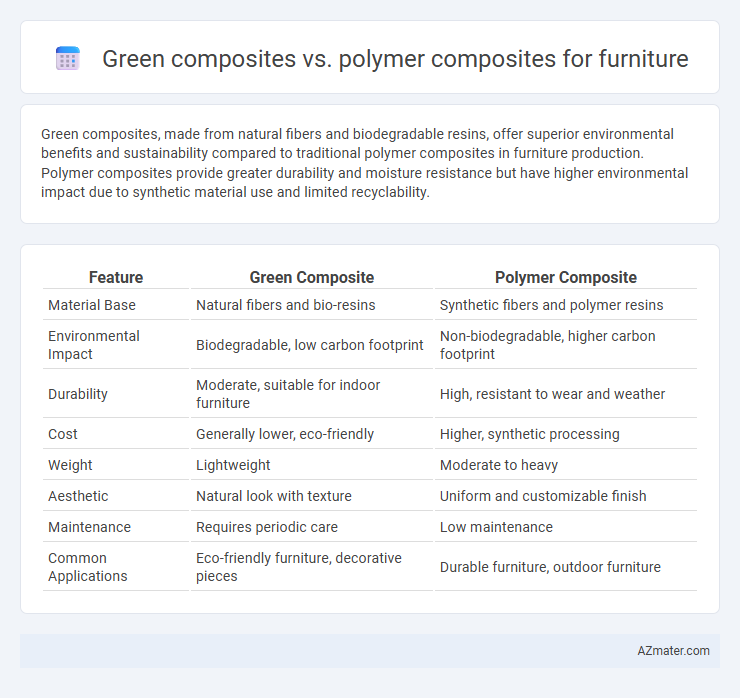
Green composites, made from natural fibers and biodegradable resins, offer superior environmental benefits and sustainability compared to traditional polymer composites in furniture production. Polymer composites provide greater durability and moisture resistance but have higher environmental impact due to synthetic material use and limited recyclability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Green Composite | Polymer Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Base | Natural fibers and bio-resins | Synthetic fibers and polymer resins |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for indoor furniture | High, resistant to wear and weather |
| Cost | Generally lower, eco-friendly | Higher, synthetic processing |
| Weight | Lightweight | Moderate to heavy |
| Aesthetic | Natural look with texture | Uniform and customizable finish |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic care | Low maintenance |
| Common Applications | Eco-friendly furniture, decorative pieces | Durable furniture, outdoor furniture |
Introduction to Composite Materials in Furniture Design
Composite materials in furniture design combine two or more distinct substances to enhance strength, durability, and aesthetics. Green composites integrate natural fibers like hemp or flax with biodegradable resins, offering eco-friendly benefits and reducing carbon footprint compared to traditional polymer composites composed of synthetic fibers and plastic matrices. These material choices significantly impact sustainability, weight, and mechanical properties crucial for modern furniture manufacturing.
Overview of Green Composites
Green composites are materials made from natural fibers combined with biodegradable or bio-based polymers, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional polymer composites often derived from petroleum. These composites provide enhanced environmental benefits, such as reduced carbon footprint, biodegradability, and lower energy consumption during production, making them ideal for eco-friendly furniture manufacturing. Green composites also exhibit comparable mechanical properties and durability to conventional polymer composites, supporting their growing use in sustainable interior design and furniture applications.
Understanding Polymer Composites
Polymer composites consist of a polymer matrix reinforced with fibers such as glass, carbon, or natural fibers, offering enhanced strength, durability, and lightweight properties ideal for furniture applications. These materials provide improved resistance to moisture, chemicals, and wear compared to traditional wood, making them suitable for indoor and outdoor furniture. Understanding polymer composites involves analyzing the compatibility between the matrix and reinforcements, processing methods, and the balance between mechanical performance and environmental impact.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Green composites, made from natural fibers and bio-based resins, offer superior sustainability compared to traditional polymer composites that rely heavily on non-renewable petroleum-based materials. These eco-friendly materials reduce carbon footprint, promote biodegradability, and minimize toxic emissions during production and disposal, making them ideal for environmentally conscious furniture manufacturing. In contrast, polymer composites, while durable and versatile, often pose challenges related to recyclability and persistent microplastic pollution in landfills and ecosystems.
Material Properties and Performance
Green composites, made from natural fibers like hemp or flax combined with biodegradable resins, offer superior environmental benefits including renewability and lower carbon footprint compared to traditional polymer composites. Polymer composites, often reinforced with synthetic fibers such as fiberglass or carbon fiber, provide higher mechanical strength, durability, and resistance to moisture and chemicals, making them more suitable for demanding furniture applications. Green composites tend to exhibit lower density and enhanced biodegradability but may have reduced impact resistance and long-term stability compared to polymer composites.
Manufacturing Processes and Techniques
Green composites for furniture manufacturing use natural fibers such as flax, hemp, or jute combined with biodegradable resins, enabling eco-friendly processing techniques like compression molding and resin transfer molding. Polymer composites, often consisting of synthetic fibers like fiberglass embedded in thermoset or thermoplastic matrices, rely on techniques such as injection molding and pultrusion for higher strength and precision. Manufacturing green composites typically results in reduced energy consumption and lower emissions compared to polymer composites, promoting sustainable production without compromising durability.
Aesthetic and Functional Considerations
Green composites, made from natural fibers like hemp or flax combined with bio-based resins, offer a unique aesthetic characterized by organic textures and earthy tones that enhance furniture design with a sustainable appeal. Polymer composites, typically based on synthetic fibers and resins, provide greater consistency in color and finish, enabling sleek, modern looks preferred in contemporary furniture styles. Functionally, green composites excel in eco-friendliness and biodegradability but may have lower moisture resistance and durability compared to polymer composites, which offer superior strength, weather resistance, and longevity for high-performance furniture applications.
Cost Analysis and Market Trends
Green composites, made from natural fibers and biodegradable matrices, often present higher initial costs compared to conventional polymer composites due to raw material sourcing and processing complexities. Market trends indicate growing demand for sustainable furniture solutions, driving innovation and economies of scale that gradually reduce green composite prices. Polymer composites dominate cost-sensitive segments with established manufacturing infrastructure but face increasing regulatory pressure and consumer preference shifts toward eco-friendly alternatives.
Applications in Modern Furniture
Green composites, composed of natural fibers like hemp, jute, and flax combined with biodegradable resins, offer eco-friendly and sustainable options for modern furniture applications such as chairs, tables, and decorative panels. Polymer composites, typically made from synthetic fibers and thermoset or thermoplastic matrices, excel in durability, water resistance, and design flexibility, making them suitable for high-traffic furniture and outdoor use. The choice between green and polymer composites in furniture manufacturing increasingly depends on sustainability goals, structural performance, and aesthetic preferences.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Green composites, made from natural fibers like hemp, flax, or jute combined with bio-based resins, offer sustainable alternatives to traditional polymer composites in furniture manufacturing, enhancing biodegradability and reducing environmental impact. Innovations include the development of hybrid composites combining green and synthetic fibers to improve mechanical performance without sacrificing eco-friendliness, alongside advancements in bio-resin formulations that increase durability and weather resistance. Future prospects emphasize scalable production techniques, integration of smart materials for adaptive furniture designs, and increased adoption driven by regulatory incentives and consumer demand for eco-conscious products.
Infographic: Green composite vs Polymer composite for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com