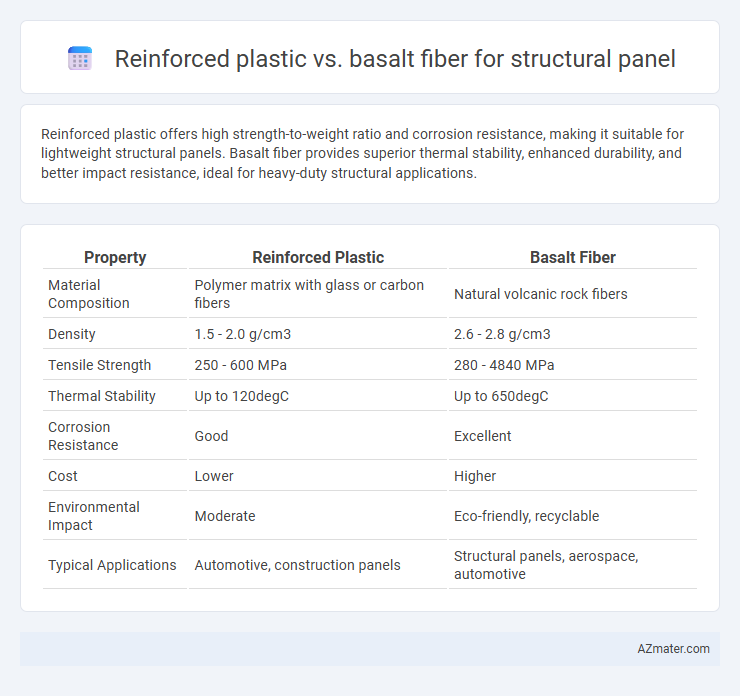
Reinforced plastic offers high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for lightweight structural panels. Basalt fiber provides superior thermal stability, enhanced durability, and better impact resistance, ideal for heavy-duty structural applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Reinforced Plastic | Basalt Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polymer matrix with glass or carbon fibers | Natural volcanic rock fibers |
| Density | 1.5 - 2.0 g/cm3 | 2.6 - 2.8 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 250 - 600 MPa | 280 - 4840 MPa |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 120degC | Up to 650degC |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate | Eco-friendly, recyclable |
| Typical Applications | Automotive, construction panels | Structural panels, aerospace, automotive |
Introduction to Structural Panels
Structural panels made from reinforced plastic offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for dynamic load-bearing applications. Basalt fiber panels, derived from volcanic rock, provide enhanced thermal stability, superior impact resistance, and environmental sustainability compared to traditional composites. Both materials serve critical roles in construction and aerospace industries, with basalt fiber increasingly favored for its natural origin and mechanical performance.
Overview of Reinforced Plastics
Reinforced plastics, commonly composed of polymer matrices embedded with glass, carbon, or aramid fibers, offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance ideal for structural panels. These composites provide versatile mechanical properties and design flexibility, enabling tailored performance for specific load-bearing applications in construction and transportation industries. Their widespread use is driven by durability, ease of fabrication, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional materials.
Basalt Fiber: Properties and Applications
Basalt fiber exhibits superior mechanical properties including high tensile strength, excellent thermal resistance, and exceptional corrosion resistance, making it ideal for structural panels in demanding environments. Its natural origin and eco-friendly production process provide a sustainable alternative to traditional reinforced plastics, often used in construction, automotive, and aerospace industries. Basalt fiber structural panels offer enhanced durability, reduced weight, and improved fire resistance compared to conventional reinforced plastic composites.
Mechanical Strength: A Comparative Analysis
Reinforced plastic and basalt fiber exhibit distinct differences in mechanical strength when used for structural panels. Basalt fiber offers superior tensile strength, often ranging between 2,800 to 4,800 MPa, compared to reinforced plastics, which typically achieve tensile strengths around 1,200 to 2,500 MPa. Its higher modulus of elasticity and enhanced impact resistance make basalt fiber an ideal choice for applications requiring greater load-bearing capacity and durability.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Reinforced plastic offers high durability with excellent resistance to corrosion, chemicals, and moisture, making it suitable for long-term structural applications in harsh environments. Basalt fiber panels enhance environmental resistance by providing superior thermal stability, UV resistance, and impact strength, reducing degradation over time under extreme weather conditions. Both materials exhibit strong mechanical properties, but basalt fiber panels often deliver improved longevity and eco-friendly performance due to their natural origin and recyclability.
Weight and Flexural Performance
Reinforced plastic panels typically feature lower density materials like fiberglass, resulting in lighter weight compared to basalt fiber panels, which possess higher density due to basalt's natural mineral composition. Basalt fiber offers superior flexural strength and stiffness, delivering enhanced load-bearing capacity and resistance to bending stress in structural applications. Weight-sensitive designs may favor reinforced plastics for ease of handling, while basalt fiber panels provide improved flexural performance for durability and structural integrity.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Reinforced plastic panels generally offer higher cost efficiency due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses compared to basalt fiber, which tends to be more expensive because of its production complexity and limited supply. Basalt fiber panels provide superior mechanical properties and durability, making them ideal for high-performance structural applications despite their higher initial cost. Availability of reinforced plastic is widespread and consistent, while basalt fiber remains less accessible due to niche production and emerging market demand.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
Reinforced plastic panels often rely on synthetic fibers and resins that can pose challenges in recyclability and contribute to environmental pollution. Basalt fiber, derived from natural volcanic rock, offers a sustainable alternative due to its low energy production requirements and full recyclability, enhancing eco-friendliness in structural applications. The inherent durability and non-toxic nature of basalt fiber panels reduce environmental impact throughout their lifecycle compared to traditional reinforced plastic composites.
Common Applications in Construction
Reinforced plastic is widely used in construction for panels in facades, roofing, and load-bearing walls due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. Basalt fiber panels are increasingly favored for structural applications requiring superior thermal stability, fire resistance, and environmental sustainability, such as bridge decks and seismic retrofitting. Both materials excel in lightweight structural components but differ in performance characteristics, influencing their selection for specific construction scenarios.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Reinforced plastic offers versatility and ease of molding, making it suitable for various structural panel applications requiring corrosion resistance and lightweight properties. Basalt fiber provides superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and environmental sustainability, ideal for high-performance and durable structural panels. Selecting the right material depends on project-specific requirements such as load-bearing capacity, environmental conditions, and long-term durability, with basalt fiber often preferred for enhanced strength and eco-friendliness, while reinforced plastic remains a cost-effective, adaptable option.
Infographic: Reinforced plastic vs Basalt fiber for Structural panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com