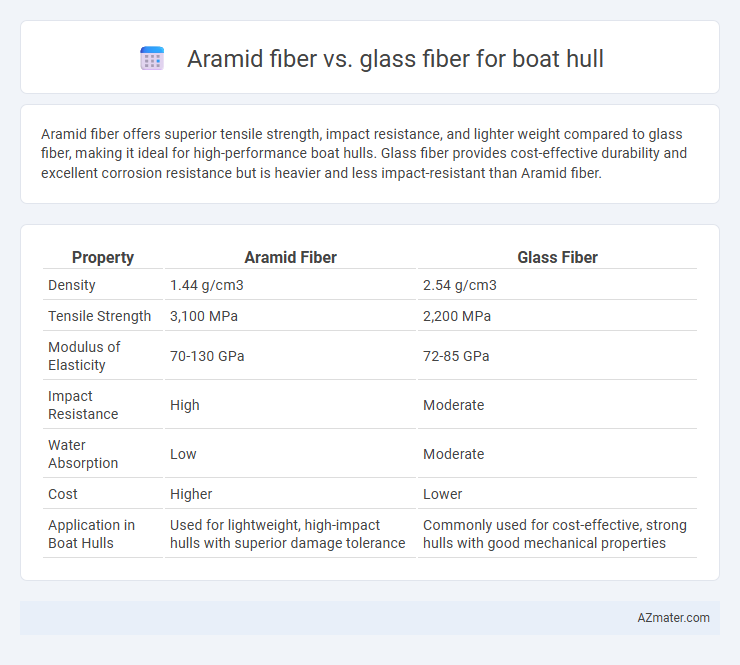
Aramid fiber offers superior tensile strength, impact resistance, and lighter weight compared to glass fiber, making it ideal for high-performance boat hulls. Glass fiber provides cost-effective durability and excellent corrosion resistance but is heavier and less impact-resistant than Aramid fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.44 g/cm3 | 2.54 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 3,100 MPa | 2,200 MPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 70-130 GPa | 72-85 GPa |
| Impact Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Water Absorption | Low | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Application in Boat Hulls | Used for lightweight, high-impact hulls with superior damage tolerance | Commonly used for cost-effective, strong hulls with good mechanical properties |
Introduction to Aramid and Glass Fibers
Aramid fiber, known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and high impact resistance, is often used in advanced boat hull constructions to enhance durability and reduce weight. Glass fiber, or fiberglass, is a widely used composite material favored for its affordability, corrosion resistance, and ease of molding in various hull designs. Both fibers offer unique mechanical properties that influence hull performance, with aramid fibers providing superior toughness and glass fibers delivering cost-effective structural reinforcement.
Material Properties Comparison
Aramid fiber offers superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to glass fiber, making it highly effective for boat hulls requiring enhanced durability and lightweight characteristics. Glass fiber provides excellent stiffness and cost-efficiency but has lower fatigue resistance and is heavier than aramid fiber. The choice between aramid and glass fiber depends on performance demands, with aramid favored for high-strength, impact-prone applications and glass fiber for economical, rigid hull structures.
Weight and Density Differences
Aramid fiber has a significantly lower density, typically around 1.44 g/cm3, compared to glass fiber's density of approximately 2.5 g/cm3, making it much lighter for boat hull construction. This reduced weight enhances fuel efficiency and improves the vessel's speed and maneuverability. Despite its lighter weight, aramid fiber offers excellent strength-to-weight ratio, contributing to durable yet lightweight boat hulls.
Strength and Durability
Aramid fiber, known for its superior tensile strength and impact resistance, provides enhanced durability and puncture resistance for boat hulls compared to glass fiber. Glass fiber offers good strength at a lower cost but is more prone to delamination and degradation from prolonged water exposure. The higher strength-to-weight ratio of aramid fiber improves hull performance and longevity in demanding marine conditions.
Impact and Fatigue Resistance
Aramid fiber offers superior impact resistance for boat hulls due to its exceptional toughness and energy absorption capabilities, significantly reducing hull damage from collisions or debris. Glass fiber provides decent impact resistance but tends to crack or shatter under heavy impact, making it less durable in rough marine environments. In terms of fatigue resistance, aramid fiber exhibits outstanding durability under repeated stress cycles, enhancing hull longevity and performance over time compared to glass fiber, which is more prone to fatigue-induced micro-cracking and structural weakening.
Cost Considerations
Aramid fiber boat hulls typically incur higher upfront costs than glass fiber due to expensive raw materials and specialized manufacturing processes. Glass fiber remains a cost-effective option, providing satisfactory strength and durability with significantly lower material and labor expenses. Long-term maintenance and potential weight savings with aramid fibers may influence overall lifecycle costs despite the initial price premium.
Ease of Manufacturing and Repairs
Aramid fiber offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, making it easier to perform precise repairs on boat hulls without compromising structural integrity. Glass fiber is widely favored for its cost-effectiveness and well-established manufacturing processes, which simplify large-scale production. While glass fiber allows for quicker layup and curing times, aramid fiber requires specialized handling and resin systems, influencing the overall ease of manufacturing.
Performance in Marine Environments
Aramid fiber offers superior impact resistance and tensile strength compared to glass fiber, making it highly effective for boat hulls exposed to harsh marine environments. Its low density provides better weight savings, which enhances vessel speed and fuel efficiency while maintaining structural integrity under repetitive stress from waves. Glass fiber, while more cost-effective and corrosion-resistant, lacks the toughness and fatigue resistance of aramid fiber, resulting in potentially shorter lifespan and higher maintenance in rough sea conditions.
Application Examples in Boat Hulls
Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, is widely used in high-performance boat hulls for its exceptional impact resistance and lightweight properties, making it ideal for racing yachts and military vessels subjected to harsh conditions. Glass fiber remains a popular choice in recreational boats and commercial vessels due to its cost-effectiveness, ease of fabrication, and good strength-to-weight ratio. Composite hulls often combine aramid fiber and glass fiber to balance durability, weight, and cost, optimizing performance for offshore sailboats and fishing boats.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Boat
Aramid fiber offers superior impact resistance and tensile strength, making it ideal for high-performance boat hulls requiring durability and weight reduction. Glass fiber provides excellent corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness, suited for traditional hulls where budget and maintenance are key considerations. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing factors such as mechanical properties, weight, cost, and exposure to marine environments to optimize boat longevity and performance.
Infographic: Aramid fiber vs Glass fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com