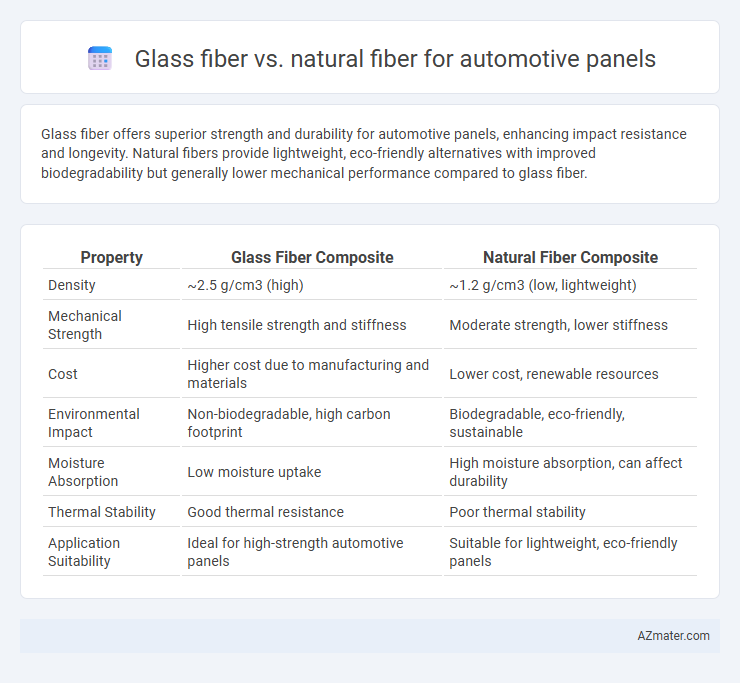
Glass fiber offers superior strength and durability for automotive panels, enhancing impact resistance and longevity. Natural fibers provide lightweight, eco-friendly alternatives with improved biodegradability but generally lower mechanical performance compared to glass fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber Composite | Natural Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Density | ~2.5 g/cm3 (high) | ~1.2 g/cm3 (low, lightweight) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and stiffness | Moderate strength, lower stiffness |
| Cost | Higher cost due to manufacturing and materials | Lower cost, renewable resources |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, high carbon footprint | Biodegradable, eco-friendly, sustainable |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture uptake | High moisture absorption, can affect durability |
| Thermal Stability | Good thermal resistance | Poor thermal stability |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for high-strength automotive panels | Suitable for lightweight, eco-friendly panels |
Introduction to Automotive Panel Materials
Glass fiber and natural fiber are widely used materials in automotive panel manufacturing, each offering distinct advantages. Glass fiber provides superior strength, durability, and resistance to heat and moisture, making it ideal for exterior panels and structural components. Natural fibers such as hemp, flax, and jute offer sustainability benefits, reduced weight, and improved biodegradability, gaining popularity in eco-friendly vehicle designs.
Overview of Glass Fiber Composites
Glass fiber composites in automotive panels offer high tensile strength, excellent durability, and resistance to corrosion and heat, outperforming many natural fiber alternatives. These composites consist of woven glass fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, providing superior rigidity and impact resistance crucial for vehicle safety and structural integrity. Their widespread adoption in automotive manufacturing results from their lightweight properties combined with cost-effective production and consistent material performance.
Overview of Natural Fiber Composites
Natural fiber composites for automotive panels offer lightweight, eco-friendly alternatives with enhanced biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional glass fiber composites. Key natural fibers include flax, hemp, jute, and kenaf, which provide adequate mechanical performance while improving recyclability and reducing vehicle weight. Advances in resin formulations and fiber treatments continue to enhance durability, moisture resistance, and impact strength of natural fiber composites, making them increasingly viable for sustainable automotive manufacturing.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Glass fiber offers superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to natural fibers, making it ideal for automotive panels requiring high structural integrity. Natural fibers such as hemp or flax provide lower density and better vibration damping, contributing to lightweight and noise reduction benefits. However, glass fiber composites excel in impact resistance and durability, essential for safety-critical automotive applications.
Weight and Fuel Efficiency Analysis
Glass fiber automotive panels typically weigh more than natural fiber panels, which directly impacts vehicle weight and fuel efficiency. Natural fibers like hemp or flax reduce overall panel mass by up to 30%, enabling lighter vehicles with improved fuel economy and lower CO2 emissions. Optimizing panel materials by substituting glass fiber with natural fiber can enhance energy efficiency and contribute to sustainable automotive design.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Glass fiber automotive panels generate significant environmental impact due to energy-intensive production and non-biodegradable waste accumulation. Natural fiber alternatives like hemp, flax, and jute offer lower carbon footprints, biodegradability, and renewable resource use, enhancing sustainability in automotive manufacturing. Lifecycle assessments show natural fiber composites reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote circular economy practices compared to traditional glass fiber materials.
Cost Considerations and Economic Viability
Glass fiber composites typically offer lower initial material costs and consistent quality for automotive panels, making them economically viable for large-scale production. Natural fibers, such as hemp or flax, have higher variability and may require more processing, increasing overall costs but provide benefits in weight reduction and sustainability. Evaluating long-term economic viability involves weighing material expenses, manufacturing complexity, and potential regulatory incentives for eco-friendly materials.
Processing and Manufacturing Techniques
Glass fiber automotive panels benefit from advanced processing methods like injection molding and compression molding, offering high precision and consistent fiber distribution that enhances mechanical properties. Natural fiber panels typically employ techniques such as resin transfer molding (RTM) and compression molding, emphasizing eco-friendly production with lower energy consumption but often require treatments to improve fiber-matrix adhesion. Manufacturing challenges for natural fibers include moisture sensitivity and variable fiber quality, whereas glass fibers provide more predictable processing outcomes and higher thermal resistance in automotive applications.
Durability and Long-term Performance
Glass fiber offers superior durability for automotive panels due to its high tensile strength, resistance to moisture, and excellent impact resistance, ensuring long-term structural integrity. Natural fibers like hemp or flax provide lightweight and eco-friendly alternatives but typically exhibit lower resistance to environmental factors such as UV exposure and moisture, which can lead to degradation over time. Advanced surface treatments and hybrid composites are being developed to improve the longevity and performance of natural fiber-reinforced panels in automotive applications.
Future Trends in Automotive Panel Materials
Glass fiber remains dominant in automotive panels due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and cost-effectiveness, but natural fibers like hemp and flax are gaining traction for their sustainability and biodegradability. Future trends emphasize hybrid composites combining glass and natural fibers to enhance performance while reducing environmental impact. Innovations in bio-resin matrices and recycled fiber integration are driving the evolution toward greener, lightweight automotive panel materials.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Natural fiber for Automotive panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com