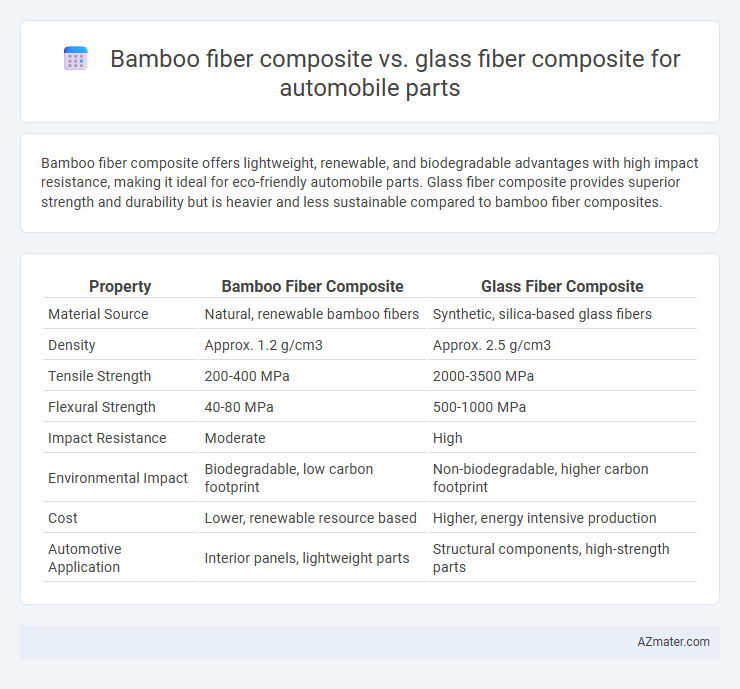
Bamboo fiber composite offers lightweight, renewable, and biodegradable advantages with high impact resistance, making it ideal for eco-friendly automobile parts. Glass fiber composite provides superior strength and durability but is heavier and less sustainable compared to bamboo fiber composites.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bamboo Fiber Composite | Glass Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Natural, renewable bamboo fibers | Synthetic, silica-based glass fibers |
| Density | Approx. 1.2 g/cm3 | Approx. 2.5 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 200-400 MPa | 2000-3500 MPa |
| Flexural Strength | 40-80 MPa | 500-1000 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Cost | Lower, renewable resource based | Higher, energy intensive production |
| Automotive Application | Interior panels, lightweight parts | Structural components, high-strength parts |
Introduction to Composite Materials in Automobiles
Bamboo fiber composites offer a sustainable alternative to traditional glass fiber composites in automobile parts, combining lightweight properties with high tensile strength for enhanced fuel efficiency and lower emissions. Glass fiber composites have long been favored for their durability and resistance to impact, providing structural integrity and safety in vehicle components. Advances in bamboo fiber technology now enable comparable mechanical performance, making it a viable choice for eco-friendly automotive manufacturing.
Overview of Bamboo Fiber Composites
Bamboo fiber composites offer a sustainable alternative to traditional glass fiber composites for automobile parts, utilizing natural fibers that provide lightweight strength and enhanced biodegradability. These composites demonstrate high tensile strength, impact resistance, and vibration damping, making them suitable for interior and non-structural exterior components. The renewable nature and lower carbon footprint of bamboo fiber composites contribute significantly to eco-friendly automotive manufacturing and reduced environmental impact.
Overview of Glass Fiber Composites
Glass fiber composites consist of fine glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, offering high tensile strength and excellent durability for automobile parts. Their superior mechanical properties, such as impact resistance and thermal stability, make them ideal for structural components like bumpers and door panels. These composites are widely used due to cost-effectiveness and compatibility with various manufacturing processes, ensuring lightweight yet robust automotive solutions.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Bamboo fiber composites exhibit lower tensile strength and modulus compared to glass fiber composites, with typical tensile strengths ranging from 200 to 350 MPa versus 600 to 1000 MPa for glass fibers. Bamboo composites offer superior impact resistance and improved energy absorption due to their natural fiber structure, while glass fiber composites provide higher stiffness and excellent fatigue resistance crucial for structural automobile parts. The density of bamboo fiber composites is significantly lower, around 1.2 g/cm3, contributing to overall weight reduction in vehicle components compared to glass fiber composites, which typically have a density near 2.5 g/cm3.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bamboo fiber composites demonstrate significantly lower environmental impact compared to glass fiber composites due to their renewable nature and biodegradability, reducing landfill waste and carbon emissions. Bamboo fibers require less energy-intensive processing and sequester CO2 during growth, enhancing sustainability in automotive part manufacturing. Glass fiber composites involve higher energy consumption and generate non-biodegradable waste, posing greater ecological challenges and limiting recyclability.
Cost Analysis and Economic Benefits
Bamboo fiber composite offers significant cost advantages over glass fiber composite due to its lower raw material expenses and renewable nature, making it an economically viable alternative for automobile parts. The reduced fabrication costs and shorter processing times associated with bamboo fiber composites contribute to lower overall production expenses while maintaining competitive mechanical properties. Furthermore, the biodegradability and lightweight characteristics of bamboo fiber composites enhance fuel efficiency and reduce end-of-life disposal costs, providing substantial long-term economic benefits for automotive manufacturers.
Weight and Performance Considerations
Bamboo fiber composites offer a significant weight reduction of up to 30-40% compared to traditional glass fiber composites, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions in automobile applications. While glass fiber composites provide superior tensile strength and durability, bamboo composites exhibit comparable performance with improved impact resistance and vibration damping due to their natural fiber structure. The choice between bamboo and glass fiber composites depends on balancing lightweight design priorities with mechanical performance requirements in automotive part manufacturing.
Processing and Manufacturing Techniques
Bamboo fiber composites utilize eco-friendly, natural fibers that require specialized treatment processes such as alkali treatment and drying to enhance adhesion with polymer matrices, often processed through resin transfer molding or compression molding. Glass fiber composites, widely used in the automotive industry, involve established manufacturing techniques like filament winding, pultrusion, and spray-up methods, offering higher thermal stability and mechanical strength. Bamboo composites offer sustainable advantages but demand precise control over fiber moisture content and matrix compatibility, whereas glass fiber composites benefit from mature, scalable manufacturing processes suited for mass production.
Durability and Lifecycle Assessment
Bamboo fiber composites offer a sustainable alternative to glass fiber composites in automobile parts, exhibiting commendable durability through high tensile strength and resistance to fatigue under cyclic loading. Lifecycle assessment indicates that bamboo fiber composites have a significantly lower environmental impact, including reduced carbon footprint and energy consumption during production and end-of-life disposal. While glass fiber composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratios, bamboo composites enhance biodegradability and promote circular economy models in automotive manufacturing.
Future Prospects in Automotive Applications
Bamboo fiber composites offer sustainable, lightweight alternatives to traditional glass fiber composites, providing comparable strength with reduced environmental impact for automotive parts. Increasing regulatory pressures and consumer demand for eco-friendly materials drive innovation in bamboo fiber composite processing and hybridization, enhancing performance and durability. Emerging technologies in bio-based resin systems and improved fiber treatments suggest promising future adoption of bamboo fiber composites in automotive structural and interior components.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber composite vs Glass fiber composite for Automobile part
 azmater.com
azmater.com