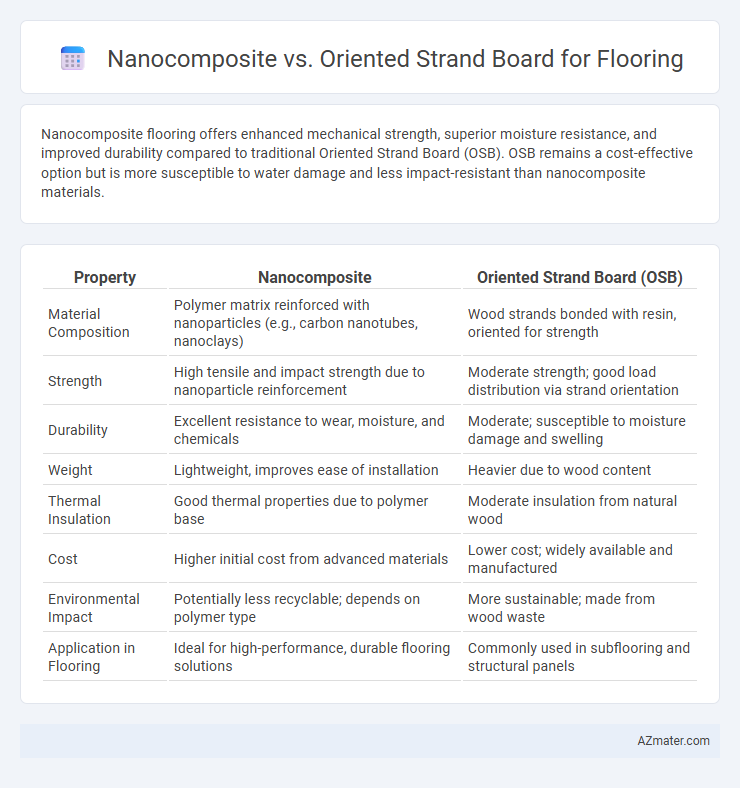
Nanocomposite flooring offers enhanced mechanical strength, superior moisture resistance, and improved durability compared to traditional Oriented Strand Board (OSB). OSB remains a cost-effective option but is more susceptible to water damage and less impact-resistant than nanocomposite materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanocomposite | Oriented Strand Board (OSB) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polymer matrix reinforced with nanoparticles (e.g., carbon nanotubes, nanoclays) | Wood strands bonded with resin, oriented for strength |
| Strength | High tensile and impact strength due to nanoparticle reinforcement | Moderate strength; good load distribution via strand orientation |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to wear, moisture, and chemicals | Moderate; susceptible to moisture damage and swelling |
| Weight | Lightweight, improves ease of installation | Heavier due to wood content |
| Thermal Insulation | Good thermal properties due to polymer base | Moderate insulation from natural wood |
| Cost | Higher initial cost from advanced materials | Lower cost; widely available and manufactured |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially less recyclable; depends on polymer type | More sustainable; made from wood waste |
| Application in Flooring | Ideal for high-performance, durable flooring solutions | Commonly used in subflooring and structural panels |
Introduction to Flooring Material Choices
Nanocomposites offer enhanced mechanical strength, moisture resistance, and durability compared to traditional flooring materials, making them ideal for high-traffic areas. Oriented strand board (OSB) presents an affordable and eco-friendly option with good structural integrity, commonly used as subflooring due to its layered wood strand composition. Selecting between nanocomposites and OSB depends on factors such as load-bearing requirements, environmental exposure, and budget constraints.
What are Nanocomposites?
Nanocomposites are materials engineered by integrating nanoparticles into a matrix to enhance mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties, making them highly durable and resistant to wear. Unlike oriented strand board (OSB), which is made from layered wood strands bonded with adhesives, nanocomposites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and improved moisture resistance essential for flooring applications. These advanced materials provide enhanced performance in terms of durability and longevity, making them a cutting-edge alternative to traditional wood-based flooring options.
