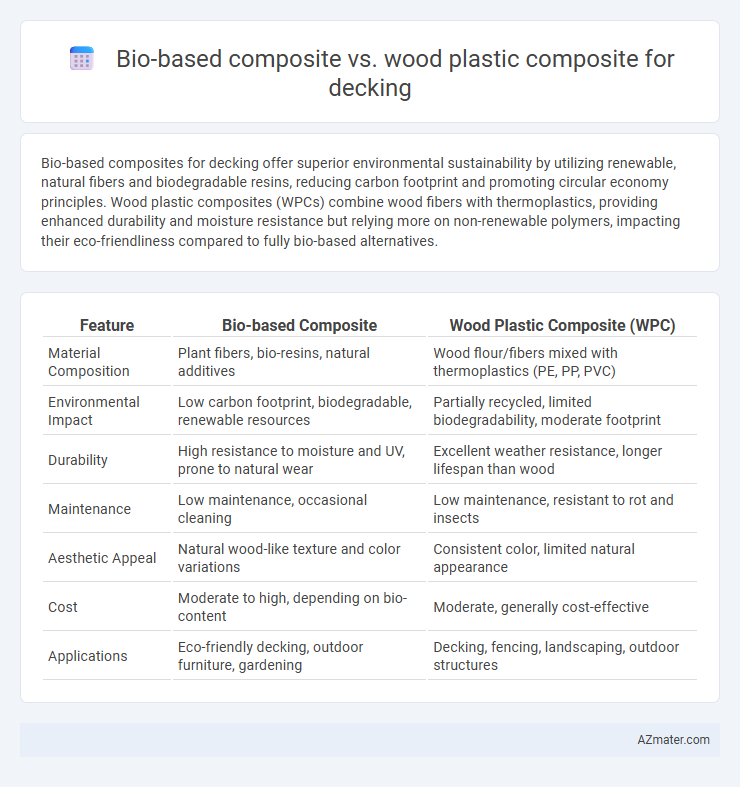
Bio-based composites for decking offer superior environmental sustainability by utilizing renewable, natural fibers and biodegradable resins, reducing carbon footprint and promoting circular economy principles. Wood plastic composites (WPCs) combine wood fibers with thermoplastics, providing enhanced durability and moisture resistance but relying more on non-renewable polymers, impacting their eco-friendliness compared to fully bio-based alternatives.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bio-based Composite | Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Plant fibers, bio-resins, natural additives | Wood flour/fibers mixed with thermoplastics (PE, PP, PVC) |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable, renewable resources | Partially recycled, limited biodegradability, moderate footprint |
| Durability | High resistance to moisture and UV, prone to natural wear | Excellent weather resistance, longer lifespan than wood |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, occasional cleaning | Low maintenance, resistant to rot and insects |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Natural wood-like texture and color variations | Consistent color, limited natural appearance |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on bio-content | Moderate, generally cost-effective |
| Applications | Eco-friendly decking, outdoor furniture, gardening | Decking, fencing, landscaping, outdoor structures |
Introduction to Decking Materials
Bio-based composites and wood plastic composites (WPC) are popular decking materials known for durability and low maintenance. Bio-based composites incorporate natural fibers like hemp or flax with biopolymers, enhancing environmental sustainability and reducing carbon footprint compared to traditional WPC, which typically combines wood fibers with petroleum-based plastics. Both materials offer resistance to moisture, rot, and insects, but bio-based composites provide improved biodegradability and eco-friendliness, making them suitable choices for sustainable decking solutions.
What Are Bio-Based Composites?
Bio-based composites for decking are materials composed primarily of natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or bamboo combined with bio-resins derived from renewable resources like plant oils or starches. Unlike traditional wood plastic composites (WPCs), which blend wood fibers with petroleum-based plastics, bio-based composites offer enhanced sustainability through reduced carbon footprints and improved biodegradability. These composites deliver comparable durability and moisture resistance while promoting eco-friendly construction practices in outdoor decking applications.
