Structural composites offer superior impact resistance and lighter weight compared to glass for bulletproof shields. Advanced composites enhance durability and energy dispersion, making them ideal for high-performance ballistic protection.
Table of Comparison
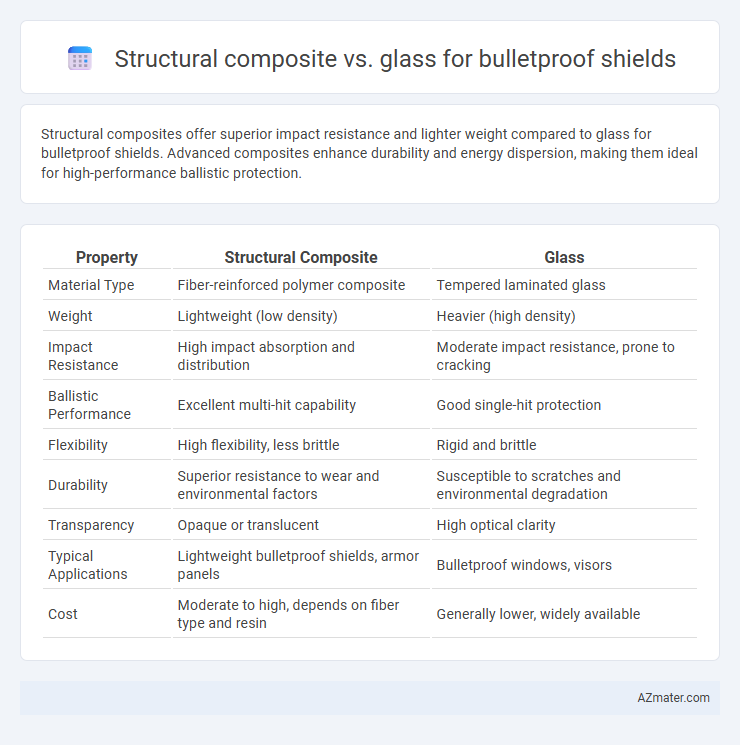
| Property | Structural Composite | Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Fiber-reinforced polymer composite | Tempered laminated glass |
| Weight | Lightweight (low density) | Heavier (high density) |
| Impact Resistance | High impact absorption and distribution | Moderate impact resistance, prone to cracking |
| Ballistic Performance | Excellent multi-hit capability | Good single-hit protection |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, less brittle | Rigid and brittle |
| Durability | Superior resistance to wear and environmental factors | Susceptible to scratches and environmental degradation |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | High optical clarity |
| Typical Applications | Lightweight bulletproof shields, armor panels | Bulletproof windows, visors |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depends on fiber type and resin | Generally lower, widely available |
Introduction to Bulletproof Shield Materials
Bulletproof shields utilize advanced materials to provide maximum protection against ballistic threats. Structural composites, including aramid fiber composites such as Kevlar, offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent energy absorption properties. Glass, specifically laminated ballistic glass, delivers transparent armor capabilities but tends to be heavier and more brittle compared to modern composite alternatives.
Overview of Structural Composites
Structural composites for bulletproof shields combine high-strength fibers such as aramid or ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene with resin matrices, providing superior ballistic resistance and lightweight durability. These composites exhibit excellent energy absorption and multi-hit capability, outperforming traditional glass in flexibility and weight reduction. Unlike glass, structural composites resist shattering upon impact, ensuring enhanced safety and longer service life in ballistic applications.
Glass as a Traditional Bulletproof Material
Glass, traditionally used in bulletproof shields, primarily consists of multiple layers of laminated glass or acrylic designed to absorb and disperse the energy from bullets. While glass offers transparency and high hardness, it tends to be heavier and more brittle compared to advanced structural composites. This brittleness can lead to cracking or shattering under repeated impacts, limiting its effectiveness in multi-hit scenarios relative to newer composite materials.
Comparative Ballistic Protection Performance
Structural composite materials used in bulletproof shields, such as aramid fiber composites and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), offer superior energy absorption and multi-hit resistance compared to traditional glass laminates. Glass shields, typically composed of layered, heat-treated borosilicate or laminated ballistic glass, provide high hardness and transparency but tend to be heavier and more brittle under repeated ballistic impacts. Composite shields outperform glass in ballistic protection by combining flexibility, lightweight characteristics, and enhanced durability, enabling better performance against high-velocity projectiles and improving overall survivability in tactical scenarios.
Weight and Portability Considerations
Structural composites offer significantly reduced weight compared to traditional glass, enhancing portability for bulletproof shields used in tactical and law enforcement operations. These composites, often made from aramid fibers or ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene, provide superior strength-to-weight ratios, allowing for easier handling and longer deployment times. Glass shields, while offering excellent transparency and ballistic resistance, tend to be heavier and more cumbersome, limiting mobility and increasing fatigue during extended use.
Durability and Longevity of Shields
Structural composite bulletproof shields exhibit superior durability and longevity compared to traditional glass shields due to their multi-layered construction combining high-strength fibers and resin matrices that resist cracking and impact degradation. Glass shields, typically made from laminated or tempered glass, offer good initial ballistic protection but are more prone to shattering and gradual weakening from microfractures and environmental exposure. Advanced composites maintain structural integrity under repeated impacts and harsh conditions, extending service life and reducing the need for frequent replacement in high-risk environments.
Cost Analysis: Structural Composite vs Glass
Structural composite bulletproof shields offer a cost-effective advantage over traditional glass shields due to lower material and manufacturing expenses. Glass shields, particularly laminated or tempered ballistic glass, involve higher production costs driven by complex layering and specialized treatments to achieve comparable protection levels. Maintenance and replacement costs for glass are also higher because of susceptibility to cracks and chips, whereas structural composites provide durability with reduced lifecycle expenditures.
Maintenance and Repair Requirements
Structural composite bulletproof shields require specialized repair techniques involving resin infusion and curing processes, often necessitating professional maintenance to restore full ballistic integrity. Glass bulletproof shields, typically laminated with multiple layers of polycarbonate and glass, offer easier spot repairs but may require complete panel replacement to maintain optical clarity and structural strength. Regular inspections for delamination, scratches, and cracks are critical to both materials to ensure ongoing protective performance and durability.
Environmental and Weather Resistance
Structural composite materials offer superior environmental and weather resistance compared to traditional glass in bulletproof shields, with enhanced durability against UV exposure, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. Composites maintain their integrity and performance in harsh conditions by resisting corrosion and thermal expansion, whereas glass is prone to cracking or weakening under extreme weather. These advantages make structural composites ideal for bulletproof shields used in outdoor and variable climate environments.
Future Trends in Bulletproof Shield Materials
Structural composites are increasingly favored over traditional glass for bulletproof shields due to superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced energy absorption capabilities. Advances in nanotechnology and bio-based resins are driving the development of lighter, more flexible composites with improved ballistic resistance. Future trends emphasize hybrid materials combining ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers with transparent ceramics to optimize protection while maintaining visibility and reducing overall shield weight.
Infographic: Structural composite vs Glass for Bulletproof shield
 azmater.com
azmater.com