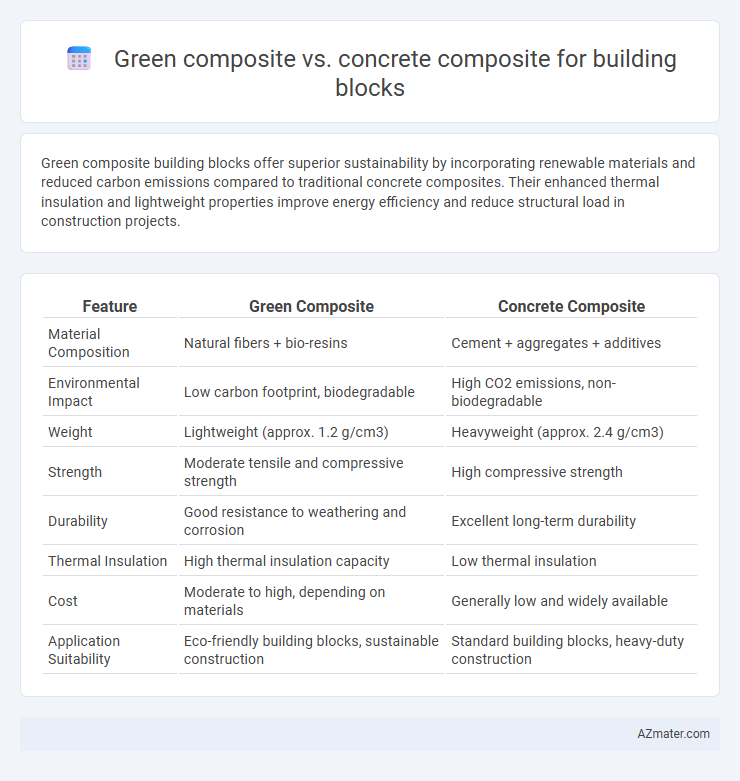
Green composite building blocks offer superior sustainability by incorporating renewable materials and reduced carbon emissions compared to traditional concrete composites. Their enhanced thermal insulation and lightweight properties improve energy efficiency and reduce structural load in construction projects.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Green Composite | Concrete Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers + bio-resins | Cement + aggregates + additives |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | High CO2 emissions, non-biodegradable |
| Weight | Lightweight (approx. 1.2 g/cm3) | Heavyweight (approx. 2.4 g/cm3) |
| Strength | Moderate tensile and compressive strength | High compressive strength |
| Durability | Good resistance to weathering and corrosion | Excellent long-term durability |
| Thermal Insulation | High thermal insulation capacity | Low thermal insulation |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on materials | Generally low and widely available |
| Application Suitability | Eco-friendly building blocks, sustainable construction | Standard building blocks, heavy-duty construction |
Introduction to Building Block Materials
Green composites incorporate natural fibers and bio-based resins, offering environmentally sustainable alternatives to traditional materials in building blocks. Concrete composites consist primarily of cement, aggregates, and supplementary materials, providing high strength and durability. The choice between green and concrete composites hinges on balancing ecological impact, mechanical properties, and long-term performance in construction applications.
Overview of Green Composites
Green composites for building blocks combine natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute with bio-based or recyclable polymers, offering enhanced sustainability and reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional concrete composites. These materials provide improved thermal insulation, lightweight properties, and biodegradability, making them ideal for eco-friendly construction practices. The eco-efficiency of green composites supports energy savings throughout the building lifecycle, aligning with green building certifications and regulatory standards for sustainable development.
Overview of Concrete Composites
Concrete composites combine cement, aggregates, and additives to enhance strength, durability, and performance in construction applications. These materials exhibit high compressive strength, resistance to environmental factors, and versatility for various structural needs, making them a standard choice for building blocks. Innovations in fiber reinforcement and admixtures improve crack resistance and mechanical properties, positioning concrete composites as reliable and cost-effective solutions for sustainable building projects.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Green composites offer significant environmental advantages over concrete composites due to their use of renewable, biodegradable materials such as natural fibers and biopolymers, which reduce carbon emissions and landfill waste. Concrete composites typically involve high energy consumption and CO2 emissions during production, primarily from cement manufacturing, contributing to environmental degradation. The adoption of green composites in building blocks supports sustainable construction practices by lowering overall ecological footprints and promoting resource circularity.
Structural Performance and Durability
Green composite building blocks, composed of natural fibers and bio-based resins, exhibit superior tensile strength and enhanced impact resistance compared to traditional concrete composites, which rely on cement and aggregates. The structural performance of green composites benefits from reduced brittleness and better energy absorption, making them ideal for seismic applications and load-bearing walls. In terms of durability, green composites resist moisture penetration and chemical corrosion more effectively, prolonging lifespan and minimizing maintenance in varied environmental conditions.
Insulation and Thermal Efficiency
Green composite building blocks offer superior insulation properties compared to traditional concrete composites, significantly reducing heat transfer due to their natural fiber reinforcement and porous structure. The thermal efficiency of green composites helps maintain consistent indoor temperatures, lowering energy consumption for heating and cooling systems. Concrete composites, while durable, generally exhibit higher thermal conductivity, resulting in less effective insulation and increased reliance on external temperature regulation.
Cost Analysis and Economic Factors
Green composites for building blocks typically offer lower production and lifecycle costs due to the use of renewable materials and less energy-intensive processes compared to traditional concrete composites, which rely heavily on cement and aggregate production. Economic factors favor green composites as they reduce carbon emissions, potentially qualifying for sustainability incentives and lowering regulatory costs over time. While initial costs for green composites may be higher in some cases, long-term savings from durability, thermal insulation, and environmental compliance make them economically competitive alternatives to concrete composites.
Health and Safety Considerations
Green composites, made from natural fibers and biodegradable resins, offer lower toxicity and reduce the risk of respiratory issues during installation compared to traditional concrete composites. Concrete composites, while durable, can release silica dust and other harmful particulates, posing significant health risks such as silicosis if proper protective measures are not taken. The use of green composites contributes to safer handling environments and reduces long-term exposure to hazardous materials for construction workers.
Adoption Challenges and Market Trends
Green composites for building blocks offer sustainability advantages, yet face adoption challenges like higher initial costs, limited long-term performance data, and lack of standardized regulations. Concrete composites dominate the market due to established supply chains, proven durability, and cost-effectiveness, though increasing environmental concerns drive interest in eco-friendly alternatives. Market trends indicate gradual growth in green composite adoption driven by government incentives, technological advancements, and rising demand for low-carbon building materials.
Future Prospects of Green and Concrete Composites
Green composites, composed of natural fibers and biodegradable resins, offer sustainable advantages such as reduced carbon footprint, enhanced recyclability, and improved energy efficiency compared to traditional concrete composites. Future prospects highlight advancements in material engineering to boost the mechanical strength and weather resistance of green composites, positioning them as viable alternatives in eco-friendly construction. Concrete composites continue to evolve through innovations like ultra-high-performance concrete and carbon fiber reinforcement, promising enhanced durability and reduced maintenance costs for long-lasting infrastructure development.
Infographic: Green composite vs Concrete composite for Building Block
 azmater.com
azmater.com