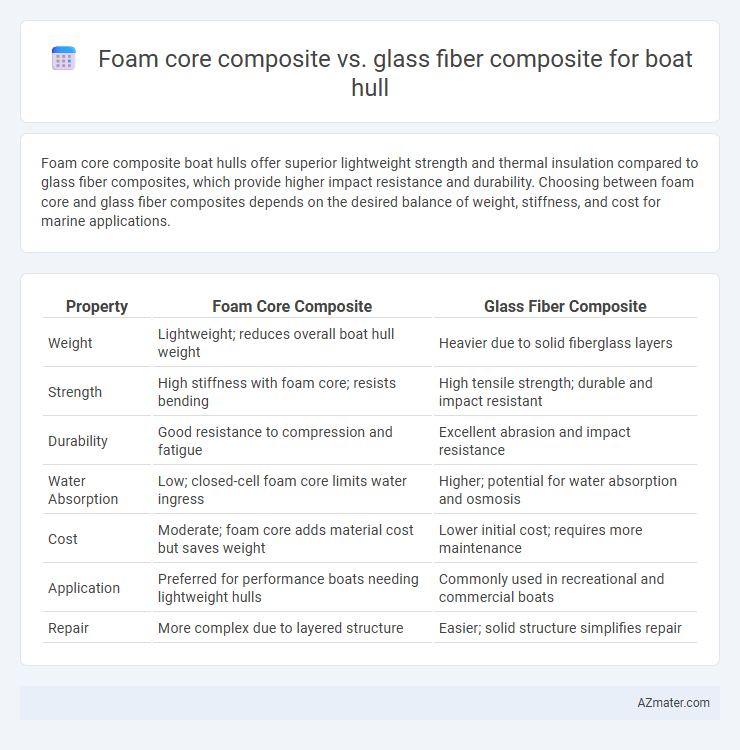
Foam core composite boat hulls offer superior lightweight strength and thermal insulation compared to glass fiber composites, which provide higher impact resistance and durability. Choosing between foam core and glass fiber composites depends on the desired balance of weight, stiffness, and cost for marine applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Foam Core Composite | Glass Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight; reduces overall boat hull weight | Heavier due to solid fiberglass layers |
| Strength | High stiffness with foam core; resists bending | High tensile strength; durable and impact resistant |
| Durability | Good resistance to compression and fatigue | Excellent abrasion and impact resistance |
| Water Absorption | Low; closed-cell foam core limits water ingress | Higher; potential for water absorption and osmosis |
| Cost | Moderate; foam core adds material cost but saves weight | Lower initial cost; requires more maintenance |
| Application | Preferred for performance boats needing lightweight hulls | Commonly used in recreational and commercial boats |
| Repair | More complex due to layered structure | Easier; solid structure simplifies repair |
Introduction to Foam Core and Glass Fiber Composites
Foam core composites consist of a lightweight foam core sandwiched between layers of fiberglass or other reinforcing materials, providing excellent strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced buoyancy for boat hull applications. Glass fiber composites are made from woven glass fibers bonded with resin, offering high tensile strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, making them a common choice for boat hull construction. Combining foam core with glass fiber layers results in a composite material that maximizes stiffness, impact resistance, and overall performance in marine environments.
Basics of Boat Hull Construction Materials
Foam core composites provide excellent strength-to-weight ratios and superior insulation, making them ideal for lightweight boat hulls with enhanced buoyancy. Glass fiber composites offer high durability, impact resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making them a popular choice for strong and affordable hull construction. Both materials are widely used in marine applications, with foam core composites often serving as sandwich cores to increase stiffness and glass fiber reinforcing structural layers.
Structural Strength: Foam Core vs Glass Fiber
Foam core composites offer enhanced structural strength by combining a lightweight foam core with strong fiberglass skins, resulting in high stiffness-to-weight ratios ideal for boat hulls. Glass fiber composites provide excellent tensile strength and impact resistance but tend to be heavier, affecting overall vessel performance. The foam core structure improves flexural rigidity and reduces weight, making it superior for strength-to-weight balance compared to solid glass fiber composites.
Weight and Buoyancy Comparison
Foam core composites offer significantly lower weight compared to glass fiber composites, enhancing overall vessel speed and fuel efficiency. The inherent buoyancy of foam cores improves flotation, reducing the risk of hull water ingress and increasing safety. Glass fiber composites, while heavier, provide greater structural strength but at the expense of increased weight and decreased buoyancy performance.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Foam core composite boat hulls offer high stiffness-to-weight ratios and excellent buoyancy, but their impact resistance can be compromised if the foam core is breached, leading to potential water ingress and core degradation. Glass fiber composite hulls provide superior durability under repeated impacts and abrasions due to the toughness of woven glass fibers embedded in resin, which also enhances resistance to cracking and fatigue over time. When considering long-term durability and impact resistance, glass fiber composites generally outperform foam core composites, especially in demanding marine environments with frequent collisions or grounding.
Ease of Fabrication and Repair
Foam core composites offer superior ease of fabrication for boat hulls due to their lightweight core material that simplifies shaping and laminating processes compared to glass fiber composites. Repairs on foam core hulls are generally more straightforward and quicker, as damaged foam sections can be easily removed and replaced without extensive structural work. In contrast, glass fiber composites require more labor-intensive handling during both fabrication and repair, often necessitating specialized resins and curing times to restore hull integrity.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Foam core composites offer a cost-effective alternative to glass fiber composites for boat hull construction due to lower material prices and reduced labor intensity during fabrication. Glass fiber composites have higher availability globally, supported by established supply chains and widespread industry use, whereas foam core composites may face limited regional accessibility and require specialized sourcing. Evaluating long-term maintenance and durability costs further influences the economic decision, as glass fiber composites typically provide more consistent performance in harsh marine environments.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Foam core composites provide superior thermal insulation due to their closed-cell structure, significantly reducing heat transfer compared to glass fiber composites. In acoustic insulation, foam cores also outperform glass fiber by absorbing and dampening sound vibrations more effectively within the boat hull. Consequently, foam core composites enhance onboard comfort by maintaining temperature stability and minimizing noise intrusion better than traditional glass fiber composites.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Foam core composites typically have a larger environmental footprint due to the petroleum-based foam cores and energy-intensive manufacturing processes, which contribute to non-biodegradable waste and higher carbon emissions. Glass fiber composites, while offering durability and strength, also pose challenges in recyclability and disposal, as fibers and resins are difficult to break down and often end up in landfills or incinerators. Sustainable alternatives focus on bio-based resins and recyclable fibers, but current foam core composites generally lag behind glass fiber composites in terms of long-term environmental impact and circularity in boat hull applications.
Best Applications and Recommendations for Boat Hulls
Foam core composites provide excellent buoyancy and thermal insulation, making them ideal for lightweight recreational boats and small to medium-sized hulls that prioritize speed and fuel efficiency. Glass fiber composites offer superior strength, durability, and impact resistance, making them well-suited for larger vessels, commercial boats, and hulls that require high structural integrity and longevity. For optimal performance, foam core composites are recommended for performance-driven applications, while glass fiber composites are preferred for heavy-duty and long-lasting marine environments.
Infographic: Foam core composite vs Glass fiber composite for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com