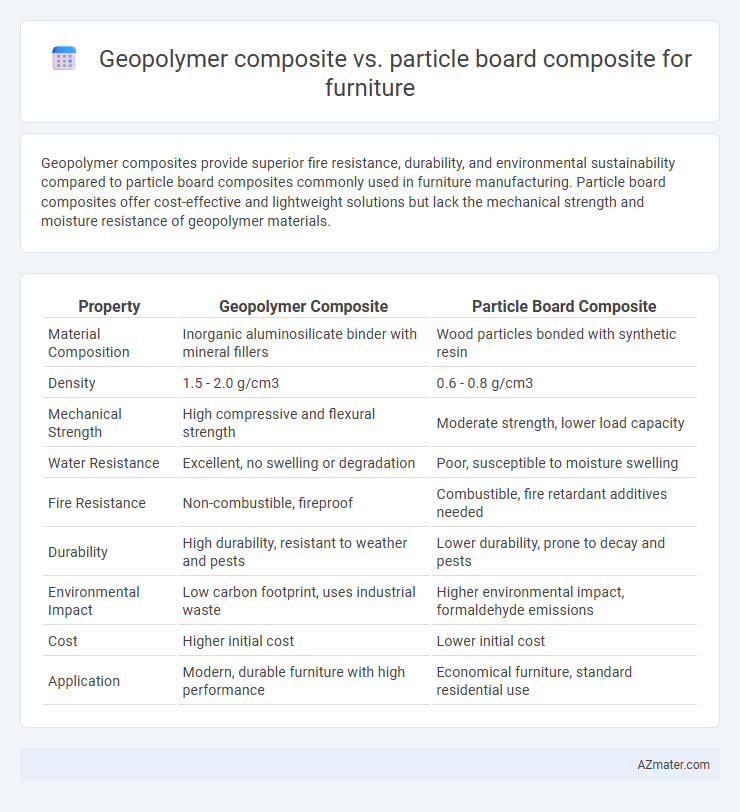
Geopolymer composites provide superior fire resistance, durability, and environmental sustainability compared to particle board composites commonly used in furniture manufacturing. Particle board composites offer cost-effective and lightweight solutions but lack the mechanical strength and moisture resistance of geopolymer materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Geopolymer Composite | Particle Board Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Inorganic aluminosilicate binder with mineral fillers | Wood particles bonded with synthetic resin |
| Density | 1.5 - 2.0 g/cm3 | 0.6 - 0.8 g/cm3 |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive and flexural strength | Moderate strength, lower load capacity |
| Water Resistance | Excellent, no swelling or degradation | Poor, susceptible to moisture swelling |
| Fire Resistance | Non-combustible, fireproof | Combustible, fire retardant additives needed |
| Durability | High durability, resistant to weather and pests | Lower durability, prone to decay and pests |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, uses industrial waste | Higher environmental impact, formaldehyde emissions |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Application | Modern, durable furniture with high performance | Economical furniture, standard residential use |
Introduction to Geopolymer and Particle Board Composites
Geopolymer composites are advanced materials composed of aluminosilicate binders activated by alkaline solutions, offering high thermal resistance, durability, and eco-friendly characteristics. Particle board composites consist of wood particles bonded with synthetic resins, widely used for cost-effective furniture fabrication due to their affordability and ease of machining. The fundamental difference lies in geopolymer composites' superior mechanical strength and fire resistance compared to the conventional, moisture-sensitive particle board composites commonly employed in furniture manufacturing.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Geopolymer composites for furniture are primarily composed of aluminosilicate materials activated by alkaline solutions, resulting in a durable, fire-resistant matrix, whereas particle board composites consist of wood particles bonded with synthetic resins such as urea-formaldehyde or phenol-formaldehyde. Manufacturing geopolymer composites involves mixing raw materials at ambient or elevated temperatures followed by curing to achieve hardness, while particle board production includes pressing wood particles under heat and pressure to form panels. The inorganic nature of geopolymer composites provides superior moisture resistance and thermal stability compared to the organic polymer binder in particle boards.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Geopolymer composites exhibit significantly higher mechanical strength and durability compared to particle board composites, making them ideal for heavy-duty furniture applications. Their inorganic polymer matrix provides superior resistance to moisture, fire, and biodegradation, unlike particle boards, which are prone to swelling, warping, and decay under similar conditions. Enhanced compressive strength and long-term structural stability position geopolymer composites as a more sustainable and robust alternative for durable furniture manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geopolymer composites exhibit significantly lower carbon emissions compared to traditional particle board composites due to their use of industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, which reduces landfill waste and conserves natural resources. Particle board composites rely heavily on wood fibers and synthetic resins, contributing to deforestation and the release of formaldehyde-based volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Geopolymer composites offer enhanced durability and resistance to moisture and fire, increasing furniture lifespan and reducing the frequency of replacement, which supports long-term sustainability goals.
Fire and Moisture Resistance
Geopolymer composites exhibit superior fire resistance due to their inorganic, non-combustible matrix that can withstand high temperatures without significant deformation or release of toxic gases. Particle board composites, composed primarily of wood fibers and adhesives, are highly susceptible to moisture absorption, leading to swelling, warping, and degradation over time. Geopolymer's enhanced moisture resistance and thermal stability make it a more durable and safer choice for furniture applications requiring stringent fire safety and moisture protection standards.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Geopolymer composites offer superior durability and fire resistance compared to particle board composites, but their higher raw material and production costs limit widespread adoption in furniture manufacturing. Particle board composites remain more cost-effective due to lower material and processing expenses, making them widely available and popular in the global furniture market. Market availability favors particle boards with established supply chains and mass production, while geopolymer composites are emerging niche materials primarily used in specialized, high-performance furniture applications.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Options
Geopolymer composites offer superior design flexibility due to their moldability and ability to incorporate various textures and pigments, enabling customized furniture aesthetics with enhanced durability. Particle board composites, while cost-effective and easy to produce, have limited design options and often require veneers or laminates to achieve appealing finishes. The inherent strength and adaptability of geopolymer composites allow for innovative shapes and finishes that outperform particle board counterparts in both modern and traditional furniture designs.
Applications in Modern Furniture
Geopolymer composites offer superior fire resistance, durability, and eco-friendliness compared to particle board composites, making them ideal for high-performance furniture in industrial and commercial settings. Particle board composites remain popular for budget-friendly furniture due to their lightweight nature and ease of machining, suited for residential and office applications. Emerging trends in modern furniture prioritize geopolymer composites for sustainable, long-lasting components in outdoor and heavy-use environments.
Health and Safety Considerations
Geopolymer composites offer superior health and safety benefits compared to particle board composites due to their non-toxic, fire-resistant, and low-emission properties, reducing indoor air pollution and exposure to formaldehyde. Particle board composites often release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from adhesives and binders, posing respiratory risks and potential long-term health hazards. The durable, inert nature of geopolymer materials enhances occupant safety by minimizing chemical off-gassing and improving fire resistance in furniture applications.
Future Trends in Furniture Composite Materials
Geopolymer composites offer superior fire resistance, durability, and eco-friendly benefits compared to traditional particle board composites, which often rely on synthetic adhesives and wood waste. Emerging trends in furniture composite materials emphasize sustainable production methods, increased use of recycled content, and enhanced mechanical properties through nanomaterial integration. Future developments point to geopolymer composites becoming a preferred choice in high-performance, environmentally conscious furniture design due to their lower carbon footprint and improved longevity.
Infographic: Geopolymer composite vs Particle board composite for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com