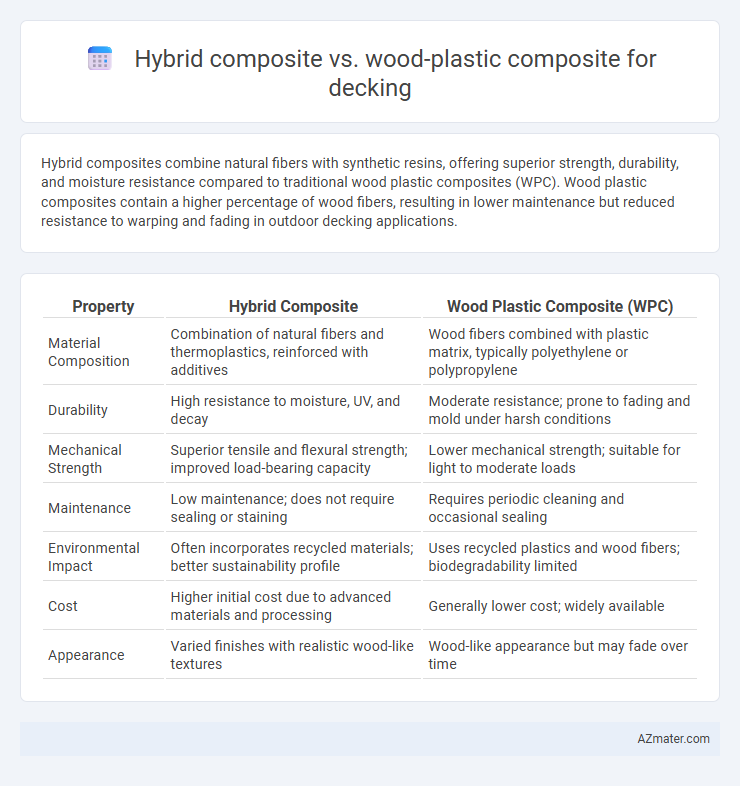
Hybrid composites combine natural fibers with synthetic resins, offering superior strength, durability, and moisture resistance compared to traditional wood plastic composites (WPC). Wood plastic composites contain a higher percentage of wood fibers, resulting in lower maintenance but reduced resistance to warping and fading in outdoor decking applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hybrid Composite | Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Combination of natural fibers and thermoplastics, reinforced with additives | Wood fibers combined with plastic matrix, typically polyethylene or polypropylene |
| Durability | High resistance to moisture, UV, and decay | Moderate resistance; prone to fading and mold under harsh conditions |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior tensile and flexural strength; improved load-bearing capacity | Lower mechanical strength; suitable for light to moderate loads |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; does not require sealing or staining | Requires periodic cleaning and occasional sealing |
| Environmental Impact | Often incorporates recycled materials; better sustainability profile | Uses recycled plastics and wood fibers; biodegradability limited |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced materials and processing | Generally lower cost; widely available |
| Appearance | Varied finishes with realistic wood-like textures | Wood-like appearance but may fade over time |
Introduction to Decking Materials
Hybrid composite decking combines natural wood fibers with recycled polymers, offering enhanced durability and resistance to moisture compared to traditional wood products. Wood plastic composite (WPC) decking is composed primarily of recycled plastics blended with wood fibers, providing low maintenance and resistance to rot, insects, and fading. Both materials serve as eco-friendly alternatives to natural wood, with Hybrid composites typically delivering superior strength and longer lifespan in outdoor decking applications.
What Are Hybrid Composites?
Hybrid composites combine wood fibers and thermoplastics with additional materials like fiberglass or mineral fillers to enhance strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. These composites offer improved structural performance and reduced moisture absorption compared to traditional wood-plastic composites (WPC), making them ideal for decking applications exposed to harsh weather. The integration of hybrid components results in decks that are more stable, longer-lasting, and require less maintenance than standard WPC products.
Understanding Wood Plastic Composites (WPC)
Wood Plastic Composites (WPC) are engineered materials combining thermoplastics and wood fibers, offering enhanced durability and low maintenance for decking applications. WPC decking resists moisture, decay, and insect damage better than traditional wood, providing a longer lifespan with minimal upkeep. The composition of WPC allows for recycling potential and consistent performance, making it a sustainable alternative to natural wood in outdoor construction.
Core Material Differences
Hybrid composite decking uses a core made from a blend of wood fibers and thermoplastics, often enhanced with fiberglass or PVC for increased strength and durability. Wood plastic composite (WPC) decking typically features a core primarily composed of recycled wood fibers and plastic, resulting in a denser but less rigid structure compared to hybrid composites. The core material differences influence moisture resistance, weight, and long-term structural stability, with hybrid composites generally offering superior performance in harsher environmental conditions.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Hybrid composite decking combines wood fibers with thermoplastic resins and often includes synthetic additives, resulting in enhanced performance characteristics such as superior moisture resistance and reduced risk of warping compared to traditional wood plastic composite (WPC) decking. Wood plastic composite decking typically contains higher plastic content which provides good resistance to rot and insect damage but may be more prone to surface scratching and fading over time. Overall, hybrid composites offer improved durability through better structural integrity and color retention, making them a preferred choice for long-lasting decking applications.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Hybrid composite decking offers a superior aesthetic appeal with a wide range of colors, textures, and finishes that closely mimic natural wood grain and provide consistent, fade-resistant beauty. Wood plastic composite (WPC) decking features a uniform appearance with fewer design variations and may exhibit color fading and surface staining over time. The enhanced design options and durability of hybrid composites make them a preferred choice for homeowners seeking long-lasting, attractive decking solutions.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Hybrid composite decking offers simpler installation due to its uniform density and engineered materials, reducing the need for pre-drilling and decreasing the risk of splitting compared to wood plastic composite (WPC). Maintenance for hybrid composites is minimal, requiring only occasional cleaning with soap and water to prevent mold and mildew, whereas WPC may demand more frequent upkeep due to higher susceptibility to surface staining and fading. Both materials resist rot and insect damage, but hybrid composites typically provide longer-lasting performance with less effort over time.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hybrid composites for decking typically combine natural fibers with recycled plastics, enhancing durability while reducing environmental impact compared to conventional wood plastic composites (WPC) that primarily use virgin plastics. The use of recycled materials in hybrid composites decreases landfill waste and lowers carbon emissions associated with production, promoting sustainability. Wood plastic composites offer improved resistance to decay and pests over traditional wood but may involve higher fossil fuel consumption and challenges in recyclability, making hybrids a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable decking solutions.
Cost Analysis and Value for Money
Hybrid composites typically offer higher durability and lower maintenance costs compared to wood plastic composites (WPC), making them a cost-effective choice over time despite a higher initial investment. Wood plastic composites, while more affordable upfront, may require more frequent repairs and replacements, increasing long-term expenses. Evaluating total lifecycle costs reveals that hybrid composites provide better value for money due to superior resistance to weathering, rot, and insect damage.
Choosing the Right Composite for Your Deck
Hybrid composites combine wood fibers with recycled plastics, offering superior durability, low maintenance, and resistance to moisture and insects, making them ideal for long-lasting decking. Wood plastic composites (WPC) consist primarily of wood fibers and plastic polymers, providing a cost-effective, eco-friendly alternative but may require more upkeep and show faster wear in harsh climates. Selecting the right composite depends on budget, desired durability, climate conditions, and maintenance preferences to ensure the deck's longevity and aesthetic appeal.
Infographic: Hybrid composite vs Wood plastic composite for Decking
 azmater.com
azmater.com