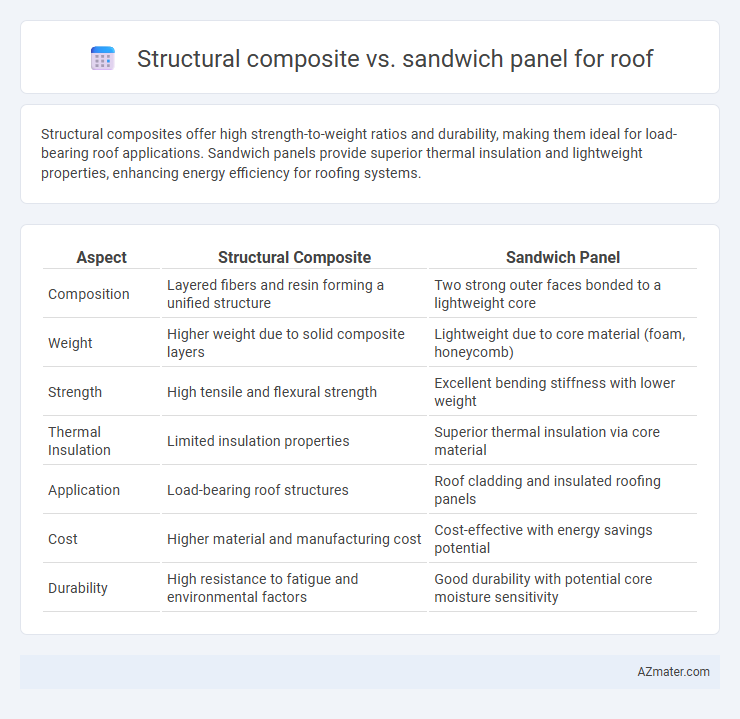
Structural composites offer high strength-to-weight ratios and durability, making them ideal for load-bearing roof applications. Sandwich panels provide superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties, enhancing energy efficiency for roofing systems.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Structural Composite | Sandwich Panel |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Layered fibers and resin forming a unified structure | Two strong outer faces bonded to a lightweight core |
| Weight | Higher weight due to solid composite layers | Lightweight due to core material (foam, honeycomb) |
| Strength | High tensile and flexural strength | Excellent bending stiffness with lower weight |
| Thermal Insulation | Limited insulation properties | Superior thermal insulation via core material |
| Application | Load-bearing roof structures | Roof cladding and insulated roofing panels |
| Cost | Higher material and manufacturing cost | Cost-effective with energy savings potential |
| Durability | High resistance to fatigue and environmental factors | Good durability with potential core moisture sensitivity |
Introduction to Roofing Panel Technologies
Structural composite panels for roofing utilize fiber-reinforced materials that provide high strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced durability under load conditions. Sandwich panels, composed of two outer metal or fiber-reinforced skins bonded to a lightweight core such as polyurethane or mineral wool, offer superior thermal insulation and moisture resistance. Both technologies are pivotal in modern roofing applications, with structural composites excelling in mechanical performance while sandwich panels optimize energy efficiency and weight reduction.
What Are Structural Composites?
Structural composites are engineered materials composed of two or more distinct constituents that combine to deliver superior strength, stiffness, and durability for roofing applications. These composites typically consist of a reinforcing fiber matrix, such as fiberglass or carbon fiber, embedded in a polymer resin, creating lightweight yet robust panels ideal for structural support. Compared to sandwich panels, which have a core material sandwiched between two facings, structural composites offer enhanced mechanical performance and resistance to environmental stresses, making them suitable for demanding roof structures.
Understanding Sandwich Panels
Sandwich panels consist of two outer metal or composite face sheets bonded to a lightweight core such as polyurethane, polystyrene, or mineral wool, providing high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent thermal insulation. Structural composite panels, typically made of oriented strand board (OSB) or plywood bonded to rigid foam cores, prioritize structural integrity and load-bearing capacity. For roofing applications, sandwich panels offer superior thermal performance and ease of installation, while structural composites excel in durability and impact resistance.
Material Composition and Structure Comparison
Structural composite panels for roofing consist of multiple reinforcing materials such as fiberglass, carbon fiber, or aramid fibers combined with a resin matrix, providing high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent durability. Sandwich panels feature a core material like expanded polystyrene (EPS), polyurethane, or mineral wool, sandwiched between two outer skins made of metal, fiberglass, or plywood, optimizing thermal insulation and structural stiffness. The composite panels emphasize mechanical performance through fiber reinforcement, whereas sandwich panels prioritize lightweight insulation with a layered construction for efficient load distribution.
Weight and Load-Bearing Capabilities
Structural composites offer high strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for load-bearing roof applications while minimizing overall weight. Sandwich panels enhance stiffness and insulation by combining lightweight core materials with strong facings, resulting in superior load distribution and reduced structural weight. Comparing both, sandwich panels generally provide better weight efficiency and thermal performance, whereas structural composites excel in customized strength and durability for heavy load demands.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Performance
Structural composite roofs provide moderate thermal insulation with higher density materials that reduce heat transfer but may have limited acoustic dampening compared to sandwich panels. Sandwich panels typically consist of two outer layers with an insulating core such as polyurethane or mineral wool, delivering superior thermal resistance (R-values up to 7.0 m2*K/W) and enhanced sound absorption due to the core's porous nature. This combination in sandwich panels results in better energy efficiency and noise reduction performance, making them ideal for environments requiring stringent thermal and acoustic controls.
Installation Methods and Ease
Structural composites for roofing involve layered materials bonded together, requiring precise alignment and secure fastening during installation, typically demanding skilled labor and specialized equipment. Sandwich panels consist of two outer facings with a lightweight core, allowing quicker installation due to pre-fabrication, simpler handling, and compatibility with various fastening systems. The ease of sandwich panel installation often reduces labor costs and time compared to structural composites, making it favorable for rapid construction projects.
Durability and Maintenance Needs
Structural composites provide superior durability for roofing applications due to their high resistance to corrosion, impact, and weathering, resulting in fewer repairs over time. Sandwich panels, with their lightweight core materials like foam or honeycomb, offer excellent thermal insulation but may require more frequent maintenance to address core degradation or moisture infiltration. Both options enhance roof longevity, but structural composites typically demand less upkeep, making them ideal for long-term durability.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Lifecycle
Structural composite roofs generally have higher upfront costs due to advanced materials like carbon fiber or fiberglass but offer superior durability that reduces maintenance expenses over the lifecycle. Sandwich panels, composed of lightweight core materials such as polyurethane foam between metal sheets, typically provide a cost-effective initial investment and improved thermal insulation, contributing to energy savings. Lifecycle cost analysis reveals that while structural composites may incur higher initial expenses, their extended lifespan and lower repair frequency can offset these costs compared to sandwich panels which might require more frequent maintenance and replacement.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Roof Panel
Structural composites offer high strength and durability ideal for industrial and commercial roofs where load-bearing capacity is critical. Sandwich panels provide excellent thermal insulation and lightweight properties, making them suitable for residential and energy-efficient buildings. Selecting the right roof panel depends on factors like structural requirements, insulation needs, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Structural composite vs Sandwich panel for Roof
 azmater.com
azmater.com