Understanding Wood Plastic Composites (WPC)
Wood Plastic Composites (WPC) are engineered materials combining wood fibers or flour with thermoplastics such as polyethylene or polypropylene, offering enhanced durability against moisture, insects, and rot compared to traditional wood. WPC decking provides low maintenance benefits, dimensional stability, and resistance to splintering, making it a popular choice for outdoor applications. The composite's polymer matrix protects natural fibers, resulting in improved weather resistance and extended lifespan relative to untreated wood products.
Material Composition Comparison
Bio-based composites typically use natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or kenaf combined with bio-resins derived from plant oils or starches, offering a higher proportion of renewable content compared to wood plastic composites (WPCs). WPCs primarily consist of wood flour or sawdust mixed with synthetic thermoplastics like polyethylene, polypropylene, or PVC, which provides enhanced moisture resistance and durability. The material composition of bio-based composites emphasizes sustainability and biodegradability, whereas WPCs focus on combining the strength of wood fibers with the resilience of plastics for long-lasting decking solutions.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Bio-based composites for decking are derived primarily from natural fibers and renewable resources, offering superior biodegradability and a reduced carbon footprint compared to wood plastic composites (WPCs), which contain a significant fraction of non-biodegradable plastics. Wood plastic composites often use recycled plastics, improving waste diversion but still pose challenges in end-of-life disposal due to limited recyclability and potential microplastic release. The sustainability advantage of bio-based composites lies in their use of renewable biomass, lower greenhouse gas emissions during production, and enhanced potential for ecological recycling, making them a more environmentally responsible choice for decking materials.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Bio-based composites exhibit superior durability in decking applications due to their natural fiber reinforcement and biodegradable resin matrix, offering enhanced resistance to UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. Wood plastic composites (WPC) combine wood fibers with thermoplastics, providing high weather resistance and low maintenance requirements, but they may suffer from surface cracking and fungal decay over time under harsh environmental conditions. Evaluating durability and weather resistance, bio-based composites typically outperform WPCs in longevity and environmental sustainability, especially in climates with extreme weather exposure.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Bio-based composites offer a wider range of natural wood-like textures and rich color variations, enhancing aesthetic appeal with a more authentic, organic look that blends seamlessly with outdoor environments. Wood plastic composites typically feature uniform textures and limited color palettes but excel in durability and low maintenance, making them ideal for modern, sleek decking designs. Both materials provide versatile design options, yet bio-based composites cater better to users prioritizing natural beauty and environmental sustainability in decking projects.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Bio-based composite decking offers easier installation due to its uniform material composition, allowing for consistent cutting and fastening compared to wood plastic composite (WPC), which can vary in density and texture. Maintenance for bio-based composites is minimal, requiring only occasional cleaning with soap and water, while WPC may need periodic sealing or staining to maintain appearance and prevent moisture absorption. Both materials resist rot and insect damage, but bio-based composites typically demonstrate greater dimensional stability, reducing the need for frequent repairs or adjustments during the deck's lifespan.
Cost Analysis and Long-term Value
Bio-based composites typically offer higher upfront costs compared to wood plastic composites due to the use of renewable raw materials and advanced manufacturing processes. Wood plastic composites tend to provide a more cost-effective solution with similar durability, benefiting from established production and lower material expenses. Long-term value favors bio-based composites for their superior environmental sustainability and resistance to decay, potentially reducing maintenance costs and extending decking lifespan.
Choosing the Right Composite for Your Deck
Bio-based composites offer superior environmental benefits by using renewable plant fibers, making them a sustainable choice for decking with enhanced biodegradability and lower carbon footprint. Wood plastic composites (WPC) provide greater durability and resistance to moisture, insects, and decay, ideal for high-traffic or wet environments due to their synthetic resin and wood fiber blend. Selecting the right composite depends on balancing eco-friendliness with performance requirements, where bio-based composites suit green building goals and WPCs excel in longevity and maintenance ease.
Infographic: Bio-based composite vs Wood plastic composite for Decking
 azmater.com
azmater.com