Overview of Oriented Strand Board (OSB)
Oriented Strand Board (OSB) is an engineered wood product composed of compressed wood strands arranged in layers with adhesives, offering strength and durability for flooring applications. Known for its cost-effectiveness and uniformity, OSB provides a stable subfloor material resistant to warping and moisture when properly treated. Its structural performance and widespread availability make it a popular choice compared to nanocomposites, which incorporate nanoparticles to enhance mechanical and thermal properties but often at a higher cost.
Key Differences Between Nanocomposites and OSB
Nanocomposites exhibit enhanced mechanical strength, durability, and moisture resistance compared to Oriented Strand Board (OSB), making them ideal for advanced flooring applications that demand longevity and stability. OSB is composed of compressed wood strands bonded with adhesives, providing cost-effective and uniform strength but lower resistance to water damage and wear. Nanocomposites incorporate nanoscale fillers like nanoclays or carbon nanotubes, which improve thermal insulation and abrasion resistance beyond the capabilities of traditional OSB panels.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Nanocomposite flooring offers superior strength and durability compared to oriented strand board (OSB) due to its reinforcement with nanoscale fillers such as clay, carbon nanotubes, or silica, which enhance mechanical properties and resistance to wear. OSB, composed of compressed wood strands bonded with adhesives, provides moderate strength but is more susceptible to moisture damage and delamination over time. Nanocomposites demonstrate higher impact resistance and long-term stability, making them ideal for high-traffic flooring applications demanding enhanced structural integrity.
Moisture and Environmental Resistance
Nanocomposite flooring exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to oriented strand board (OSB) due to its enhanced polymer matrix that prevents water infiltration and swelling. OSB, composed of wood strands bonded with adhesives, tends to absorb moisture, leading to potential warping and reduced structural integrity in humid environments. Nanocomposite materials also offer improved environmental resistance by resisting microbial growth and chemical degradation, making them a more durable option for moisture-prone flooring applications.
Installation and Maintenance Factors
Nanocomposite flooring offers quick installation due to its lightweight panels and tongue-and-groove design, reducing labor time compared to oriented strand board (OSB), which often requires additional subfloor preparation. Maintenance for nanocomposites commonly involves resistance to moisture and wear, minimizing refinishing needs, whereas OSB floors demand regular sealing and are more prone to water damage and swelling. The durability and ease of upkeep make nanocomposite materials favorable for high-traffic areas compared to the traditional OSB installation and upkeep challenges.
Cost Analysis and Value for Money
Nanocomposite flooring offers higher durability and moisture resistance at a premium cost compared to oriented strand board (OSB), which is more affordable but less resilient under heavy wear conditions. OSB provides a cost-effective solution for budget-conscious projects, while nanocomposites deliver enhanced longevity and reduced maintenance expenses, contributing to better long-term value for money. Investing in nanocomposite materials often results in lower replacement frequency and sustained floor performance, offsetting their initial higher price.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanocomposite flooring materials offer enhanced environmental benefits by utilizing recycled nanoparticles, reducing raw material consumption, and increasing durability, which extends product lifespan and minimizes waste. Oriented strand board (OSB) is made from fast-growing, renewable wood strands bonded with synthetic resins, contributing to sustainable forest management but raising concerns regarding formaldehyde emissions and biodegradability. Choosing nanocomposite flooring promotes lower carbon footprint and waste production, while OSB flooring supports renewable resource utilization but requires careful consideration of chemical emissions and end-of-life disposal.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Flooring Material
Nanocomposites offer superior mechanical strength, moisture resistance, and durability compared to oriented strand board (OSB), making them ideal for high-performance flooring applications. OSB remains a cost-effective solution with sufficient structural integrity for standard residential use but may fall short in longevity and moisture susceptibility. Selecting between nanocomposite and OSB flooring depends on balancing budget constraints against long-term performance requirements and environmental exposure.
Infographic: Nanocomposite vs Oriented strand board for Flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com