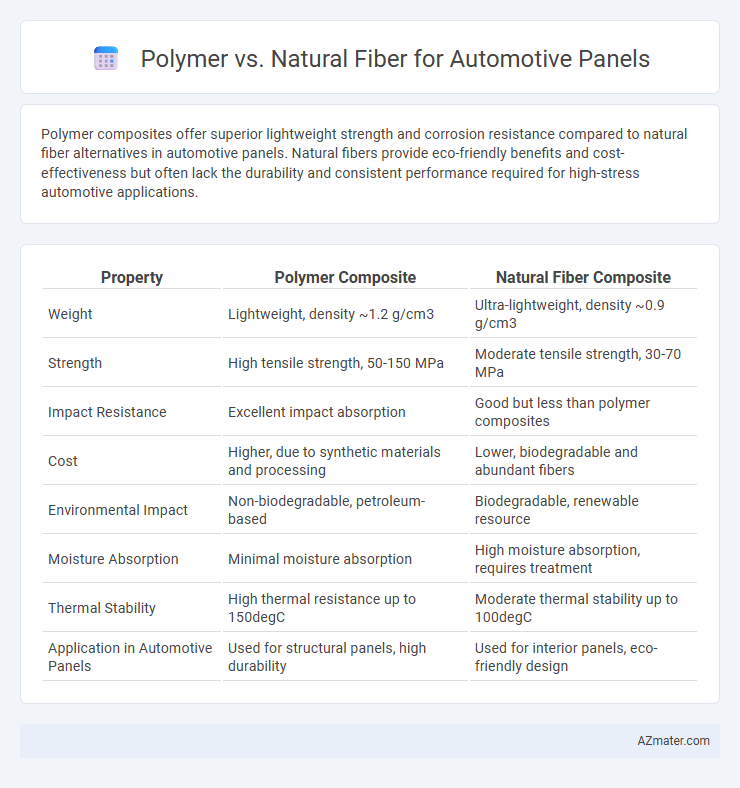
Polymer composites offer superior lightweight strength and corrosion resistance compared to natural fiber alternatives in automotive panels. Natural fibers provide eco-friendly benefits and cost-effectiveness but often lack the durability and consistent performance required for high-stress automotive applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymer Composite | Natural Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight, density ~1.2 g/cm3 | Ultra-lightweight, density ~0.9 g/cm3 |
| Strength | High tensile strength, 50-150 MPa | Moderate tensile strength, 30-70 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent impact absorption | Good but less than polymer composites |
| Cost | Higher, due to synthetic materials and processing | Lower, biodegradable and abundant fibers |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based | Biodegradable, renewable resource |
| Moisture Absorption | Minimal moisture absorption | High moisture absorption, requires treatment |
| Thermal Stability | High thermal resistance up to 150degC | Moderate thermal stability up to 100degC |
| Application in Automotive Panels | Used for structural panels, high durability | Used for interior panels, eco-friendly design |
Introduction to Automotive Panel Materials
Automotive panels commonly utilize polymer and natural fiber materials, each offering distinct advantages in weight reduction and durability. Polymers, such as polypropylene and ABS, provide excellent impact resistance and ease of molding, enhancing vehicle safety and design flexibility. Natural fibers like flax and hemp contribute to sustainability by reducing carbon footprint and improving biodegradability without compromising mechanical properties.
Overview of Polymer-Based Panels
Polymer-based panels in automotive applications offer superior lightweight characteristics, enhancing fuel efficiency compared to traditional metal or natural fiber alternatives. These panels exhibit excellent durability, impact resistance, and design flexibility, allowing manufacturers to produce complex shapes with consistent performance. Common polymers used include polypropylene, polyurethane, and thermoplastic composites, which contribute to improved noise reduction and corrosion resistance in vehicle interiors and exteriors.
Natural Fiber Panels: Types and Sources
Natural fiber panels in automotive applications predominantly utilize fibers such as flax, hemp, jute, and kenaf, sourced from renewable plant materials. These fibers are valued for their lightweight properties, biodegradability, and ability to reduce vehicle weight, leading to improved fuel efficiency and lower carbon emissions. Emerging advancements in natural fiber composites enhance mechanical strength and durability, positioning them as sustainable alternatives to traditional polymer-based panels.
Material Properties: Strength and Durability
Polymer composites exhibit high tensile strength and impact resistance, making them ideal for automotive panels requiring lightweight durability. Natural fibers, such as hemp and flax, offer moderate strength with excellent vibration damping and biodegradability, but generally have lower impact resistance compared to polymers. Advanced polymer-natural fiber hybrids leverage the strengths of both materials, enhancing overall durability while reducing vehicle weight and environmental impact.
Weight and Fuel Efficiency Implications
Polymer-based automotive panels typically weigh 30-50% less than natural fiber composites, significantly reducing overall vehicle mass and improving fuel efficiency by up to 10%. Natural fibers such as hemp or flax offer sustainable alternatives with lower carbon footprints but generally result in slightly heavier panels, which can marginally reduce fuel economy. Optimizing polymer composites with natural fibers can balance lightweight performance and eco-friendly attributes, enhancing vehicle efficiency while supporting sustainability goals.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Natural fiber composites offer a sustainable alternative to traditional polymer panels in automotive applications by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions during production. These fibers, such as hemp, flax, and jute, are renewable, biodegradable, and contribute to lighter vehicle weight, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing overall environmental impact. Polymers, while durable and versatile, typically involve higher energy consumption and generate more non-biodegradable waste, making natural fibers an eco-friendly choice for sustainable automotive panel manufacturing.
Cost Comparison and Economic Viability
Polymer automotive panels typically have lower upfront manufacturing costs due to mass production scalability, whereas natural fiber panels incur higher material costs but benefit from renewable sourcing and biodegradability, presenting long-term economic advantages. Natural fiber composites can reduce vehicle weight, improving fuel efficiency and potentially lowering operational expenses over the vehicle's lifespan. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including raw materials, processing, durability, and end-of-life disposal, reveals that natural fiber panels offer competitive economic viability aligned with sustainability trends and regulatory incentives.
Manufacturing Processes and Scalability
Polymer automotive panels benefit from injection molding and extrusion, enabling high-volume, precise production with consistent quality and reduced cycle times. Natural fiber composites require specialized processes like compression molding or resin transfer molding, which may involve longer curing times and more variability, impacting scalability. Scaling natural fiber panels involves challenges in raw material consistency and processing, whereas polymers offer established manufacturing infrastructure supporting mass production.
Performance in Real-World Conditions
Polymer composites offer superior impact resistance and durability under varying temperatures and humidity compared to natural fibers, making them highly reliable for automotive panels in extreme weather. Natural fibers, while eco-friendly and lightweight, tend to absorb moisture, leading to reduced mechanical strength and dimensional stability over time. Real-world testing shows polymers maintain consistent performance in vibration and UV exposure, whereas natural fibers may degrade faster without proper treatment.
Future Trends in Automotive Panel Materials
Future trends in automotive panel materials emphasize the integration of polymer composites reinforced with natural fibers such as hemp, flax, and jute, due to their lightweight properties and sustainability benefits. These hybrid materials offer enhanced mechanical strength, improved impact resistance, and reduced environmental footprint compared to traditional synthetic composites. Advancements in bio-based polymers and fiber treatments are accelerating the adoption of eco-friendly automotive panels, aligning with industry goals for lightweight construction and carbon emission reduction.
Infographic: Polymer vs Natural fiber for Automotive panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com