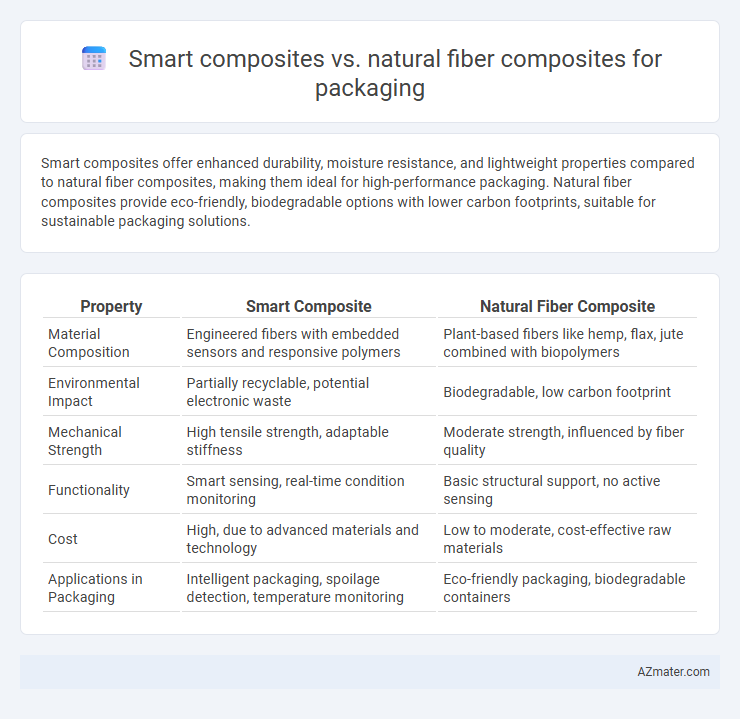
Smart composites offer enhanced durability, moisture resistance, and lightweight properties compared to natural fiber composites, making them ideal for high-performance packaging. Natural fiber composites provide eco-friendly, biodegradable options with lower carbon footprints, suitable for sustainable packaging solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Smart Composite | Natural Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Engineered fibers with embedded sensors and responsive polymers | Plant-based fibers like hemp, flax, jute combined with biopolymers |
| Environmental Impact | Partially recyclable, potential electronic waste | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, adaptable stiffness | Moderate strength, influenced by fiber quality |
| Functionality | Smart sensing, real-time condition monitoring | Basic structural support, no active sensing |
| Cost | High, due to advanced materials and technology | Low to moderate, cost-effective raw materials |
| Applications in Packaging | Intelligent packaging, spoilage detection, temperature monitoring | Eco-friendly packaging, biodegradable containers |
Introduction to Composite Materials in Packaging
Composite materials in packaging combine two or more distinct substances to leverage enhanced mechanical and barrier properties, improving durability and functionality. Smart composites integrate advanced sensors or responsive components, enabling real-time monitoring and adaptability within packaging solutions. Natural fiber composites utilize renewable fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute embedded in polymer matrices, offering biodegradability and reduced environmental impact while maintaining sufficient strength for protective packaging applications.
Overview of Smart Composites
Smart composites in packaging integrate advanced materials such as shape-memory polymers and stimuli-responsive fibers to enhance adaptability, durability, and functionality. These composites offer superior mechanical strength, self-healing capabilities, and environmental responsiveness compared to natural fiber composites, making them ideal for dynamic and protective packaging applications. Incorporating nanotechnology and embedded sensors, smart composites provide real-time monitoring and improved performance, revolutionizing packaging solutions beyond traditional materials.
Understanding Natural Fiber Composites
Natural fiber composites consist of renewable, biodegradable fibers such as jute, hemp, or flax combined with polymer matrices, making them an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic composites in packaging applications. These composites offer advantages like low density, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced mechanical properties, which contribute to lightweight, sustainable packaging solutions. Understanding the fiber-matrix interface, moisture absorption behavior, and processing techniques is essential to optimize natural fiber composites for durable, high-performance packaging materials.
