Wood plastic composite siding offers superior moisture resistance and low maintenance compared to fiber cement, which provides exceptional fire resistance and durability against extreme weather. Choosing between these materials depends on prioritizing water resistance and eco-friendliness or enhanced fire protection and long-term structural strength.
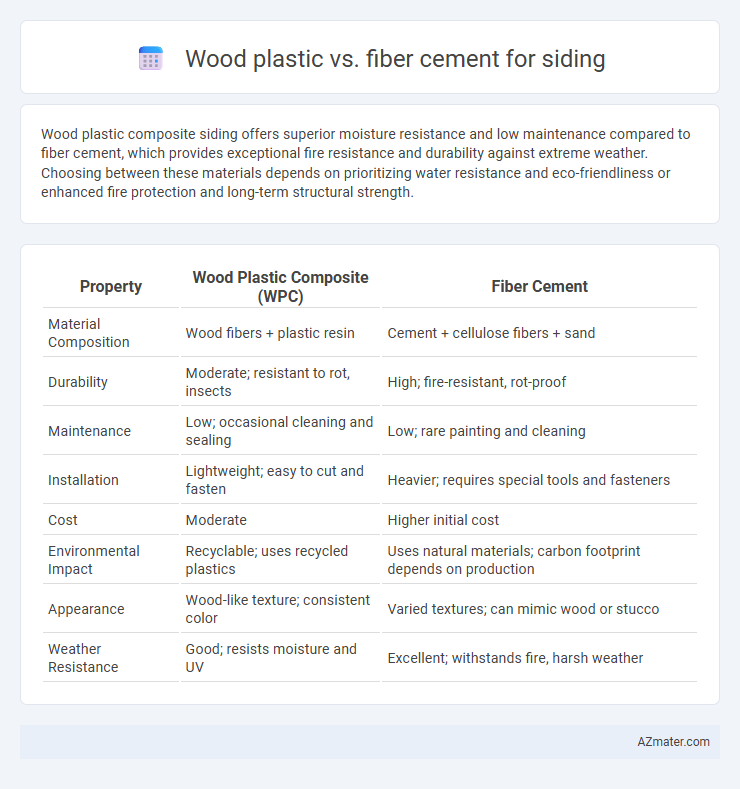
Table of Comparison
| Property | Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) | Fiber Cement |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood fibers + plastic resin | Cement + cellulose fibers + sand |
| Durability | Moderate; resistant to rot, insects | High; fire-resistant, rot-proof |
| Maintenance | Low; occasional cleaning and sealing | Low; rare painting and cleaning |
| Installation | Lightweight; easy to cut and fasten | Heavier; requires special tools and fasteners |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher initial cost |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable; uses recycled plastics | Uses natural materials; carbon footprint depends on production |
| Appearance | Wood-like texture; consistent color | Varied textures; can mimic wood or stucco |
| Weather Resistance | Good; resists moisture and UV | Excellent; withstands fire, harsh weather |
Introduction to Siding Materials
Wood plastic composite (WPC) siding combines the durability of plastic with natural wood fibers, offering resistance to rot, insects, and moisture. Fiber cement siding, made from a mixture of cement, sand, and cellulose fibers, provides exceptional fire resistance and low maintenance while mimicking wood textures. Both materials serve as durable alternatives to traditional wood siding, with fiber cement excelling in longevity and WPC in environmental sustainability.
Overview of Wood Plastic Siding
Wood plastic siding combines recycled wood fibers and plastic polymers to create a durable, low-maintenance exterior cladding option resistant to rot, insects, and moisture. Its composite structure offers enhanced flexibility, impact resistance, and color retention compared to traditional wood siding. The eco-friendly material also provides insulation benefits and can mimic the appearance of natural wood without the drawbacks of frequent painting or sealing.
Overview of Fiber Cement Siding
Fiber cement siding is a durable exterior cladding material composed of cement, sand, and cellulose fibers, offering resistance to fire, rot, and insect damage. It provides a strong, low-maintenance alternative to wood plastic composites, with enhanced weather resistance and longevity in diverse climates. Fiber cement siding also closely mimics the appearance of traditional wood while requiring less frequent painting and upkeep.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Fiber cement siding offers superior durability and longevity compared to wood plastic composites, with resistance to moisture, rot, insects, and fire. Wood plastic siding, while more resistant to moisture than natural wood and less prone to splitting, generally has a shorter lifespan and can degrade under prolonged UV exposure or extreme weather conditions. Fiber cement siding typically lasts 30 to 50 years with minimal maintenance, whereas wood plastic siding usually endures around 20 to 30 years before requiring replacement.
Weather Resistance and Maintenance Needs
Fiber cement siding offers superior weather resistance compared to wood plastic composites, with enhanced durability against moisture, rot, and insect damage, making it ideal for harsh climates. Wood plastic siding requires regular maintenance such as sealing and painting to prevent degradation from UV exposure and moisture over time. Fiber cement's low maintenance needs and resistance to warping and swelling ensure a longer-lasting exterior with less upkeep.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Wood plastic composite (WPC) siding incorporates recycled plastics and wood fibers, reducing landfill waste and promoting circular economy principles, while fiber cement siding relies on cement, sand, and cellulose fibers, which require significant mining and energy during production. WPC offers lower embodied carbon and better recyclability compared to fiber cement, which has a higher carbon footprint due to cement manufacturing emissions. Both materials have durability benefits, but WPC's use of post-consumer plastics enhances sustainability through waste reduction and resource efficiency.
Installation Process and Costs
Wood plastic composite siding offers easier installation with lightweight panels that require fewer specialized tools, reducing labor time and overall costs; it typically costs between $7 and $12 per square foot. Fiber cement siding demands skilled labor due to its heavier weight and need for cutting with special tools, driving installation costs higher, ranging from $8 to $15 per square foot. Both materials offer durability, but wood plastic siding provides a more budget-friendly and less labor-intensive installation process compared to fiber cement.
Appearance and Design Versatility
Wood plastic composite siding offers a wide range of colors and textures that closely mimic natural wood, providing a warm and authentic aesthetic with enhanced durability and low maintenance. Fiber cement siding, while available in diverse finishes including smooth, wood-grain, and stucco textures, excels in offering a more rigid and substantial look suitable for traditional and modern designs. Both materials support versatile architectural styles but differ in tactile feel and long-term appearance retention under varying weather conditions.
Pros and Cons: Wood Plastic vs Fiber Cement
Wood plastic siding offers durability and low maintenance, resisting rot and insect damage better than traditional wood while being lightweight and eco-friendly; however, it may be more susceptible to fading and warping under extreme heat. Fiber cement siding excels in fire resistance, excellent durability, and low moisture absorption, making it ideal for harsh climates, but it is heavier, requires professional installation, and can be prone to cracking if not properly maintained. Cost-wise, wood plastic tends to be more affordable upfront but may need periodic refinishing, whereas fiber cement has higher initial costs with longer-lasting performance and minimal upkeep.
Which Siding is Best for Your Home?
Wood plastic composite siding offers enhanced durability, low maintenance, and resistance to rot and insects, making it ideal for homeowners seeking eco-friendly, long-lasting materials. Fiber cement siding excels in fire resistance, dimensional stability, and aesthetic versatility, often preferred in regions with harsh weather conditions and strict building codes. Choosing the best siding depends on climate factors, maintenance preferences, budget constraints, and desired curb appeal for your home.
Infographic: Wood plastic vs Fiber cement for Siding
 azmater.com
azmater.com