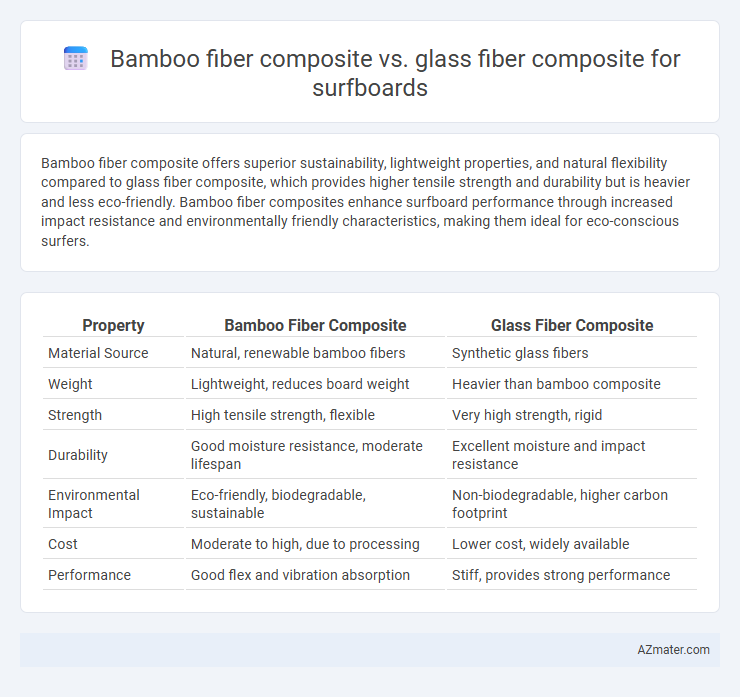
Bamboo fiber composite offers superior sustainability, lightweight properties, and natural flexibility compared to glass fiber composite, which provides higher tensile strength and durability but is heavier and less eco-friendly. Bamboo fiber composites enhance surfboard performance through increased impact resistance and environmentally friendly characteristics, making them ideal for eco-conscious surfers.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bamboo Fiber Composite | Glass Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Natural, renewable bamboo fibers | Synthetic glass fibers |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces board weight | Heavier than bamboo composite |
| Strength | High tensile strength, flexible | Very high strength, rigid |
| Durability | Good moisture resistance, moderate lifespan | Excellent moisture and impact resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable, sustainable | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Cost | Moderate to high, due to processing | Lower cost, widely available |
| Performance | Good flex and vibration absorption | Stiff, provides strong performance |
Introduction to Surfboard Composite Materials
Surfboard composite materials significantly impact performance, durability, and environmental footprint, with bamboo fiber and glass fiber composites being prominent choices. Bamboo fiber composites offer lightweight strength, flexibility, and sustainable sourcing, making them ideal for eco-friendly surfboards. Glass fiber composites provide high tensile strength and abrasion resistance but are heavier and less environmentally friendly due to synthetic production processes.
Overview of Bamboo Fiber Composites
Bamboo fiber composites for surfboards offer a sustainable and lightweight alternative to traditional glass fiber composites, providing excellent flexibility and strength-to-weight ratio. Bamboo fibers are naturally renewable and biodegradable, contributing to eco-friendly surfboard manufacturing while maintaining durability and resistance to impact. These composites enhance performance by improving board responsiveness and reducing overall environmental impact compared to glass fiber reinforced boards.
Glass Fiber Composites: Properties and Applications
Glass fiber composites offer high strength-to-weight ratios, excellent durability, and superior impact resistance, making them ideal for surfboard construction. Their resistance to water absorption and UV degradation ensures long-lasting performance in marine environments, while the flexibility of glass fibers provides enhanced shock absorption on waves. Widely used in both recreational and professional surfboards, glass fiber composites contribute to improved board stiffness and overall ride quality.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Bamboo fiber composites for surfboards exhibit exceptional tensile strength and flexibility, offering enhanced impact resistance compared to traditional glass fiber composites. Glass fiber composites provide high stiffness and durability but are prone to brittleness under extreme stress, while bamboo fibers maintain structural integrity through natural shock absorption. The sustainable and lightweight nature of bamboo fiber composites also contributes to improved board longevity without compromising performance in demanding surf conditions.
Environmental Impact: Bamboo vs. Glass Fiber
Bamboo fiber composites significantly reduce environmental impact compared to glass fiber composites due to bamboo's rapid renewability and biodegradability, which lower carbon emissions and landfill waste. Glass fiber production involves high energy consumption and generates non-biodegradable waste that persists in ecosystems, contributing to pollution. Choosing bamboo fiber composites supports sustainable surfboard manufacturing by minimizing ecological footprint and promoting resource efficiency.
Weight and Flexibility in Surfboard Performance
Bamboo fiber composites offer a significant advantage in weight reduction for surfboards, being lighter than traditional glass fiber composites, which enhances maneuverability and responsiveness on waves. The natural elasticity of bamboo fibers provides superior flexibility and improved impact resistance, contributing to a more dynamic ride and better energy absorption under stress. Conversely, glass fiber composites, while stronger and more rigid, add considerable weight that can reduce agility and slow down the surfboard's overall responsiveness during performance.
Cost Analysis and Material Availability
Bamboo fiber composites offer a cost-effective alternative to glass fiber composites in surfboard manufacturing, with raw material costs typically 20-30% lower due to the renewable and fast-growing nature of bamboo. Glass fiber composites incur higher expenses related to energy-intensive production and synthetic resin use, resulting in increased overall manufacturing costs. Material availability for bamboo fiber varies regionally but is generally more sustainable and less susceptible to supply chain disruptions compared to glass fibers, which depend heavily on petrochemical sources and global trade networks.
Manufacturing Processes and Challenges
Bamboo fiber composites in surfboard manufacturing require careful handling due to the natural variability and moisture content of bamboo fibers, which can affect resin bonding and curing times. Glass fiber composites benefit from well-established processes like wet lay-up and vacuum infusion, offering consistent fiber orientation and strength but generate heavier boards compared to bamboo composites. Challenges in bamboo composites include achieving uniform fiber dispersion and durability under marine conditions, while glass fiber composites face environmental concerns related to non-biodegradable waste and higher energy input during production.
Surfboard Lifespan and Maintenance Needs
Bamboo fiber composites offer enhanced durability and flexibility compared to glass fiber composites, contributing to a longer surfboard lifespan by resisting dings and cracks more effectively. Bamboo's natural moisture resistance reduces maintenance needs, as it is less prone to water absorption and delamination than traditional glass fiber boards. Consequently, surfboards reinforced with bamboo fiber composites require fewer repairs and less frequent upkeep, making them a cost-effective and eco-friendly choice for surfers.
Choosing the Right Composite for Your Surfboard
Bamboo fiber composites offer exceptional flexibility and lightweight strength, making them ideal for surfboards that require enhanced maneuverability and eco-friendly materials. Glass fiber composites provide superior durability, impact resistance, and a lower cost, which suits more traditional surfboard designs needing robustness and longevity. Selecting the right composite depends on balancing performance needs with environmental impact, where bamboo excels in sustainability and glass fiber dominates in structural resilience.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber composite vs Glass fiber composite for Surfboard
 azmater.com
azmater.com