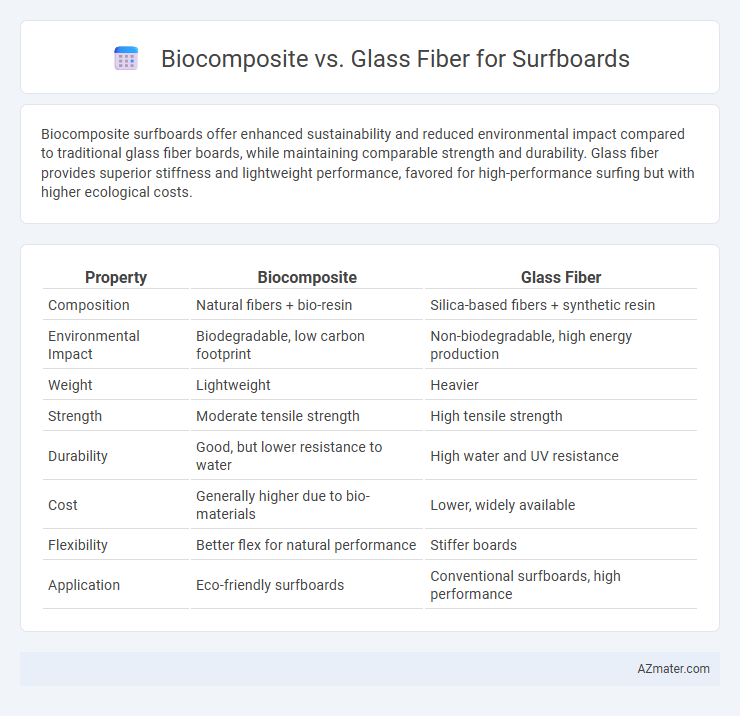
Biocomposite surfboards offer enhanced sustainability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional glass fiber boards, while maintaining comparable strength and durability. Glass fiber provides superior stiffness and lightweight performance, favored for high-performance surfing but with higher ecological costs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Biocomposite | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Natural fibers + bio-resin | Silica-based fibers + synthetic resin |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, high energy production |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Durability | Good, but lower resistance to water | High water and UV resistance |
| Cost | Generally higher due to bio-materials | Lower, widely available |
| Flexibility | Better flex for natural performance | Stiffer boards |
| Application | Eco-friendly surfboards | Conventional surfboards, high performance |
Introduction to Surfboard Material Innovations
Surfboard material innovations have increasingly shifted towards sustainable solutions, with biocomposites emerging as eco-friendly alternatives to traditional glass fiber. Biocomposites utilize natural fibers like flax or hemp combined with bio-resins, reducing environmental impact while maintaining performance attributes such as strength and flexibility. Glass fiber remains popular for its durability and cost-effectiveness, but the surf industry is progressively adopting biocomposite materials to enhance sustainability without compromising ride quality.
What Are Biocomposites?
Biocomposites are materials made from natural fibers like flax, hemp, or jute combined with biodegradable or bio-based resins, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional fiberglass used in surfboard construction. These composites reduce environmental impact by utilizing renewable resources and enhancing board sustainability without compromising strength and durability. Biocomposites also provide improved biodegradability and lower carbon footprint compared to conventional glass fiber surfboards.
Understanding Glass Fiber: Properties and Uses
Glass fiber offers exceptional tensile strength, durability, and resistance to moisture, making it a preferred reinforcement material in surfboard construction. Its lightweight nature and flexibility contribute to enhanced board performance, while its ability to bond well with resin systems ensures structural integrity and longevity. Commonly used in combination with polyurethane or EPS foam cores, glass fiber provides surfers with a reliable balance of strength and responsiveness.
Sustainability Comparison: Biocomposite vs Glass Fiber
Biocomposite materials for surfboards significantly reduce environmental impact compared to traditional glass fiber by utilizing renewable plant-based fibers and bio-resins, which lower carbon emissions and enhance biodegradability. Glass fiber composites, derived from non-renewable silica and epoxy resins, contribute to higher energy consumption and persistent waste in landfills. The sustainable advantages of biocomposites include improved recyclability and reduced reliance on fossil fuels, making them a preferable choice for eco-conscious surfers seeking performance without compromising the planet.
Performance Differences in Surfing Conditions
Biocomposite surfboards generally offer enhanced flexibility and responsiveness compared to glass fiber boards, making them superior in small to medium waves due to better energy absorption and maneuverability. Glass fiber surfboards excel in durability and stiffness, providing greater control and speed in powerful, larger wave conditions where rigidity is crucial. Performance differences are pronounced in surf zones, with biocomposites favoring dynamic turns and smooth rides, while glass fiber boards support aggressive, high-speed surfing.
Weight and Flexibility: Which Scores Higher?
Biocomposite surfboards typically weigh less than glass fiber boards, offering enhanced maneuverability and ease of transport. Their natural fiber composition provides superior flexibility, adapting better to wave dynamics compared to the stiffer glass fiber counterparts. Glass fiber surfboards score higher in durability but often sacrifice weight and flexibility benefits that biocomposites deliver.
Durability and Longevity on the Water
Biocomposite surfboards offer enhanced durability through eco-friendly materials like flax and hemp fibers combined with bio-resins, providing resistance against water damage and UV exposure. Glass fiber surfboards are traditionally strong and impact-resistant but can be prone to delamination and yellowing over time with prolonged water exposure. Choosing biocomposites improves longevity by reducing material degradation while maintaining comparable strength to glass fiber alternatives in marine environments.
Environmental Impact: From Production to Disposal
Biocomposites for surfboards significantly reduce environmental impact by utilizing renewable natural fibers and bio-based resins, leading to lower carbon emissions compared to traditional glass fiber production, which relies heavily on energy-intensive processes and non-renewable petroleum-based materials. At disposal, biocomposite surfboards offer enhanced biodegradability or recyclability, minimizing landfill waste and pollution, whereas glass fiber boards often persist in the environment for decades due to their non-biodegradable, synthetic composition. The overall life cycle assessment clearly favors biocomposites for sustainability, making them a crucial innovation for eco-conscious surfboard manufacturing.
Cost Analysis: Affordability for Manufacturers and Surfers
Biocomposite surfboards typically offer lower material costs compared to glass fiber due to the use of renewable resources like hemp or flax fibers, which are increasingly accessible and sustainable. Manufacturing with biocomposites can reduce labor-intensive processes, potentially lowering production expenses, while glass fiber surfboards often require specialized resin and fabrication techniques that increase costs. For surfers, biocomposite boards generally present a competitive price point with added environmental benefits, whereas glass fiber boards might be priced higher but provide established performance and durability standards.
Future Trends in Eco-Friendly Surfboard Materials
Biocomposite materials are emerging as a sustainable alternative to traditional glass fiber for surfboards, utilizing natural fibers like flax, hemp, and recycled resins to reduce environmental impact. Innovations in bio-based polymers and natural fiber composites enhance durability and performance, targeting lower carbon footprints while maintaining strength and flexibility. Future trends emphasize closed-loop recycling, ocean-safe resins, and lightweight biocomposites that align with eco-conscious consumer demand and stricter environmental regulations in the surfboard industry.
Infographic: Biocomposite vs Glass Fiber for Surfboard
 azmater.com
azmater.com