Carbon fiber bicycle frames offer superior strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness compared to reinforced plastic frames, making them ideal for high-performance cycling. Reinforced plastic frames provide more affordable durability and impact resistance, suitable for entry-level and recreational riders.
Table of Comparison
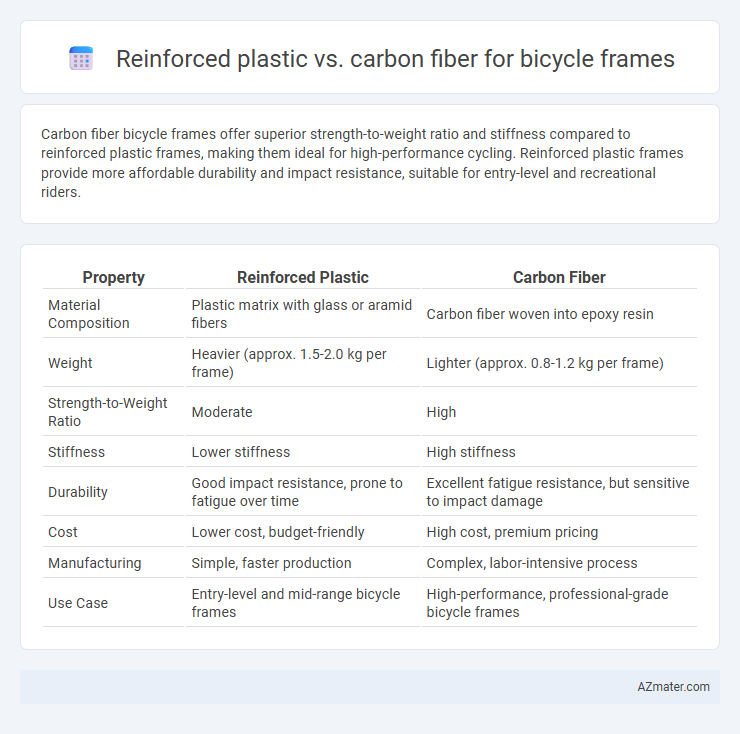
| Property | Reinforced Plastic | Carbon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Plastic matrix with glass or aramid fibers | Carbon fiber woven into epoxy resin |
| Weight | Heavier (approx. 1.5-2.0 kg per frame) | Lighter (approx. 0.8-1.2 kg per frame) |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Moderate | High |
| Stiffness | Lower stiffness | High stiffness |
| Durability | Good impact resistance, prone to fatigue over time | Excellent fatigue resistance, but sensitive to impact damage |
| Cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly | High cost, premium pricing |
| Manufacturing | Simple, faster production | Complex, labor-intensive process |
| Use Case | Entry-level and mid-range bicycle frames | High-performance, professional-grade bicycle frames |
Introduction to Bicycle Frame Materials
Reinforced plastic and carbon fiber are prominent materials used in bicycle frame construction, each offering distinct benefits. Reinforced plastic typically combines fiber materials like fiberglass with a polymer matrix, providing durability and cost-effectiveness. Carbon fiber consists of tightly woven fibers bonded with resin, delivering exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness, making it a preferred choice for high-performance cycling frames.
What is Reinforced Plastic?
Reinforced plastic, commonly known as fiberglass or composite material, consists of a polymer matrix embedded with strong fibers such as glass or carbon to enhance durability and strength. This material offers excellent impact resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for affordable and lightweight bicycle frames. Compared to carbon fiber, reinforced plastic is generally less stiff and lighter but provides better shock absorption and cost efficiency.
Understanding Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness, making it a superior choice for high-performance bicycle frames compared to reinforced plastic. Its molecular structure allows for precise layering and orientation, resulting in frames that are lightweight yet highly durable under stress. This advanced composite material also absorbs road vibrations effectively, enhancing rider comfort and control on diverse terrains.
Weight Comparison: Reinforced Plastic vs Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber bicycle frames weigh significantly less than reinforced plastic frames, often by 20-30%, due to carbon fiber's superior strength-to-weight ratio. Reinforced plastic, typically composed of fiberglass or other composites, is denser and adds more bulk, increasing the overall frame weight. Choosing carbon fiber results in lighter bikes that enhance speed and maneuverability, making it a preferred material for high-performance cycling.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Carbon fiber bicycle frames exhibit superior strength-to-weight ratios, providing exceptional tensile strength and stiffness compared to reinforced plastic frames, which primarily rely on glass fiber composites. Reinforced plastic frames offer enhanced impact resistance and flexibility, contributing to greater durability in rough terrain but at the cost of increased weight and lower fatigue strength. Carbon fiber's resistance to corrosion and fatigue failure extends frame longevity under high stress, making it ideal for performance-focused cycling applications.
Cost Differences and Affordability
Reinforced plastic bicycle frames are significantly more affordable than carbon fiber frames, with costs often ranging from $200 to $500 compared to $1,000 to $5,000 for carbon fiber counterparts. The manufacturing process for reinforced plastic is less complex, leading to lower production expenses and making it accessible for budget-conscious cyclists. Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio but at a premium price, positioning reinforced plastic as a cost-effective option for entry-level and mid-range bicycles.
Ride Quality and Performance
Reinforced plastic bicycle frames offer excellent vibration damping, resulting in a smoother ride quality ideal for casual and endurance cyclists. Carbon fiber frames provide superior stiffness-to-weight ratios, enhancing power transfer and overall performance for competitive riders. The choice between these materials depends on the rider's priority for comfort versus lightweight responsiveness.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reinforced plastic bicycle frames generally have a higher environmental impact due to non-biodegradable resins and energy-intensive manufacturing processes, resulting in limited recyclability and increased landfill waste. Carbon fiber frames, while offering superior strength-to-weight ratios and durability, pose significant challenges for recycling because of complex fiber-matrix composites, contributing to end-of-life disposal issues. Sustainable alternatives are emerging with bio-based resins and improved recycling technologies, but current production methods for both materials still demand considerable energy and resources, underscoring the need for advancements in circular economy practices within the cycling industry.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Reinforced plastic bicycle frames generally require less maintenance due to their resistance to corrosion and impact damage, making them ideal for casual riders. Carbon fiber frames, while offering superior strength-to-weight ratio and performance, demand careful inspection for cracks or delamination to ensure longevity. Proper maintenance and timely repair of carbon fiber frames significantly extend their lifespan, often surpassing reinforced plastic when used under high-stress cycling conditions.
Which Is Better for Your Bicycle Frame?
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness, making it ideal for high-performance bicycle frames that demand lightweight durability. Reinforced plastic, often found in fiberglass composites, provides greater flexibility and impact resistance at a lower cost but weighs more and lacks the rigidity preferred in racing or competitive cycling. Choosing between carbon fiber and reinforced plastic depends on your priorities for performance, budget, and ride comfort, with carbon fiber favored for speed and rigidity, while reinforced plastic suits casual riding and affordability.
Infographic: Reinforced plastic vs Carbon fiber for Bicycle frame
 azmater.com
azmater.com