Green composites offer superior environmental sustainability and biodegradability compared to traditional glass composites used in boat hull construction. These eco-friendly materials provide comparable strength and durability while significantly reducing carbon footprint and end-of-life waste.
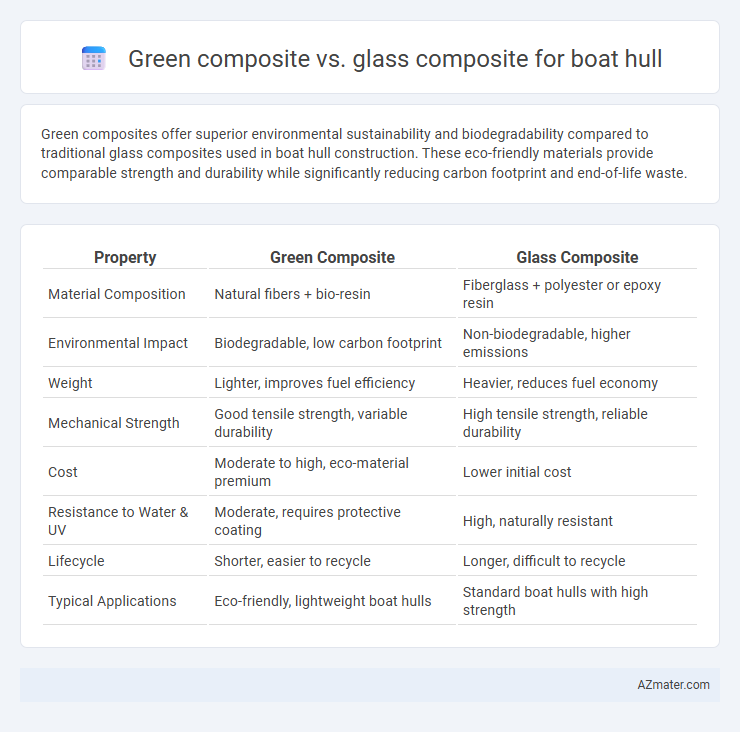
Table of Comparison
| Property | Green Composite | Glass Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers + bio-resin | Fiberglass + polyester or epoxy resin |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher emissions |
| Weight | Lighter, improves fuel efficiency | Heavier, reduces fuel economy |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength, variable durability | High tensile strength, reliable durability |
| Cost | Moderate to high, eco-material premium | Lower initial cost |
| Resistance to Water & UV | Moderate, requires protective coating | High, naturally resistant |
| Lifecycle | Shorter, easier to recycle | Longer, difficult to recycle |
| Typical Applications | Eco-friendly, lightweight boat hulls | Standard boat hulls with high strength |
Introduction to Boat Hull Composites
Boat hull composites, including green composites and glass composites, are engineered for durability, weight efficiency, and environmental performance. Green composites utilize natural fibers such as flax or hemp combined with bio-based resins, offering enhanced sustainability and reduced ecological impact. Glass composites, primarily made from fiberglass and synthetic resins, provide high strength-to-weight ratios and widespread use in marine applications due to their proven performance and cost-effectiveness.
Overview of Green Composites
Green composites for boat hulls utilize natural fibers such as flax, hemp, or jute combined with bio-based or recyclable resins, offering enhanced sustainability and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional glass composites. These composites provide lightweight strength, corrosion resistance, and improved biodegradability while minimizing carbon footprint during production and disposal. Although glass composites remain widely used for their high durability and cost-effectiveness, green composites continue to gain popularity in marine applications focused on eco-friendly innovation and regulatory compliance.
Essentials of Glass Fiber Composites
Glass fiber composites dominate boat hull construction due to their high tensile strength, impact resistance, and durability in marine environments. Essential characteristics include excellent mechanical properties, superior resistance to water absorption, and ease of fabrication, which contribute to structural integrity and long-term performance. Compared to green composites, glass fiber composites offer more consistent quality and proven reliability for demanding marine applications.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Green composites, made from natural fibers like flax or hemp combined with biodegradable resins, significantly reduce carbon footprint and landfill waste compared to conventional glass composites. Glass composites rely on synthetic fiberglass and polyester resins, which involve energy-intensive manufacturing and generate non-biodegradable waste that persists in marine environments. The biodegradability and lower embodied energy of green composites contribute to a more sustainable lifecycle, minimizing pollution and resource depletion associated with boat hull production and disposal.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Green composites, often reinforced with natural fibers like flax or hemp combined with bio-based resins, offer competitive tensile strength and improved impact resistance compared to traditional glass composites, which rely on glass fibers and synthetic resins. Green composites exhibit superior vibration damping and enhanced fatigue resistance, contributing to prolonged structural integrity in marine environments. While glass composites demonstrate higher compressive strength and greater stiffness, green composites provide better environmental durability by resisting UV degradation and reducing ecological impact during manufacturing and disposal.
Weight and Performance Factors
Green composites for boat hulls, typically made from natural fibers like flax or hemp combined with bio-resins, offer significant weight reduction compared to traditional glass composites, improving fuel efficiency and speed. Glass composites, composed of fiberglass and epoxy or polyester resins, provide higher strength and durability but tend to be heavier, impacting acceleration and maneuverability. The choice between these materials hinges on balancing lightweight benefits of green composites with the superior strength and resistance characteristics of glass composites for optimal performance in marine applications.
Cost Analysis: Green vs Glass Composites
Green composites typically offer a cost advantage over glass composites in boat hull manufacturing due to the use of renewable natural fibers like flax or hemp, reducing raw material expenses. Although green composites may require specialized processing techniques, lower material costs and potential environmental incentives lead to better overall cost efficiency. Glass composites, while well-established and high-performing, often incur higher costs related to fiberglass reinforcement and synthetic resin, increasing total production expenses.
Manufacturability and Repairability
Green composites for boat hulls, made from bio-based fibers and resins, offer enhanced manufacturability through improved compatibility with eco-friendly production processes and lower emissions compared to traditional glass composites, which rely on synthetic fibers like fiberglass. Repairability of green composites can be more challenging due to limited standardized methods and variability in material properties, whereas glass composites benefit from well-established repair techniques and widespread availability of matching materials. Manufacturers prioritize green composites for sustainable innovation, but the ease of repair and established protocols still make glass composites a preferred choice for maintenance and long-term serviceability in marine applications.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Case studies of boat hulls fabricated with green composites demonstrate enhanced environmental sustainability and reduced weight compared to traditional glass composites, yielding improved fuel efficiency and lower carbon emissions. Projects such as the Eco-Boat initiative in Scandinavia revealed that natural fiber composites maintained competitive mechanical properties while significantly reducing ecological impact. Analysis of the MarineTech aluminum-green composite prototype showed increased durability in marine environments, confirming green composites as a viable alternative to glass fiber reinforced polymers in real-world marine applications.
Future Trends in Boat Hull Materials
Green composite boat hulls, composed of bio-based resins and natural fibers, offer enhanced environmental sustainability and reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional glass composite hulls made from fiberglass and synthetic resins. Future trends indicate a significant shift towards green composites due to increasing regulatory pressures and consumer demand for eco-friendly marine solutions, while advanced glass composites continue evolving with improved strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. Innovations in hybrid composites combining green and glass fibers aim to optimize performance, durability, and sustainability in next-generation boat hull materials.
Infographic: Green composite vs Glass composite for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com