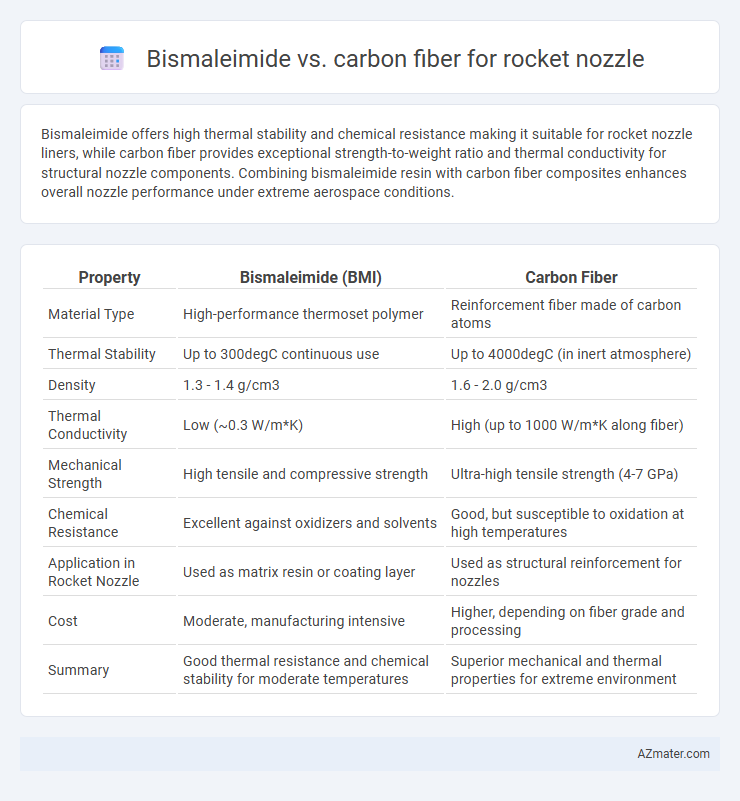
Bismaleimide offers high thermal stability and chemical resistance making it suitable for rocket nozzle liners, while carbon fiber provides exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and thermal conductivity for structural nozzle components. Combining bismaleimide resin with carbon fiber composites enhances overall nozzle performance under extreme aerospace conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bismaleimide (BMI) | Carbon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-performance thermoset polymer | Reinforcement fiber made of carbon atoms |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 300degC continuous use | Up to 4000degC (in inert atmosphere) |
| Density | 1.3 - 1.4 g/cm3 | 1.6 - 2.0 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (~0.3 W/m*K) | High (up to 1000 W/m*K along fiber) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile and compressive strength | Ultra-high tensile strength (4-7 GPa) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against oxidizers and solvents | Good, but susceptible to oxidation at high temperatures |
| Application in Rocket Nozzle | Used as matrix resin or coating layer | Used as structural reinforcement for nozzles |
| Cost | Moderate, manufacturing intensive | Higher, depending on fiber grade and processing |
| Summary | Good thermal resistance and chemical stability for moderate temperatures | Superior mechanical and thermal properties for extreme environment |
Introduction to Rocket Nozzle Materials
Rocket nozzle materials must withstand extreme thermal and mechanical stresses while maintaining structural integrity during propulsion. Bismaleimide composites offer high thermal stability and excellent mechanical strength, making them suitable for moderate-temperature nozzle applications. Carbon fiber composites provide superior heat resistance and stiffness, ideal for high-temperature environments in advanced rocket nozzles.
Overview of Bismaleimide Composites
Bismaleimide (BMI) composites offer exceptional thermal stability and mechanical strength, making them ideal for high-temperature applications such as rocket nozzles. Their high glass transition temperature, typically above 250degC, ensures durability under extreme thermal stress compared to traditional carbon fiber alone. BMI composites enhance structural integrity and resist thermal degradation, providing a superior alternative to conventional materials in aerospace propulsion systems.
Properties of Carbon Fiber Composites
Carbon fiber composites, characterized by high tensile strength, low weight, and exceptional thermal stability, offer superior performance in rocket nozzle applications compared to bismaleimide resins alone. Their excellent resistance to thermal expansion and high-temperature oxidation enhances nozzle durability under extreme combustion conditions. The anisotropic mechanical properties of carbon fiber composites contribute to optimized load-bearing capacity and improved thermal shock resistance critical for efficient rocket propulsion.
