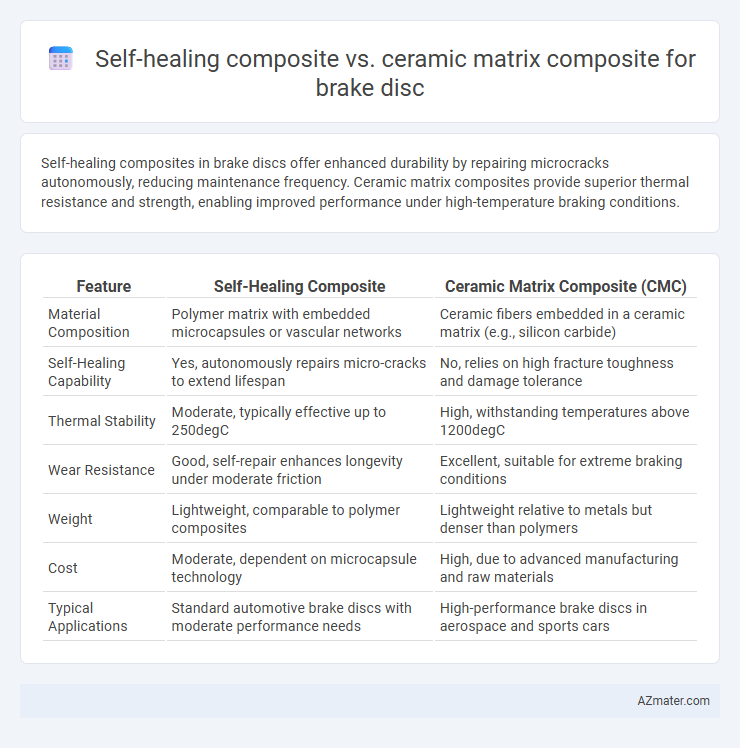
Self-healing composites in brake discs offer enhanced durability by repairing microcracks autonomously, reducing maintenance frequency. Ceramic matrix composites provide superior thermal resistance and strength, enabling improved performance under high-temperature braking conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Self-Healing Composite | Ceramic Matrix Composite (CMC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polymer matrix with embedded microcapsules or vascular networks | Ceramic fibers embedded in a ceramic matrix (e.g., silicon carbide) |
| Self-Healing Capability | Yes, autonomously repairs micro-cracks to extend lifespan | No, relies on high fracture toughness and damage tolerance |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate, typically effective up to 250degC | High, withstanding temperatures above 1200degC |
| Wear Resistance | Good, self-repair enhances longevity under moderate friction | Excellent, suitable for extreme braking conditions |
| Weight | Lightweight, comparable to polymer composites | Lightweight relative to metals but denser than polymers |
| Cost | Moderate, dependent on microcapsule technology | High, due to advanced manufacturing and raw materials |
| Typical Applications | Standard automotive brake discs with moderate performance needs | High-performance brake discs in aerospace and sports cars |
Introduction to Advanced Brake Disc Materials
Self-healing composites and ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) represent cutting-edge materials enhancing brake disc performance under extreme conditions. Self-healing composites incorporate microcapsules or vascular networks that autonomously repair microcracks, extending brake disc longevity and reliability. In contrast, CMCs offer superior thermal stability, wear resistance, and lightweight properties, making them ideal for high-performance and aerospace braking systems.
Understanding Self-Healing Composites
Self-healing composites for brake discs incorporate materials that can autonomously repair microcracks caused by mechanical stress, enhancing durability and safety in high-temperature braking conditions. Unlike ceramic matrix composites (CMCs), which rely on inherent high thermal resistance and fracture toughness, self-healing composites use embedded healing agents or thermoplastic matrices to restore structural integrity after damage. This active repair mechanism reduces maintenance frequency and extends the lifespan of brake discs in automotive and aerospace applications.
Overview of Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMC)
Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMCs) are advanced materials composed of ceramic fibers embedded within a ceramic matrix, offering exceptional high-temperature resistance and superior mechanical strength for brake disc applications. Their inherent fracture toughness and thermal stability enable them to withstand extreme braking conditions, outperforming traditional metal alloys. CMCs provide lightweight solutions with enhanced wear resistance and thermal shock tolerance, making them ideal for high-performance braking systems in automotive and aerospace industries.
