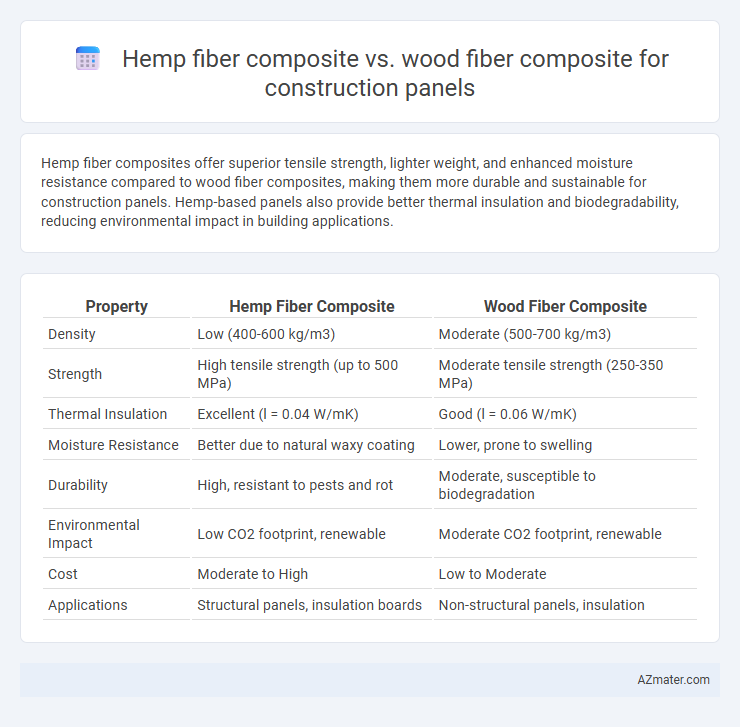
Hemp fiber composites offer superior tensile strength, lighter weight, and enhanced moisture resistance compared to wood fiber composites, making them more durable and sustainable for construction panels. Hemp-based panels also provide better thermal insulation and biodegradability, reducing environmental impact in building applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Fiber Composite | Wood Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low (400-600 kg/m3) | Moderate (500-700 kg/m3) |
| Strength | High tensile strength (up to 500 MPa) | Moderate tensile strength (250-350 MPa) |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent (l = 0.04 W/mK) | Good (l = 0.06 W/mK) |
| Moisture Resistance | Better due to natural waxy coating | Lower, prone to swelling |
| Durability | High, resistant to pests and rot | Moderate, susceptible to biodegradation |
| Environmental Impact | Low CO2 footprint, renewable | Moderate CO2 footprint, renewable |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
| Applications | Structural panels, insulation boards | Non-structural panels, insulation |
Introduction to Hemp Fiber and Wood Fiber Composites
Hemp fiber composites consist of natural hemp fibers combined with a resin matrix, offering lightweight, high tensile strength and excellent thermal insulation properties, making them suitable for eco-friendly construction panels. Wood fiber composites use wood fibers bound with resin to create durable, moisture-resistant panels with good mechanical properties widely used in building and furniture industries. Both composites are sustainable alternatives to synthetic materials with differing performance profiles in terms of strength, weight, and environmental impact.
Material Properties: Hemp vs. Wood Fiber
Hemp fiber composites exhibit superior tensile strength and improved impact resistance compared to wood fiber composites, making them more durable for construction panels. Hemp fibers provide better moisture resistance and higher thermal insulation due to their hollow core structure, which enhances energy efficiency in building applications. Wood fiber composites typically offer greater rigidity but are more prone to degradation from moisture and insects, resulting in shorter lifespan under harsh environmental conditions.
Manufacturing Processes of Bio-based Composites
Hemp fiber composites are manufactured through processes such as compression molding and resin infusion, leveraging the high tensile strength and flexibility of hemp fibers to enhance mechanical properties in construction panels. Wood fiber composites typically involve extrusion or hot pressing methods, where wood fibers are combined with thermoplastic or thermoset resins to achieve structural stability and moisture resistance. Both manufacturing processes prioritize fiber-matrix adhesion and uniform dispersion to optimize the bio-based composite's durability, thermal insulation, and environmental sustainability in building applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Hemp fiber composites exhibit superior tensile strength and flexibility compared to wood fiber composites, making them more resistant to cracking and deformation under stress. The natural lignin content in hemp fibers enhances durability by providing better resistance to moisture, rot, and microbial attack than wood fiber composites. Mechanical testing indicates hemp-based panels maintain structural integrity longer in varying environmental conditions, supporting longer service life in construction applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp fiber composites offer significantly lower carbon footprints compared to wood fiber composites due to rapid hemp growth cycles and higher CO2 absorption rates during cultivation. Hemp fibers are highly renewable, requiring fewer pesticides and less water, which enhances the sustainability of construction panels made from them. Wood fiber composites, while renewable, involve longer growth periods and contribute to deforestation concerns, making hemp fiber composites a preferable eco-friendly alternative for sustainable building materials.
Moisture Resistance and Dimensional Stability
Hemp fiber composites exhibit superior moisture resistance compared to wood fiber composites, as their natural cellulose and lignin structures reduce water absorption and swelling. This enhanced moisture resistance translates into improved dimensional stability, minimizing warping and expansion in fluctuating humidity environments common in construction panels. Wood fiber composites tend to absorb more moisture, leading to greater dimensional changes that can compromise the structural integrity and lifespan of building materials.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Hemp fiber composites offer a competitive cost advantage due to faster cultivation cycles and lower pesticide requirements compared to wood fiber composites, which often incur higher costs linked to deforestation and longer growth periods. Market availability of wood fiber composites remains more established, supported by extensive supply chains and widespread usage in construction, whereas hemp fiber composites are emerging with growing demand driven by sustainability trends but limited by regional agricultural regulations and processing infrastructure. Cost analysis reveals hemp composites can reduce long-term expenses through enhanced durability and insulation properties, though initial investment in processing technology and limited industrial scale impact pricing compared to conventional wood fiber panels.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Performance
Hemp fiber composites exhibit superior thermal insulation properties compared to wood fiber composites, with lower thermal conductivity values typically around 0.04 W/m*K, enhancing energy efficiency in construction panels. Acoustic insulation performance is also higher in hemp fiber composites due to their porous structure, effectively dampening sound frequencies and reducing noise transmission. These advantages make hemp fiber composites a preferred choice for sustainable building applications requiring enhanced thermal comfort and soundproofing.
Applications in Construction Panel Industry
Hemp fiber composites exhibit superior durability, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation compared to wood fiber composites, making them ideal for construction panels in environmentally sustainable building projects. These composites enhance the strength-to-weight ratio in structural panels used for wall cladding, roofing, and flooring systems, providing improved acoustic performance and fire resistance. The construction panel industry increasingly adopts hemp-based composites to meet green building standards and reduce carbon footprints without compromising mechanical properties.
Future Trends and Innovations in Bio-composite Panels
Hemp fiber composites exhibit superior durability, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation compared to traditional wood fiber composites, driving innovation in sustainable construction panels. Emerging technologies emphasize enhancing hemp composites with nanocellulose and bio-based resins to improve mechanical strength and biodegradability, optimizing performance for eco-friendly building applications. Future trends point to scalable production methods and hybrid bio-composite integration, enabling lightweight, high-strength panels with reduced environmental impact in green construction.
Infographic: Hemp fiber composite vs Wood fiber composite for Construction panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com