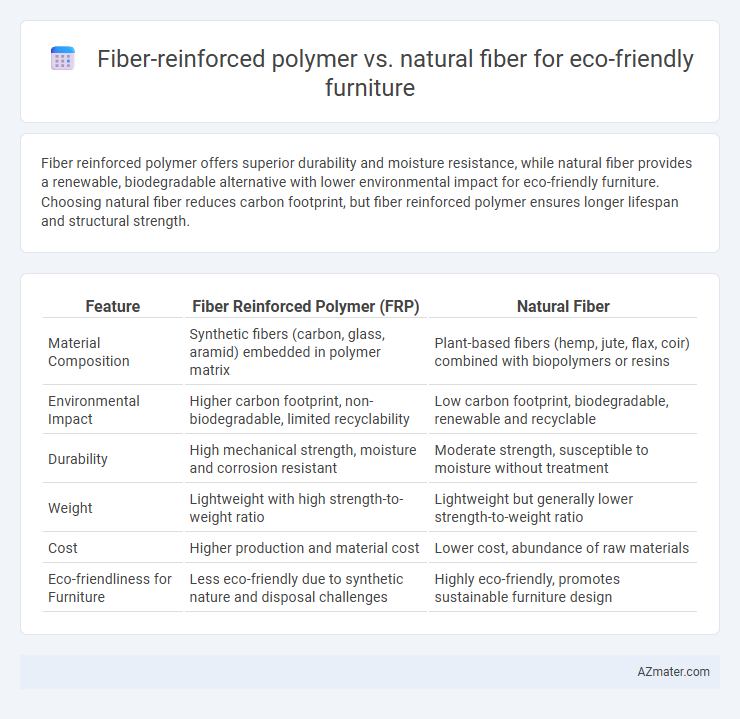
Fiber reinforced polymer offers superior durability and moisture resistance, while natural fiber provides a renewable, biodegradable alternative with lower environmental impact for eco-friendly furniture. Choosing natural fiber reduces carbon footprint, but fiber reinforced polymer ensures longer lifespan and structural strength.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP) | Natural Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Synthetic fibers (carbon, glass, aramid) embedded in polymer matrix | Plant-based fibers (hemp, jute, flax, coir) combined with biopolymers or resins |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint, non-biodegradable, limited recyclability | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable, renewable and recyclable |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, moisture and corrosion resistant | Moderate strength, susceptible to moisture without treatment |
| Weight | Lightweight with high strength-to-weight ratio | Lightweight but generally lower strength-to-weight ratio |
| Cost | Higher production and material cost | Lower cost, abundance of raw materials |
| Eco-friendliness for Furniture | Less eco-friendly due to synthetic nature and disposal challenges | Highly eco-friendly, promotes sustainable furniture design |
Introduction to Eco-Friendly Furniture Materials
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) offers exceptional durability and lightweight properties, making it a popular choice for eco-friendly furniture that requires longevity and minimal maintenance. Natural fibers such as jute, hemp, and flax provide biodegradable and renewable alternatives, enhancing sustainability by reducing environmental impact through lower carbon footprints. Both materials contribute to eco-friendly furniture production by balancing performance with environmental responsibility, catering to increasing consumer demand for green living solutions.
What Are Fiber Reinforced Polymers?
Fiber reinforced polymers (FRPs) are composite materials composed of a polymer matrix reinforced with fibers such as glass, carbon, or aramid, offering high strength-to-weight ratios and durability. FRPs provide superior resistance to moisture, corrosion, and wear, making them ideal for long-lasting, maintenance-free eco-friendly furniture. Unlike natural fibers, FRPs can be engineered for specific performance characteristics, enhancing sustainability by increasing furniture longevity and reducing resource consumption.
Overview of Natural Fibers in Furniture Design
Natural fibers such as jute, hemp, coir, and flax are increasingly utilized in eco-friendly furniture design due to their biodegradability, low environmental impact, and renewable nature. These fibers offer excellent mechanical properties, including good tensile strength and flexibility, which make them suitable for weaving, reinforcement, and composite formation in furniture manufacturing. Their lightweight and sustainable characteristics contribute to reducing the carbon footprint compared to synthetic alternatives like fiber reinforced polymers.
Environmental Impact: Synthetic vs. Natural Fibers
Fiber reinforced polymers (FRPs) typically exhibit higher carbon footprints due to their reliance on petroleum-based resins and energy-intensive manufacturing processes. Natural fibers such as hemp, flax, and jute offer significantly lower environmental impacts by being biodegradable, renewable, and requiring less energy for production. The disposal and recycling challenges of synthetic fibers further emphasize the sustainability advantages of natural fiber composites in eco-friendly furniture applications.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) offers superior durability and strength compared to natural fibers, making it highly resistant to environmental factors such as moisture, UV radiation, and mechanical stress, which enhances the longevity of eco-friendly furniture. Natural fibers, while biodegradable and sustainable, typically exhibit lower tensile strength and are more susceptible to degradation from exposure to humidity and pests, requiring additional treatment to improve their performance. FRP's high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to wear make it ideal for long-lasting furniture, whereas natural fiber composites provide a greener option with moderate durability suitable for indoor or low-stress applications.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) offers superior design flexibility with its ability to be molded into complex shapes, enabling sleek and modern aesthetics in eco-friendly furniture. Natural fibers provide a warm, organic texture that enhances a rustic or earthy design appeal but have limited malleability compared to FRP. The choice between FRP and natural fiber materials significantly influences the visual style and creative possibilities in sustainable furniture design.
Cost Analysis: Production and Lifecycle
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) furniture typically incurs higher initial production costs due to complex manufacturing processes and synthetic raw materials, but offers superior durability and lower maintenance expenses over its lifecycle. Natural fiber furniture, sourced from renewable materials like bamboo or jute, benefits from lower production costs and biodegradability, yet may require more frequent replacements or repairs due to reduced longevity. Lifecycle cost analysis reveals that while FRP demands greater upfront investment, natural fiber furniture provides a cost-effective eco-friendly alternative with environmental advantages despite potential durability trade-offs.
Sustainability and Biodegradability Factors
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) offers high durability and strength but often relies on non-renewable, non-biodegradable synthetic resins, limiting its eco-friendliness in furniture applications. Natural fibers, such as jute, hemp, and flax, provide renewable, biodegradable alternatives that reduce environmental impact through lower carbon footprints and end-of-life compostability. Furniture crafted from natural fiber composites supports sustainable practices by promoting resource regeneration and enabling easier waste management compared to conventional FRP materials.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) dominates the eco-friendly furniture market due to its durability, lightweight properties, and resistance to corrosion, attracting consumers prioritizing longevity and low maintenance. Natural fiber materials such as jute, hemp, and flax gain consumer preference for sustainable, biodegradable options and aesthetic appeal, especially in eco-conscious segments emphasizing organic and renewable resources. Market trends reveal a growing hybrid approach combining FRP with natural fibers to balance strength and environmental impact, responding to evolving consumer demands for functionality and sustainability.
Future Prospects in Eco-Friendly Furniture Materials
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) offers superior durability and moisture resistance, making it a long-lasting choice for eco-friendly furniture, whereas natural fibers like hemp and jute provide renewability and biodegradability benefits. Advances in bio-based resins and hybrid composites combining FRP with natural fibers are enhancing sustainability without compromising strength. Future prospects include scaling production of these hybrid materials to create furniture with a reduced carbon footprint while maintaining performance and aesthetic appeal.
Infographic: Fiber reinforced polymer vs Natural fiber for Eco-friendly furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com