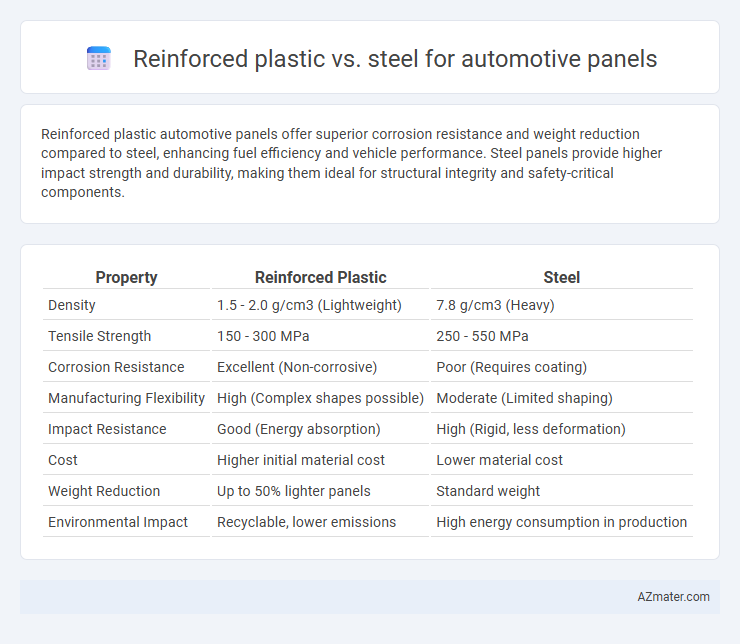
Reinforced plastic automotive panels offer superior corrosion resistance and weight reduction compared to steel, enhancing fuel efficiency and vehicle performance. Steel panels provide higher impact strength and durability, making them ideal for structural integrity and safety-critical components.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Reinforced Plastic | Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.5 - 2.0 g/cm3 (Lightweight) | 7.8 g/cm3 (Heavy) |
| Tensile Strength | 150 - 300 MPa | 250 - 550 MPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (Non-corrosive) | Poor (Requires coating) |
| Manufacturing Flexibility | High (Complex shapes possible) | Moderate (Limited shaping) |
| Impact Resistance | Good (Energy absorption) | High (Rigid, less deformation) |
| Cost | Higher initial material cost | Lower material cost |
| Weight Reduction | Up to 50% lighter panels | Standard weight |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, lower emissions | High energy consumption in production |
Introduction to Automotive Panel Materials
Automotive panels require materials that balance strength, weight, and durability, with reinforced plastic and steel being the primary options. Reinforced plastic offers advantages like corrosion resistance, reduced weight, and design flexibility, which contribute to improved fuel efficiency and performance. Steel remains favored for its superior strength, crash resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it a reliable choice for structural integrity in vehicle panels.
Overview of Reinforced Plastic in Automotive Applications
Reinforced plastics in automotive panels offer high strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, and design flexibility, making them ideal for lightweight vehicle construction. These composites typically combine polymers with fibers such as glass or carbon, improving impact resistance and durability compared to traditional materials. Their growing adoption in automotive manufacturing supports fuel efficiency and performance enhancements while reducing overall vehicle weight.
Steel Panels: Traditional Choice and Advancements
Steel panels have long been the traditional choice for automotive bodies due to their strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Recent advancements in high-strength steel alloys and advanced manufacturing techniques have improved crash resistance and reduced vehicle weight without compromising structural integrity. These innovations ensure steel remains a competitive option compared to reinforced plastics, offering enhanced safety performance and recyclability in automotive panel applications.
Weight Comparison: Reinforced Plastic vs Steel
Reinforced plastic panels in automotive applications offer a significant weight reduction compared to steel, often achieving up to 40-60% lighter components. This weight advantage enhances fuel efficiency, vehicle handling, and overall performance by reducing unsprung mass. Steel panels, while heavier, provide superior stiffness and impact resistance but contribute more to the vehicle's total weight, impacting fuel consumption negatively.
Durability and Impact Resistance
Reinforced plastic automotive panels offer superior corrosion resistance and maintain structural integrity under repeated stress, outperforming steel in moisture-prone environments. Steel panels provide exceptional impact resistance due to their high tensile strength and energy absorption capacity, making them ideal for crash safety. However, reinforced plastics balance durability with weight reduction, enhancing fuel efficiency without compromising panel longevity.
Manufacturing Processes and Cost Efficiency
Reinforced plastic automotive panels are manufactured primarily through processes such as injection molding, compression molding, or resin transfer molding, offering high precision and lower tooling costs compared to steel stamping used for steel panels. The lower weight of reinforced plastics reduces energy consumption in forming and assembly, leading to improved overall manufacturing efficiency. While steel panels offer greater strength and impact resistance, reinforced plastics provide cost-effective benefits in material usage, shorter cycle times, and reduced labor, making them advantageous for high-volume production and lightweight vehicle design.
Corrosion Resistance and Environmental Factors
Reinforced plastic panels exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to steel, as they do not oxidize or rust when exposed to moisture and road salts, enhancing vehicle durability in harsh weather conditions. Steel panels, while strong, require protective coatings such as galvanization or paint to prevent corrosion, which can degrade over time due to environmental factors like humidity, salt spray, and temperature fluctuations. The use of reinforced plastics reduces maintenance costs and environmental impact by minimizing the need for chemical coatings and extending the lifespan of automotive panels under exposure to UV radiation and acidic rain.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Possibilities
Reinforced plastic offers superior design flexibility compared to steel in automotive panels, allowing complex shapes and intricate detailing that enhance aerodynamic performance and vehicle aesthetics. Its moldability supports seamless integration of features like textured surfaces and vibrant color options, enabling customized and innovative designs. Steel provides structural strength but limits aesthetic possibilities due to its rigidity and weight constraints, often requiring additional treatments to achieve desired finishes.
Sustainability and Recycling Considerations
Reinforced plastic automotive panels offer significant weight reduction, enhancing fuel efficiency and lowering carbon emissions, which contributes to sustainability goals compared to traditional steel panels. Although steel panels are highly recyclable with established processes, reinforced plastics pose recycling challenges due to composite material complexity, often requiring specialized treatment to recover fibers and resins. Innovations in thermoplastic composites improve recyclability of reinforced plastics, but steel remains dominant in circular economy frameworks due to its magnetic separation and high recycling rates in automotive manufacturing.
Future Trends in Automotive Panel Materials
Reinforced plastic panels offer significant weight reduction and corrosion resistance compared to traditional steel, driving their growing adoption in automotive manufacturing. Advances in carbon fiber and glass fiber composites enhance the mechanical strength and recyclability of reinforced plastics, aligning with industry goals for sustainability and fuel efficiency. Emerging trends emphasize hybrid materials combining steel and reinforced plastics to optimize durability, cost, and environmental impact in future automotive panel designs.
Infographic: Reinforced plastic vs Steel for Automotive panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com