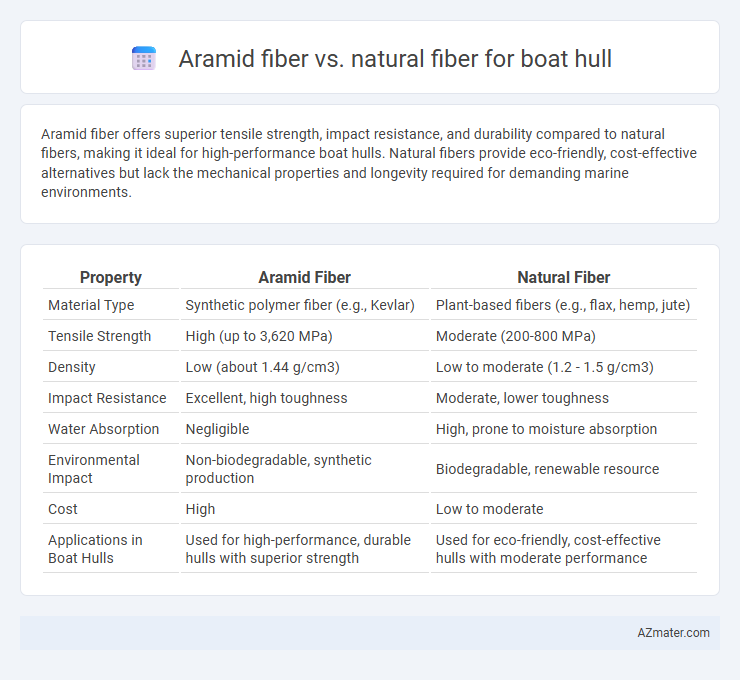
Aramid fiber offers superior tensile strength, impact resistance, and durability compared to natural fibers, making it ideal for high-performance boat hulls. Natural fibers provide eco-friendly, cost-effective alternatives but lack the mechanical properties and longevity required for demanding marine environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid Fiber | Natural Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic polymer fiber (e.g., Kevlar) | Plant-based fibers (e.g., flax, hemp, jute) |
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 3,620 MPa) | Moderate (200-800 MPa) |
| Density | Low (about 1.44 g/cm3) | Low to moderate (1.2 - 1.5 g/cm3) |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent, high toughness | Moderate, lower toughness |
| Water Absorption | Negligible | High, prone to moisture absorption |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, synthetic production | Biodegradable, renewable resource |
| Cost | High | Low to moderate |
| Applications in Boat Hulls | Used for high-performance, durable hulls with superior strength | Used for eco-friendly, cost-effective hulls with moderate performance |
Introduction to Aramid and Natural Fibers in Boat Hull Construction
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and high resistance to impact and abrasion, are increasingly used in boat hull construction to enhance durability and performance. Natural fibers such as flax, hemp, and jute offer sustainable alternatives, providing lightweight reinforcement with good vibration damping but lower mechanical strength compared to aramid fibers. The choice between aramid and natural fibers in boat hulls depends on the balance between performance requirements and environmental considerations.
Key Properties of Aramid Fibers for Marine Applications
Aramid fibers exhibit exceptional tensile strength, high impact resistance, and excellent thermal stability, making them ideal for boat hull reinforcement in demanding marine environments. Their low density combined with superior fatigue resistance enhances boat performance by reducing weight while maintaining structural integrity. Unlike natural fibers, aramids offer superior durability against moisture, UV radiation, and chemical exposure, ensuring long-term reliability in harsh sea conditions.
Characteristics of Natural Fibers Used in Boat Building
Natural fibers used in boat hull construction, such as flax, hemp, and jute, offer biodegradability, low density, and excellent vibration damping properties. These fibers provide a sustainable and cost-effective alternative to synthetic materials but generally exhibit lower tensile strength and water resistance compared to aramid fibers. Their natural moisture absorption necessitates treatment with resins or coatings to enhance durability and prevent degradation in marine environments.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aramid fiber, known for its exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, offers superior durability compared to natural fibers in boat hull construction. Its high strength-to-weight ratio ensures enhanced structural integrity and longevity under harsh marine conditions, outperforming natural fibers like hemp or flax which are more prone to moisture absorption and degradation. While natural fibers provide eco-friendly benefits, aramid fibers deliver unmatched performance in strength and durability essential for demanding boat hull applications.
Weight and Buoyancy Considerations
Aramid fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to natural fibers, significantly reducing the overall weight of boat hulls and enhancing fuel efficiency and speed. Its low density and high tensile strength contribute to improved buoyancy and stability, crucial for marine applications. Natural fibers, while environmentally friendly, tend to be heavier and less durable, potentially compromising hull performance and lifespan in water conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Factors
Aramid fiber offers superior strength and durability for boat hulls but has a higher environmental footprint due to energy-intensive production and limited recyclability. Natural fibers like flax, hemp, or jute provide renewable, biodegradable alternatives with lower carbon emissions and reduced reliance on fossil fuels, enhancing sustainability in marine applications. Selecting natural fiber composites promotes eco-friendly boat manufacturing, minimizing long-term environmental impact compared to synthetic aramid-based materials.
Cost Analysis: Aramid vs. Natural Fibers
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and excellent impact resistance but come at a significantly higher cost compared to natural fibers like hemp or flax. While natural fibers provide a more eco-friendly and cost-effective option for boat hull construction, their lower durability and susceptibility to moisture absorption may lead to increased maintenance expenses over time. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including material price, lifespan, and repair frequency, is crucial for making an informed decision between aramid and natural fibers in boat hull applications.
Ease of Fabrication and Repair
Aramid fiber offers enhanced ease of fabrication for boat hulls due to its superior strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to moisture, facilitating precise molding and reduced curing times compared to natural fibers. Repairing aramid fiber hulls is more straightforward because the material's consistent structure allows for seamless patching and bonding without significant degradation in performance. In contrast, natural fibers, while eco-friendly, often pose challenges in fabrication due to their variability and higher susceptibility to water absorption, which complicates both manufacturing and long-term repairs.
Performance in Harsh Marine Environments
Aramid fiber exhibits superior resistance to impact, abrasion, and chemical corrosion compared to natural fibers, making it highly suitable for boat hulls in harsh marine environments. Its low moisture absorption and high tensile strength ensure enhanced durability and structural integrity under constant exposure to saltwater and UV radiation. Natural fibers, while eco-friendly and cost-effective, often degrade faster due to higher water absorption and lower mechanical resilience in aggressive marine conditions.
Future Trends in Boat Hull Materials
Aramid fibers, known for their superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent impact resistance, are increasingly favored over natural fibers in boat hull construction due to advancements in resin compatibility and durability under marine conditions. Emerging trends indicate a shift toward hybrid composites that combine aramid fibers with bio-based resins to enhance sustainability without compromising performance. The future of boat hull materials is focused on optimizing fiber-reinforced composites to achieve lighter, stronger, and more environmentally friendly vessels.
Infographic: Aramid fiber vs Natural fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com