisture, and thermal stability, making it ideal for components subjected to frequent stress and varying environmental conditions. Natural fibers, while environmentally friendly and lightweight, generally exhibit lower resistance to wear, moisture absorption, and UV degradation, which can reduce their lifespan in automotive applications. The enhanced mechanical properties of glass fiber composites ensure sustained performance and structural integrity over the vehicle's operational life.
Future Trends in Automotive Interior Materials
Glass fiber remains a dominant reinforcement in automotive interiors due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and durability, supporting lightweight and fuel-efficient vehicle designs. Emerging trends show a growing shift towards natural fibers like hemp, flax, and kenaf, driven by increasing demand for sustainability and reduced carbon footprints in vehicle manufacturing. Advances in hybrid composites combining glass and natural fibers aim to optimize mechanical performance while enhancing recyclability and environmental impact in future automotive interior materials.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Natural fiber for Automotive interior
 azmater.com
azmater.com