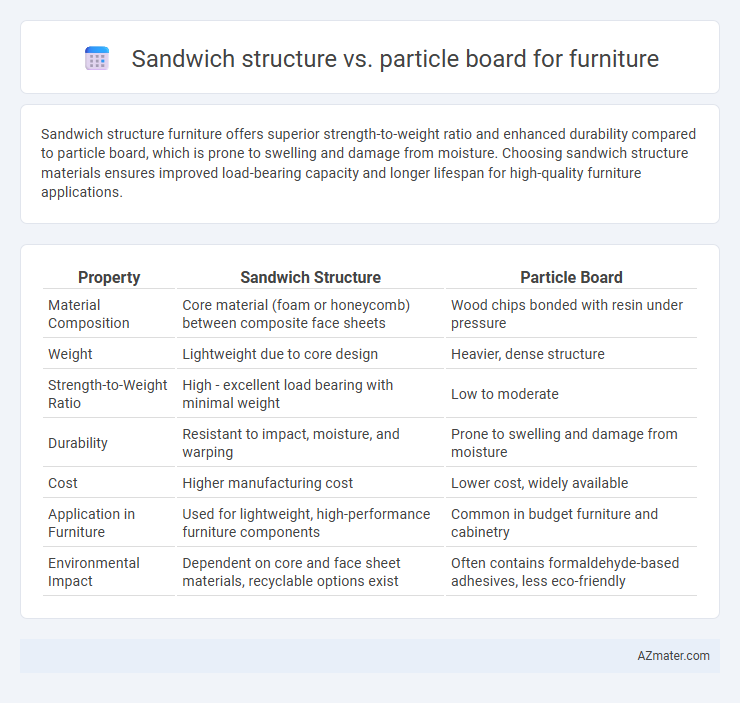
Sandwich structure furniture offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced durability compared to particle board, which is prone to swelling and damage from moisture. Choosing sandwich structure materials ensures improved load-bearing capacity and longer lifespan for high-quality furniture applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sandwich Structure | Particle Board |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Core material (foam or honeycomb) between composite face sheets | Wood chips bonded with resin under pressure |
| Weight | Lightweight due to core design | Heavier, dense structure |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | High - excellent load bearing with minimal weight | Low to moderate |
| Durability | Resistant to impact, moisture, and warping | Prone to swelling and damage from moisture |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application in Furniture | Used for lightweight, high-performance furniture components | Common in budget furniture and cabinetry |
| Environmental Impact | Dependent on core and face sheet materials, recyclable options exist | Often contains formaldehyde-based adhesives, less eco-friendly |
Introduction to Sandwich Structure and Particle Board
Sandwich structure furniture consists of two strong face layers bonded to a lightweight core, offering high strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced durability. Particle board, made from wood chips and resin compressed into panels, provides cost-effective and uniform material but tends to have lower strength and moisture resistance. Both materials serve distinct purposes in furniture manufacturing, balancing between structural performance and affordability.
Material Composition: Comparing Core Elements
Sandwich structures for furniture typically feature a lightweight core made of foam, honeycomb, or balsa wood, encapsulated by thin layers of plywood, MDF, or metal, offering superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced durability. Particle board consists of wood chips, sawdust, and resin compressed into dense sheets, providing an affordable and uniform material but with lower resistance to moisture and mechanical stress. The core composition directly influences furniture performance, where sandwich cores contribute to increased rigidity and impact resistance, while particle board cores prioritize cost-efficiency and ease of machining.
Strength and Durability Differences
Sandwich structures exhibit superior strength-to-weight ratios due to their layered composition, combining rigid face sheets and a lightweight core, which enhances load distribution and impact resistance in furniture applications. Particle board, composed of compressed wood particles bonded with resin, tends to be less durable and more prone to swelling and damage from moisture over time. For long-lasting furniture, sandwich panels provide enhanced structural integrity and longevity compared to particle board, especially in high-stress or high-use environments.
Weight Considerations in Furniture Design
Sandwich structures significantly outperform particle board in weight efficiency, offering a high strength-to-weight ratio essential for lightweight furniture design. The core materials in sandwich structures, such as foam or honeycomb, reduce overall weight while maintaining rigidity and durability. Particle board, being denser and heavier, limits mobility and increases transportation costs, making sandwich structures preferable for applications prioritizing weight reduction without sacrificing structural integrity.
Cost Analysis: Which Is More Economical?
Sandwich structure furniture typically incurs higher initial costs due to advanced materials like foam cores and laminated veneers, but offers superior durability and lightweight advantages. Particle board is more economical upfront, made from compressed wood chips and resin, making it a budget-friendly option for mass-produced furniture. Long-term cost analysis favors sandwich structures as they resist warping and damage better, reducing replacement and maintenance expenses compared to particle board.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sandwich structures utilize lightweight core materials such as foam or honeycomb, reducing raw material use and enhancing recyclability compared to particle board composed of wood particles bonded with synthetic resins that often contain formaldehyde emissions. The production of sandwich panels typically results in lower carbon footprints due to less intensive processing and longer lifespan, contributing to sustainability goals by minimizing waste generation and resource depletion. Particle board's reliance on adhesives and shorter durability leads to increased environmental burdens, making sandwich structures a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable furniture manufacturing.
Moisture Resistance and Longevity
Sandwich structure panels offer superior moisture resistance compared to particle board due to their combination of water-resistant outer layers and a lightweight core, preventing swelling and warping in humid environments. Particle board, made from compressed wood particles and resin, is more susceptible to moisture damage leading to swelling, degradation, and reduced structural integrity over time. Furniture crafted with sandwich panels generally demonstrates enhanced longevity and durability, especially in areas with high humidity or frequent cleaning.
Application Suitability for Various Furniture Types
Sandwich structure panels offer superior strength-to-weight ratio and moisture resistance, making them ideal for lightweight furniture like office desks, shelves, and cabinets. Particle board provides cost-effective bulk material suited for flat-pack furniture, wardrobes, and general-purpose cabinetry but lacks durability in high-moisture or heavy-load environments. Selection depends on application demands where sandwich panels serve premium furniture requiring durability and particle board suits budget-friendly, low-stress uses.
Finishing Options and Surface Quality
Sandwich structure furniture offers superior finishing options with smooth surfaces that easily accept veneers, laminates, and paints, resulting in high-quality aesthetics and durability. Particle board, while cost-effective, often requires additional surface treatments like melamine or laminate coatings to mask its rough texture and improve appearance. The enhanced surface quality of sandwich structures typically leads to longer-lasting finishes and a more refined look compared to particle board.
Conclusion: Which Material Is Better for Furniture?
Sandwich structure offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced durability compared to particle board, making it ideal for high-quality furniture requiring longevity and structural integrity. Particle board is more cost-effective and easier to work with, but it lacks the moisture resistance and load-bearing capacity of sandwich materials. For premium furniture applications prioritizing performance and lifespan, sandwich structure is the better material choice.
Infographic: Sandwich structure vs Particle board for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com