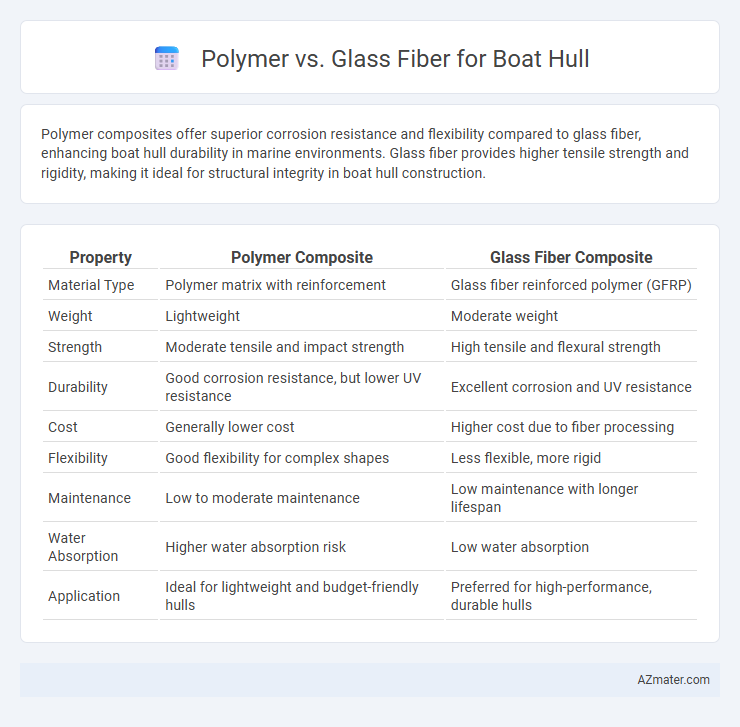
Polymer composites offer superior corrosion resistance and flexibility compared to glass fiber, enhancing boat hull durability in marine environments. Glass fiber provides higher tensile strength and rigidity, making it ideal for structural integrity in boat hull construction.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymer Composite | Glass Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polymer matrix with reinforcement | Glass fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP) |
| Weight | Lightweight | Moderate weight |
| Strength | Moderate tensile and impact strength | High tensile and flexural strength |
| Durability | Good corrosion resistance, but lower UV resistance | Excellent corrosion and UV resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to fiber processing |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility for complex shapes | Less flexible, more rigid |
| Maintenance | Low to moderate maintenance | Low maintenance with longer lifespan |
| Water Absorption | Higher water absorption risk | Low water absorption |
| Application | Ideal for lightweight and budget-friendly hulls | Preferred for high-performance, durable hulls |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Boat hull materials primarily consist of polymer composites and glass fiber, each offering distinct advantages for marine applications. Polymer composites provide lightweight, corrosion-resistant properties that enhance fuel efficiency and durability in harsh marine environments. Glass fiber, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and cost-effectiveness, remains a popular choice for constructing robust and impact-resistant boat hulls.
Overview of Polymer Composites
Polymer composites, especially fiberglass-reinforced polymers, are widely used for boat hull construction due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ease of molding into complex shapes. Unlike traditional glass fiber alone, polymer composites combine resin matrices such as polyester, vinyl ester, or epoxy with reinforcement fibers to enhance mechanical properties and durability in marine environments. These composites provide superior impact resistance, reduced maintenance, and improved fuel efficiency compared to conventional materials, making them a preferred choice in modern boat manufacturing.
Understanding Glass Fiber in Boat Construction
Glass fiber is a favored material in boat hull construction due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, providing durability and longevity in marine environments. Its ability to be molded into complex shapes allows for sleek, hydrodynamic designs essential for efficient watercraft performance. Compared to polymer composites, glass fiber offers superior stiffness and impact resistance, making it a reliable choice for structural integrity in various boat types.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Glass fiber exhibits higher tensile strength and stiffness compared to common polymers used in boat hulls, making it more resistant to impact and deformation under load. Polymer composites reinforced with glass fiber, such as fiberglass, combine polymer matrix flexibility with enhanced mechanical properties, offering superior durability and resistance to fatigue. Pure polymer hulls typically have lower modulus of elasticity and strength, resulting in reduced load-bearing capacity and increased susceptibility to wear and damage in marine environments.
Weight and Buoyancy Differences
Polymer boat hulls typically weigh less than glass fiber hulls, providing enhanced buoyancy and improved fuel efficiency due to reduced displacement. Glass fiber hulls, while heavier, offer increased structural strength and stiffness, which can affect overall weight but contribute to durability and impact resistance. The lower density of polymer materials results in higher buoyancy, making them ideal for applications requiring lightweight and easily maneuverable vessels.
Durability and Longevity
Polymer boat hulls, particularly those made from fiberglass reinforced polymer (FRP), offer superior durability due to their resistance to corrosion, impact, and UV degradation compared to traditional glass fiber. Glass fiber hulls can be prone to delamination and structural fatigue over time, especially in harsh marine environments, reducing their longevity. High-quality polymer composites with advanced resins and treatments significantly extend hull lifespan, making them a preferred material for long-term boat durability.
Maintenance Requirements
Polymer boat hulls, commonly made from fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP), demand routine maintenance such as washing, waxing, and inspecting for gelcoat cracks or osmosis to prevent water intrusion and structural damage. Glass fiber hulls require similar upkeep, including periodic sanding, resealing, and repair of any delamination or fiber exposure to maintain strength and appearance. Both materials benefit from UV protection treatments and careful monitoring of any surface damage to ensure longevity and minimize costly repairs.
Cost Analysis
Polymer boat hulls typically offer lower initial material and manufacturing costs compared to glass fiber hulls, making them a budget-friendly option for small to medium-sized vessels. Glass fiber, while more expensive upfront due to higher raw material and labor expenses, provides enhanced durability and longer lifespan, which can reduce long-term maintenance and replacement costs. The cost efficiency of polymers arises from easier moldability and faster production cycles, whereas glass fiber's superior strength-to-weight ratio justifies its premium price in performance-sensitive applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymer boat hulls, often made from fiberglass reinforced with polymer resins, present challenges in recycling and contribute to microplastic pollution, impacting marine ecosystems. Glass fiber, while durable and strong, involves energy-intensive manufacturing processes and generates non-biodegradable waste that complicates sustainable disposal. Advancements in bio-based polymers and recyclable composites are critical to improving the environmental footprint of both materials in boat hull construction.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Boat Hull
Polymer composites offer lightweight advantages and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for speed and fuel efficiency in boat hull construction, while glass fiber provides superior strength and durability against impact and fatigue. Selecting the right material depends on factors such as boat size, intended use, and maintenance preferences; polymer hulls require less upkeep, whereas glass fiber hulls tolerate harsher marine environments better. Balancing weight, cost, performance, and longevity is crucial to optimize hull integrity and operational efficiency.
Infographic: Polymer vs Glass fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com