Thermal Resistance: Bismaleimide vs Carbon Fiber
Bismaleimide resins exhibit exceptional thermal resistance, maintaining stability and mechanical integrity at temperatures up to 250degC, making them suitable for high-temperature aerospace applications. Carbon fiber composites, when combined with appropriate matrices, can withstand even higher temperatures, often exceeding 300degC, while providing superior thermal conductivity and strength-to-weight ratio. For rocket nozzle applications, carbon fiber's enhanced heat tolerance and thermal conductivity offer a significant advantage over bismaleimide resins in managing extreme thermal loads.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Bismaleimide (BMI) resins offer high thermal stability and exceptional mechanical strength, making them suitable for rocket nozzles exposed to extreme temperatures, while carbon fiber composites provide outstanding tensile strength and stiffness with lightweight properties vital for aerospace applications. Carbon fiber reinforced composites typically exhibit superior fatigue resistance and impact durability compared to BMI matrices alone, which can be brittle under cyclic loading without fiber reinforcement. Integrating carbon fiber with bismaleimide matrices results in a composite material that maximizes mechanical strength and durability, optimizing performance in high-stress rocket nozzle environments.
Weight Considerations for Rocket Nozzle Design
Bismaleimide resins offer a lightweight matrix with high thermal stability, making them ideal for bonding carbon fiber composites in rocket nozzle applications where weight reduction is critical. Carbon fiber materials provide exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, significantly lowering the overall mass of the nozzle while maintaining structural integrity under extreme thermal and mechanical stresses. Optimizing the combination of bismaleimide and carbon fiber can achieve superior performance by balancing weight savings with thermal resistance in advanced rocket nozzle designs.
Manufacturing and Processing Differences
Bismaleimide (BMI) composites exhibit higher thermal stability but require more complex curing cycles involving precise temperature control and extended processing times compared to carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP), which allow faster, more flexible manufacturing methods such as resin transfer molding (RTM) or autoclave curing. CFRP materials benefit from widespread availability and compatibility with various manufacturing techniques, enabling cost-effective production of rocket nozzles with tailored mechanical properties, whereas BMI's chemical resistance and heat resistance make it a preferred choice for high-temperature applications despite longer processing. The inherent differences in viscosity, cure kinetics, and thermal characteristics between BMI and CFRP significantly influence tooling requirements, cycle times, and final material performance in nozzle fabrication.
Cost Analysis: Bismaleimide vs Carbon Fiber
Bismaleimide composites generally have a higher material cost compared to carbon fiber but offer superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, which can reduce long-term maintenance expenses in rocket nozzles. Carbon fiber materials provide an excellent strength-to-weight ratio at a relatively lower cost, making them cost-effective for high-performance applications where temperature exposure is moderate. Evaluating the total lifecycle cost, including manufacturing and operational factors, is crucial to determine the most economical choice for rocket nozzle materials.
Real-World Applications in Aerospace
Bismaleimide (BMI) composites offer high thermal stability and excellent chemical resistance, making them ideal for rocket nozzles exposed to extreme temperatures and aggressive rocket exhaust environments. Carbon fiber composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratios and exceptional thermal conductivity, enhancing nozzle durability and structural performance under intense aerodynamic and thermal stresses. In aerospace applications, BMI composites are often used as resin matrices combined with carbon fiber reinforcements to achieve optimal performance in rocket nozzle liners and structural components.
Conclusion: Optimal Material for Rocket Nozzle
Bismaleimide offers excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, but carbon fiber composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratio and thermal conductivity crucial for rocket nozzle performance. The optimal material for a rocket nozzle is carbon fiber reinforced with high-temperature matrices, balancing lightweight characteristics with exceptional mechanical and thermal endurance. Advanced carbon fiber composites ensure enhanced durability and efficiency under extreme aerospace conditions, making them the preferred choice.
Infographic: Bismaleimide vs Carbon fiber for Rocket nozzle
 azmater.com
azmater.com