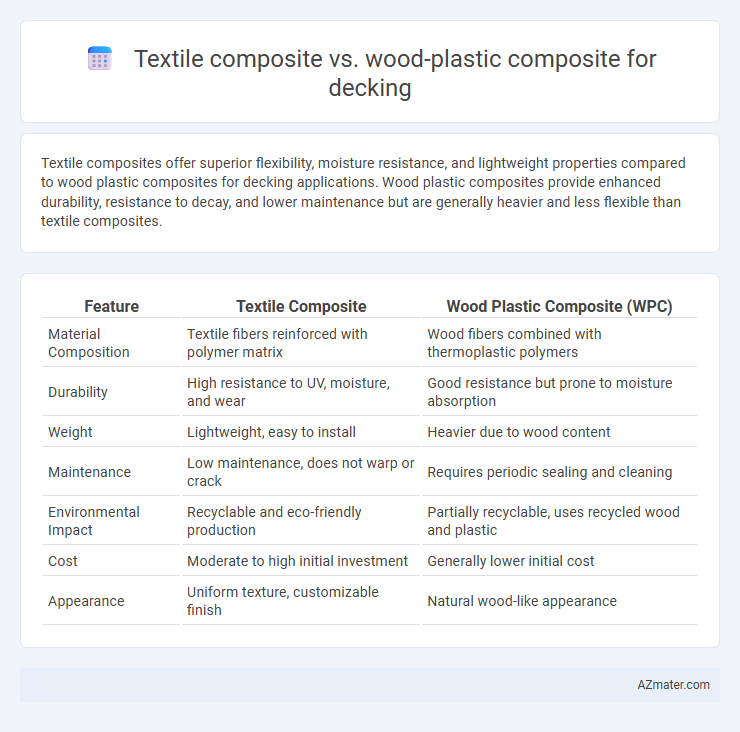
Textile composites offer superior flexibility, moisture resistance, and lightweight properties compared to wood plastic composites for decking applications. Wood plastic composites provide enhanced durability, resistance to decay, and lower maintenance but are generally heavier and less flexible than textile composites.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Textile Composite | Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Textile fibers reinforced with polymer matrix | Wood fibers combined with thermoplastic polymers |
| Durability | High resistance to UV, moisture, and wear | Good resistance but prone to moisture absorption |
| Weight | Lightweight, easy to install | Heavier due to wood content |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, does not warp or crack | Requires periodic sealing and cleaning |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable and eco-friendly production | Partially recyclable, uses recycled wood and plastic |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment | Generally lower initial cost |
| Appearance | Uniform texture, customizable finish | Natural wood-like appearance |
Introduction to Decking Materials
Textile composites and wood plastic composites (WPC) are popular materials for decking, each offering distinct advantages. Textile composites provide enhanced strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to wear, making them suitable for high-traffic areas. Wood plastic composites combine recycled wood fibers and plastic polymers, delivering durability, low maintenance, and resistance to moisture and insects, which are critical for outdoor decking applications.
What Are Textile Composites?
Textile composites for decking are engineered materials combining textile fibers such as carbon, glass, or natural fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, offering superior strength-to-weight ratio and flexibility compared to traditional wood plastic composites (WPC). Unlike WPC, which blends wood fibers with plastic resins, textile composites deliver enhanced durability, resistance to cracking, and better moisture management due to their fiber reinforcement. These advanced composites provide longer lifespan and improved structural performance, making them ideal for high-performance decking applications.
Understanding Wood Plastic Composites (WPC)
Wood Plastic Composites (WPC) combine wood fibers with thermoplastics like polyethylene or PVC, providing enhanced durability and low maintenance for decking applications. WPC decking exhibits superior resistance to moisture, rot, and insect damage compared to natural wood, making it ideal for outdoor environments. Its synthetic matrix offers improved dimensional stability and consistent performance, outperforming traditional textile composites in longevity and weather resistance.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Textile composites for decking primarily consist of natural or synthetic fibers embedded in polymer matrices, offering high tensile strength and flexibility through processes like pultrusion or compression molding. Wood plastic composites (WPC) combine wood fibers or flour with thermoplastics such as polyethylene, polypropylene, or PVC, manufactured typically via extrusion or injection molding to achieve enhanced durability and moisture resistance. The key distinction lies in fiber type and processing methods, where textile composites emphasize fiber alignment and mechanical properties, whereas WPC focuses on blending wood's aesthetic and thermoplastic's processability for weather-resistant decking.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Textile composites offer superior durability and weather resistance for decking applications due to their high tensile strength and resistance to moisture absorption, preventing warping and rotting. Wood plastic composites (WPC) incorporate recycled wood fibers and thermoplastics, providing moderate durability but are more prone to swelling and surface degradation under prolonged exposure to moisture and UV rays. Choosing textile composite decking ensures enhanced longevity and lower maintenance requirements in harsh environmental conditions compared to traditional WPC materials.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Textile composites offer enhanced aesthetics with a smoother, more fabric-like texture and greater customization options in color and pattern, providing a sleek, modern appearance for decking. Wood plastic composites (WPC) deliver a more natural wood-like look with traditional grain patterns, ideal for replicating classic outdoor designs. Textile composites allow for innovative shapes and curved designs due to their superior flexibility, whereas WPC is generally more rigid, limiting design variations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Textile composites for decking use recycled fibers such as cotton or polyester, reducing waste and lowering carbon footprints compared to virgin materials. Wood plastic composites (WPC) blend wood fibers with recycled plastics, diverting plastic waste from landfills and minimizing deforestation. Both materials offer sustainable alternatives; textile composites excel in biodegradability while WPC provides durability with reduced wood harvesting.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Textile composite decking offers lightweight installation with easy cutting and fastening, reducing labor time compared to wood plastic composite (WPC), which is heavier and may require specialized tools. Maintenance for textile composites involves minimal cleaning with mild detergents, whereas WPC decking often needs regular power washing to prevent mold and staining due to its denser composition. Both materials resist rot and insect damage, but textile composites generally provide a quicker, less labor-intensive installation and lower maintenance frequency.
Cost Analysis and Long-term Value
Textile composites generally offer higher initial costs compared to wood plastic composites (WPC) due to advanced material engineering and durability features. WPC decking provides a more cost-effective upfront investment with moderate maintenance expenses, but textile composites deliver superior long-term value by resisting moisture, UV damage, and wear, reducing replacement frequency. Evaluating lifecycle costs reveals textile composites often achieve better return on investment through extended lifespan and minimal upkeep requirements despite their higher initial price.
Choosing the Right Composite for Your Decking Project
Textile composites offer superior flexibility and enhanced moisture resistance, making them ideal for decking in humid climates or areas with frequent exposure to water. Wood plastic composites combine the natural aesthetic of wood with increased durability and low maintenance, perfect for heavy foot traffic and outdoor use. Selecting the right composite depends on project-specific needs such as environmental conditions, desired appearance, and long-term performance requirements.
Infographic: Textile composite vs Wood plastic composite for Decking
 azmater.com
azmater.com