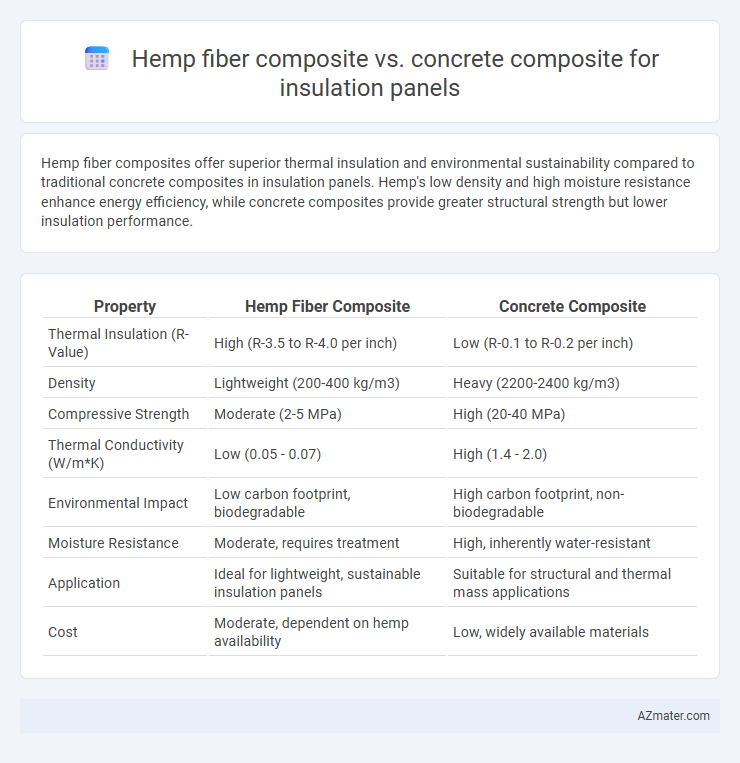
Hemp fiber composites offer superior thermal insulation and environmental sustainability compared to traditional concrete composites in insulation panels. Hemp's low density and high moisture resistance enhance energy efficiency, while concrete composites provide greater structural strength but lower insulation performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Fiber Composite | Concrete Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation (R-Value) | High (R-3.5 to R-4.0 per inch) | Low (R-0.1 to R-0.2 per inch) |
| Density | Lightweight (200-400 kg/m3) | Heavy (2200-2400 kg/m3) |
| Compressive Strength | Moderate (2-5 MPa) | High (20-40 MPa) |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m*K) | Low (0.05 - 0.07) | High (1.4 - 2.0) |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | High carbon footprint, non-biodegradable |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate, requires treatment | High, inherently water-resistant |
| Application | Ideal for lightweight, sustainable insulation panels | Suitable for structural and thermal mass applications |
| Cost | Moderate, dependent on hemp availability | Low, widely available materials |
Introduction to Insulation Panel Materials
Hemp fiber composites offer a sustainable alternative to traditional concrete composites for insulation panels, leveraging natural fibers that provide excellent thermal performance and breathability. Concrete composites, while durable and strong, have higher thermal conductivity, which limits their insulation efficiency compared to hemp-based panels. The lightweight nature and renewable properties of hemp fiber composites enhance energy efficiency and reduce the environmental impact in building insulation applications.
Overview of Hemp Fiber Composites
Hemp fiber composites exhibit exceptional thermal insulation properties, making them a sustainable alternative to traditional concrete composites in construction panels. The natural cellulose and lignin content in hemp fibers contribute to high moisture regulation and breathability, enhancing indoor air quality and reducing energy consumption. Their lightweight nature and biodegradability further position hemp fiber composites as eco-friendly, efficient materials for insulation applications.
Overview of Concrete Composites
Concrete composites for insulation panels typically combine Portland cement with aggregates and various additives to enhance thermal performance and durability. These composites offer high compressive strength and fire resistance but generally have lower thermal insulation properties compared to hemp fiber composites. Optimization of mix design and incorporation of lightweight materials aim to improve insulation while maintaining structural integrity in concrete-based panels.
Material Properties Comparison
Hemp fiber composites exhibit superior thermal insulation properties due to their low thermal conductivity (approximately 0.04 W/m*K) and high porosity, making them highly effective in reducing energy consumption. Concrete composites offer greater compressive strength, typically above 20 MPa, but have higher thermal conductivity values around 1.1 W/m*K, leading to less effective insulation performance. The lightweight nature and enhanced moisture regulation of hemp fiber composites provide advantages in sustainable building applications compared to the denser and heavier concrete composites.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Hemp fiber composites exhibit superior thermal insulation properties compared to concrete composites, with thermal conductivity values typically ranging between 0.04 to 0.06 W/m*K, significantly lower than concrete's average of 0.80 to 1.50 W/m*K. The porous cellular structure of hemp fibers enhances heat resistance and reduces thermal bridging, making hemp fiber panels highly effective for energy-efficient building envelopes. Studies show that hemp fiber insulation panels not only improve R-value but also provide better moisture regulation, contributing to more stable indoor temperatures compared to denser concrete composite panels.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp fiber composites for insulation panels significantly reduce environmental impact by utilizing renewable, biodegradable materials with low embodied energy compared to traditional concrete composites, which rely on high-energy cement production contributing to substantial CO2 emissions. Hemp fibers enhance carbon sequestration during growth, supporting carbon neutrality, while concrete composites generate large carbon footprints through cement manufacturing and limited recyclability. Sustainability advantages of hemp fiber panels include improved biodegradability, less resource depletion, and lower lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions, making them preferable for eco-friendly building insulation solutions.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Hemp fiber composites exhibit superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to concrete composites, making them more resistant to cracking under mechanical stress. The natural fibers in hemp composites enhance impact resistance and contribute to long-term durability by resisting moisture-induced degradation better than traditional concrete panels. While concrete composites excel in compressive strength, hemp fiber composites offer a balanced combination of mechanical resilience and environmental durability for insulation panels.
Cost Effectiveness and Manufacturing
Hemp fiber composites offer a cost-effective alternative to concrete composites for insulation panels due to lower raw material costs and reduced energy consumption during manufacturing. Hemp fibers provide excellent thermal insulation properties while being lightweight, which simplifies handling and reduces transportation expenses. Manufacturing hemp fiber panels involves less CO2 emission and shorter curing times compared to energy-intensive concrete composites, enhancing overall sustainability and economic efficiency.
Applications in Building Construction
Hemp fiber composites offer superior thermal insulation and moisture regulation compared to concrete composites, making them ideal for eco-friendly building envelopes, interior wall panels, and roof insulation. Concrete composites provide excellent structural strength and fire resistance but have lower insulating properties, suitable for load-bearing walls and foundations. Preference for hemp fiber composites in sustainable construction emphasizes energy efficiency and indoor air quality, while concrete composites are favored for durability and longevity in demanding structural applications.
Future Trends in Insulation Panel Technology
Hemp fiber composites are gaining traction in insulation panel technology due to their superior thermal properties, biodegradability, and low carbon footprint compared to conventional concrete composites. Advances in material science are focusing on enhancing the durability and fire resistance of hemp-based panels, positioning them as a sustainable alternative in green building trends. Emerging regulations and growing demand for eco-friendly construction materials are driving innovation toward hybrid composites combining hemp fibers with other natural or recycled materials to optimize insulation performance.
Infographic: Hemp fiber composite vs Concrete composite for Insulation panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com