Material Properties: Self-Healing Composite vs CMC
Self-healing composites exhibit excellent damage tolerance and microcrack repair capabilities, enhancing longevity and reducing maintenance in brake discs, while ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) provide superior thermal stability and wear resistance under extreme temperatures. The self-healing matrix typically involves polymeric or metal-based materials with embedded healing agents, enabling autonomous restoration of structural integrity, whereas CMCs rely on ceramic fibers within a ceramic matrix to maintain high stiffness and strength at elevated temperatures. Consequently, self-healing composites offer improved durability against microstructural damage, and CMCs excel in thermal performance and mechanical robustness for high-performance braking applications.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Self-healing composites exhibit superior thermal performance in brake discs by autonomously repairing microcracks that develop under high thermal stress, maintaining structural integrity and enhancing heat dissipation over time. Ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) deliver high-temperature resistance and thermal stability with low thermal expansion, but lack autonomous damage recovery, potentially leading to performance degradation during thermal cycling. Comparative studies show self-healing composites can sustain consistent braking efficiency and reduce maintenance frequency, while CMCs provide reliable high-temperature endurance essential for demanding braking applications.
Wear Resistance and Longevity
Self-healing composites for brake discs exhibit enhanced wear resistance by autonomously repairing micro-cracks during operation, significantly extending component longevity under high friction conditions. Ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) offer superior thermal stability and hardness, providing excellent wear resistance at elevated temperatures but lack intrinsic self-repair capabilities, which can limit lifespan in dynamic loading environments. Comparing both, self-healing composites deliver improved durability through damage mitigation, while CMCs excel in maintaining structural integrity under extreme thermal and mechanical stress.
Self-Healing Capabilities and Mechanisms
Self-healing composites for brake discs incorporate microcapsules or vascular networks containing healing agents that activate upon crack formation, effectively restoring mechanical integrity and enhancing lifespan. Ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) rely on intrinsic crack-bridging fibers and oxidation-resistant coatings but lack autonomous repair mechanisms, resulting in progressive damage accumulation under thermal and mechanical stresses. The autonomous self-healing functionality in composites significantly improves durability and safety by mitigating microcracks before catastrophic failure, unlike traditional CMCs which require external maintenance.
Cost Analysis and Manufacturing Considerations
Self-healing composites for brake discs offer potential cost savings through reduced maintenance and longer service life but face higher initial manufacturing costs due to complex material formulations and curing processes. Ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) present significant manufacturing challenges, such as high-temperature processing and machining difficulties, leading to elevated production expenses despite superior thermal resistance and wear performance. Cost analysis favors self-healing composites in applications prioritizing lifecycle economy, whereas CMCs remain suitable for high-performance scenarios where manufacturing complexity is justified by exceptional mechanical and thermal properties.
Real-World Applications in Automotive and Aerospace
Self-healing composites for brake discs enhance durability by autonomously repairing micro-cracks, reducing maintenance costs and extending service life in automotive and aerospace sectors. Ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) offer superior thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making them ideal for high-performance aerospace braking systems where extreme heat and wear are prevalent. Real-world applications demonstrate that self-healing composites improve safety and longevity in passenger vehicles, while CMCs dominate aircraft braking systems due to their lightweight and high-temperature capabilities.
Future Trends and Innovations in Brake Disc Technology
Future trends in brake disc technology emphasize the development of self-healing composites and ceramic matrix composites, which offer enhanced durability and heat resistance. Self-healing composites integrate microcapsules containing healing agents that autonomously repair cracks, extending the lifespan of brake discs under extreme conditions. Ceramic matrix composites provide superior thermal stability and wear resistance, making them ideal for high-performance and electric vehicles, with ongoing innovations focusing on improving their cost-effectiveness and repairability.
Infographic: Self-healing composite vs Ceramic matrix composite for Brake disc
 azmater.com
azmater.com