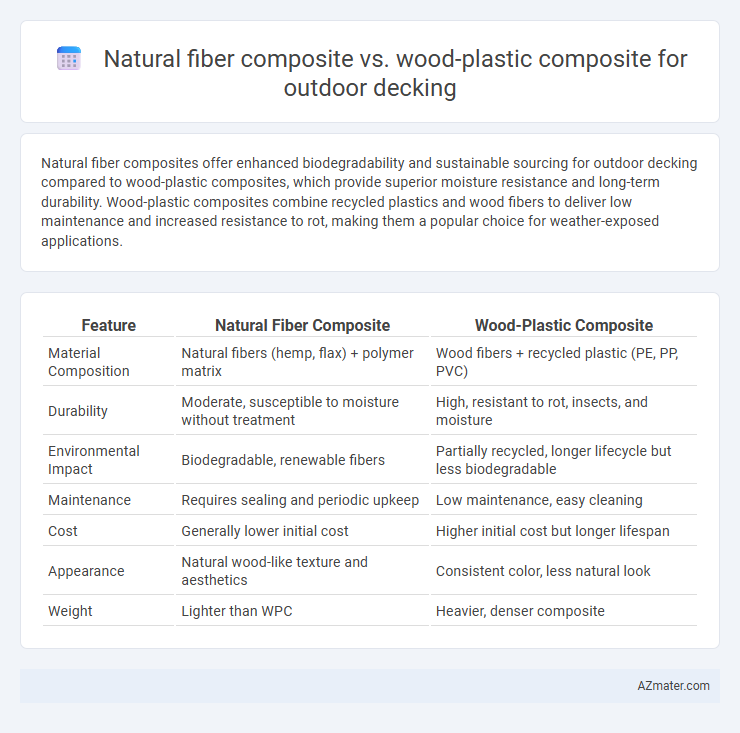
Natural fiber composites offer enhanced biodegradability and sustainable sourcing for outdoor decking compared to wood-plastic composites, which provide superior moisture resistance and long-term durability. Wood-plastic composites combine recycled plastics and wood fibers to deliver low maintenance and increased resistance to rot, making them a popular choice for weather-exposed applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Natural Fiber Composite | Wood-Plastic Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers (hemp, flax) + polymer matrix | Wood fibers + recycled plastic (PE, PP, PVC) |
| Durability | Moderate, susceptible to moisture without treatment | High, resistant to rot, insects, and moisture |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable fibers | Partially recycled, longer lifecycle but less biodegradable |
| Maintenance | Requires sealing and periodic upkeep | Low maintenance, easy cleaning |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial cost but longer lifespan |
| Appearance | Natural wood-like texture and aesthetics | Consistent color, less natural look |
| Weight | Lighter than WPC | Heavier, denser composite |
Introduction: Choosing the Right Material for Outdoor Decking
Natural fiber composites offer superior environmental benefits and biodegradability compared to wood-plastic composites, making them a sustainable choice for outdoor decking. Wood-plastic composites provide enhanced durability, moisture resistance, and lower maintenance requirements due to their synthetic resin content. Selecting between these materials depends on balancing factors such as ecological impact, longevity, and performance under outdoor conditions.
Overview of Natural Fiber Composites
Natural fiber composites consist of renewable fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute combined with polymer matrices to create durable, eco-friendly decking materials. These composites offer enhanced biodegradability, reduced carbon footprint, and superior moisture resistance compared to traditional wood-plastic composites. Advances in fiber treatment and matrix bonding improve mechanical strength and dimensional stability, making natural fiber composites an increasingly viable choice for sustainable outdoor decking applications.
Overview of Wood-Plastic Composites
Wood-plastic composites (WPCs) are engineered materials combining wood fibers and thermoplastic polymers, offering enhanced durability and resistance to moisture, rot, and insect damage compared to natural fiber composites. Their high-density structure provides excellent dimensional stability and reduced maintenance requirements, making WPCs a popular choice for outdoor decking applications. WPCs also allow for customization in color and texture, closely mimicking natural wood while improving lifespan and environmental resistance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Natural fiber composites, derived from renewable resources like hemp or flax, offer superior biodegradability and lower carbon footprints compared to wood-plastic composites, which integrate synthetic polymers that challenge recyclability and contribute to microplastic pollution. Wood-plastic composites utilize recycled plastics and wood fibers, providing durability and resistance to weathering, but their production and end-of-life disposal pose environmental concerns due to polymer additives and limited biodegradability. For sustainable outdoor decking, natural fiber composites align better with circular economy principles and reduced ecological impact, supporting long-term environmental stewardship in construction materials.
Weather Resistance and Durability Comparison
Natural fiber composites for outdoor decking offer superior breathability but tend to absorb moisture, leading to potential swelling and reduced weather resistance compared to wood-plastic composites (WPC). Wood-plastic composites combine wood fibers with thermoplastic polymers, resulting in enhanced durability, better resistance to UV rays, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. WPC decking generally outperforms natural fiber composites in long-term weather resistance and structural stability, making it a preferred choice for outdoor environments exposed to variable weather conditions.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Natural fiber composites offer a warm, organic aesthetic with natural texture variations that enhance outdoor decking's visual appeal, closely resembling traditional wood. Wood-plastic composites provide greater design flexibility, allowing for a wide range of colors, shapes, and finishes while maintaining durability and low maintenance. Both materials support diverse architectural styles, but natural fiber composites excel in authentic appearance, whereas wood-plastic composites afford customizable design options.
Maintenance Requirements and Long-Term Care
Natural fiber composites for outdoor decking require regular sealing and protection from moisture to prevent degradation and maintain structural integrity, as natural fibers are more susceptible to rot and mold. Wood-plastic composites (WPC) offer lower maintenance with enhanced resistance to fading, staining, and insect damage due to their synthetic polymer content, requiring only periodic cleaning. Over the long term, WPC decking typically outperforms natural fiber composites by retaining appearance and durability with less intensive care, making it a preferred choice for low-maintenance outdoor applications.
Installation Methods and Ease of Handling
Natural fiber composites offer lightweight properties and flexibility, allowing for easier cutting and fastening with standard woodworking tools during outdoor decking installation. Wood-plastic composites are denser and provide consistent dimensions, requiring specialized fasteners and sometimes pre-drilling, which can extend installation time compared to natural fiber composites. Both materials benefit from hidden fastener systems, but natural fiber composites tend to be more forgiving during handling and adjustment on-site.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Lifecycle Expenses
Natural fiber composites generally have lower upfront costs compared to wood-plastic composites due to the abundance and lower price of raw materials like hemp or flax fibers. Lifecycle expenses favor wood-plastic composites as they offer superior durability, resistance to moisture, insects, and UV radiation, reducing maintenance and replacement costs over time. Despite higher initial investment, wood-plastic composites often provide better long-term value through extended lifespan and lower repair needs in outdoor decking applications.
Conclusion: Which Composite is Best for Outdoor Decking?
Natural fiber composites offer superior sustainability and biodegradability, while wood-plastic composites excel in durability, moisture resistance, and low maintenance for outdoor decking. For long-lasting performance and minimal upkeep, wood-plastic composites are generally the preferred choice. However, natural fiber composites provide an eco-friendly alternative ideal for environmentally conscious projects where biodegradability is prioritized.
Infographic: Natural fiber composite vs Wood-plastic composite for Outdoor decking
 azmater.com
azmater.com