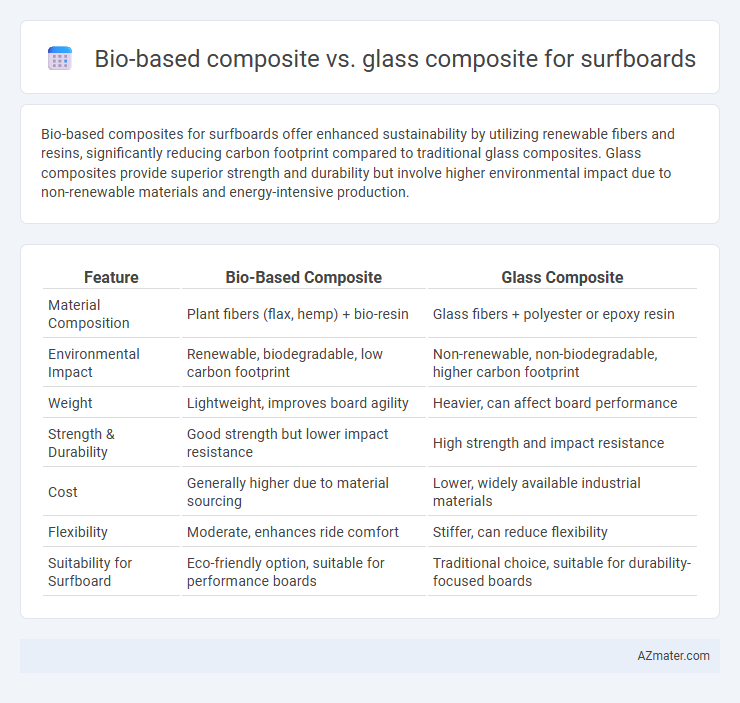
Bio-based composites for surfboards offer enhanced sustainability by utilizing renewable fibers and resins, significantly reducing carbon footprint compared to traditional glass composites. Glass composites provide superior strength and durability but involve higher environmental impact due to non-renewable materials and energy-intensive production.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bio-Based Composite | Glass Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Plant fibers (flax, hemp) + bio-resin | Glass fibers + polyester or epoxy resin |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-renewable, non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Weight | Lightweight, improves board agility | Heavier, can affect board performance |
| Strength & Durability | Good strength but lower impact resistance | High strength and impact resistance |
| Cost | Generally higher due to material sourcing | Lower, widely available industrial materials |
| Flexibility | Moderate, enhances ride comfort | Stiffer, can reduce flexibility |
| Suitability for Surfboard | Eco-friendly option, suitable for performance boards | Traditional choice, suitable for durability-focused boards |
Introduction to Surfboard Materials
Bio-based composites for surfboards utilize natural fibers like flax or hemp combined with bio-resins, offering enhanced sustainability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional glass composites. Glass composites, primarily made from fiberglass and epoxy or polyester resin, provide high strength, durability, and resistance to water absorption, which are critical for performance in water sports. Recent advancements in bio-based materials aim to match the mechanical properties and longevity of glass composites while addressing ecological concerns in surfboard manufacturing.
Overview of Bio-based Composites
Bio-based composites for surfboards incorporate renewable natural fibers such as flax, hemp, or jute combined with bio-resins derived from plant oils, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional materials. These composites provide comparable strength and durability to glass composites while significantly reducing environmental impact through lower carbon footprints and improved biodegradability. Manufacturers emphasize bio-based composites to align with eco-friendly practices and meet the growing demand for green sports equipment.
Characteristics of Glass Composites
Glass composites used in surfboards offer high tensile strength and excellent durability, making them resistant to impact and fatigue over extended use. These composites feature a lightweight structure with high stiffness and good flexibility, providing reliable performance in various wave conditions. The moisture resistance and relatively low cost of glass composites contribute to their widespread adoption in traditional surfboard manufacturing.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Bio-based composites in surfboards significantly reduce carbon footprint by utilizing renewable materials such as hemp, flax, or recycled bio-resins, whereas glass composites rely heavily on petroleum-based fiberglass and epoxy resins with high embodied energy. The biodegradability and lower toxicity of bio-based composites minimize marine pollution and end-of-life disposal issues compared to glass composites, which contribute to persistent microplastic pollution. Life cycle assessments show bio-based surfboards generally achieve up to 40% lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduced reliance on non-renewable resources, promoting a more sustainable surf industry.
Performance and Durability Analysis
Bio-based composites for surfboards offer enhanced environmental sustainability with comparable flexural strength ranging from 60 to 90 MPa, yet glass composites typically provide superior impact resistance and fatigue durability, lasting up to 30% longer under repeated wave stresses. The bio-based composites exhibit increased biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint by up to 40%, but their moisture absorption rates can lead to longer-term structural degradation compared to glass fiber laminates. Performance metrics show glass composites maintain consistent stiffness above 2 GPa, crucial for high-speed maneuvers, while bio-based materials are improving with hybrid fiber blends that strive to match these mechanical benchmarks.
Weight and Flexibility Factors
Bio-based composites in surfboards offer reduced weight compared to traditional glass composites, enhancing maneuverability and reducing rider fatigue. These materials provide superior flexibility, allowing for more responsive and dynamic board performance in various wave conditions. Glass composites, while durable, tend to be heavier and less flexible, potentially limiting agility and comfort during extended use.
Cost Effectiveness and Market Trends
Bio-based composites for surfboards offer increasing cost-effectiveness due to advancements in sustainable materials and production technologies, reducing reliance on expensive petroleum-based resins used in traditional glass composites. Market trends indicate a growing consumer preference for eco-friendly surfboards, driving demand and investment in bio-based composites despite their current slightly higher upfront costs. The shift towards sustainability is expected to lower manufacturing expenses over time, making bio-based composites more competitive with glass composites in price and performance.
Repairability and Longevity
Bio-based composites offer enhanced repairability due to their natural resin systems, allowing easier patching and reshaping with sustainable materials, while glass composites often require specialized epoxy or polyester resins and complex curing processes for repairs. Longevity in bio-based composites can rival glass composites when properly maintained, benefiting from biodegradable components that reduce environmental impact without sacrificing structural integrity. Glass composites provide superior durability in harsh marine conditions but may suffer from more challenging repairability and potential long-term degradation of synthetic resins under UV exposure.
User Experiences and Professional Feedback
Bio-based composites in surfboards offer enhanced environmental sustainability while maintaining comparable strength and flexibility to traditional glass composites. Professional surfers report a distinct difference in board responsiveness, citing bio-based materials as providing a lighter, more natural feel on the water. User experiences highlight improved durability against wear and impact, with bio-based composites often praised for their reduced environmental footprint without compromising performance.
Future Trends in Surfboard Material Innovation
Bio-based composites for surfboards are gaining traction due to their sustainability, using materials like flax fibers and bio-resins to reduce environmental impact compared to traditional glass composites. Advances in bio-composite technology are improving durability and performance, narrowing the gap with glass composites, which have long been favored for their strength and stiffness. Future trends point towards hybrid materials combining bio-based fibers with optimized resin systems to enhance eco-friendliness without compromising the high performance required in modern surfboards.
Infographic: Bio-based composite vs Glass composite for Surfboard
 azmater.com
azmater.com