Material Properties Comparison
Smart composites for packaging exhibit superior mechanical strength, enhanced durability, and tailored moisture resistance due to the integration of functional additives and nanomaterials. Natural fiber composites offer biodegradability, lightweight characteristics, and cost-effectiveness, yet tend to have lower impact resistance and moisture sensitivity compared to smart composites. The choice between smart and natural fiber composites depends on the packaging requirements for strength, environmental impact, and barrier performance.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Smart composites in packaging often incorporate engineered materials with enhanced durability and lightweight properties, leading to reduced waste and lower carbon footprints during transportation, while natural fiber composites utilize renewable resources like hemp, flax, or jute, offering biodegradability and reduced dependence on fossil fuels. The sustainability of natural fiber composites is heightened by their ability to decompose naturally, minimizing landfill accumulation and microplastic pollution compared to synthetic smart composites. Lifecycle assessments consistently show natural fiber composites outperform smart composites in environmental impact metrics such as greenhouse gas emissions, resource depletion, and energy consumption.
Performance and Durability in Packaging Applications
Smart composites in packaging offer enhanced performance through tailored mechanical properties, superior barrier resistance, and improved durability under varying environmental conditions compared to natural fiber composites. Natural fiber composites provide biodegradability and reduced environmental impact but generally exhibit lower moisture resistance and mechanical strength, limiting their use in high-performance packaging applications. Advances in smart composite technology integrate nanomaterials and responsive polymers, significantly increasing packaging lifespan and protection, making them ideal for demanding industrial and food packaging sectors.
Cost Analysis: Smart vs Natural Fiber Composites
Smart composites, often incorporating advanced polymers and nanomaterials, generally incur higher initial manufacturing costs than natural fiber composites due to their complex production processes and material expenses. Natural fiber composites benefit from lower raw material costs and renewable sourcing, making them economically attractive for large-scale packaging applications where cost-efficiency is critical. However, the enhanced durability and performance of smart composites may reduce long-term expenses by decreasing product waste and improving lifecycle sustainability in packaging solutions.
Technological Innovations in Composite Packaging
Smart composites integrate advanced sensors and responsive materials, enabling real-time monitoring of packaging conditions to enhance product safety and shelf life. Natural fiber composites utilize renewable resources like flax, hemp, and jute, offering biodegradable and lightweight alternatives that reduce environmental impact. Innovations such as nanocellulose reinforcements and bio-based resin formulations improve the mechanical properties and sustainability of composite packaging solutions.
Market Trends and Industry Adoption
Smart composites in packaging incorporate advanced materials like conductive polymers and sensors, driving innovation for real-time monitoring and enhancing product protection, which is gaining traction in electronics and pharmaceuticals sectors. Natural fiber composites, derived from renewable sources such as hemp, jute, and flax, appeal to sustainability-focused markets, particularly in food and consumer goods packaging, due to their biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint. Market trends indicate accelerated adoption of natural fiber composites fueled by regulatory pressures and consumer demand for eco-friendly packaging, while smart composites are expanding in niche, high-value applications requiring smart functionalities.
Future Prospects in Sustainable Packaging Solutions
Smart composites incorporating advanced polymers and nano-materials offer enhanced mechanical strength, durability, and functional properties such as self-healing and biodegradability, positioning them as promising candidates for next-generation sustainable packaging; natural fiber composites, derived from renewable sources like hemp, flax, and jute, provide eco-friendly alternatives with lower carbon footprints, improved recyclability, and compostability. Future prospects emphasize integrating smart composites' adaptability with natural fibers' biodegradability to create hybrid packaging solutions that meet growing environmental regulations and consumer demand for zero-waste products. Innovations in material engineering, lifecycle analysis, and circular economy models will drive adoption in industries seeking to reduce plastic pollution while maintaining packaging performance and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Smart composite vs Natural fiber composite for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com