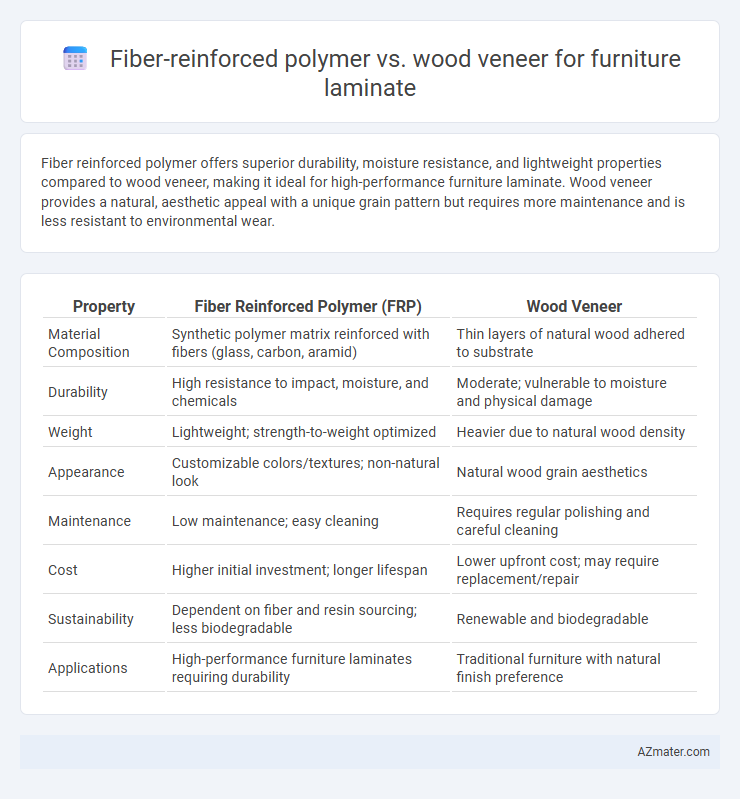
Fiber reinforced polymer offers superior durability, moisture resistance, and lightweight properties compared to wood veneer, making it ideal for high-performance furniture laminate. Wood veneer provides a natural, aesthetic appeal with a unique grain pattern but requires more maintenance and is less resistant to environmental wear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP) | Wood Veneer |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Synthetic polymer matrix reinforced with fibers (glass, carbon, aramid) | Thin layers of natural wood adhered to substrate |
| Durability | High resistance to impact, moisture, and chemicals | Moderate; vulnerable to moisture and physical damage |
| Weight | Lightweight; strength-to-weight optimized | Heavier due to natural wood density |
| Appearance | Customizable colors/textures; non-natural look | Natural wood grain aesthetics |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; easy cleaning | Requires regular polishing and careful cleaning |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; longer lifespan | Lower upfront cost; may require replacement/repair |
| Sustainability | Dependent on fiber and resin sourcing; less biodegradable | Renewable and biodegradable |
| Applications | High-performance furniture laminates requiring durability | Traditional furniture with natural finish preference |
Introduction to Furniture Laminate Materials
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) and wood veneer represent distinct furniture laminate materials with unique properties and applications. FRP offers high durability, resistance to moisture, and excellent structural strength, making it suitable for environments requiring long-lasting surfaces. Wood veneer provides natural aesthetics and warmth, favored for its authentic wood grain appearance, though it demands more maintenance and is less resistant to wear compared to FRP.
What is Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP)?
Fiber Reinforced Polymer (FRP) is a composite material consisting of a polymer matrix reinforced with fibers such as glass, carbon, or aramid, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and durability. FRP laminates offer superior resistance to moisture, chemicals, and impact compared to traditional wood veneer, making them ideal for furniture exposed to varying environmental conditions. The material's customizable properties allow furniture designers to achieve enhanced structural integrity and long-lasting aesthetic appeal.
Understanding Wood Veneer Laminate
Wood veneer laminate consists of thin slices of natural wood bonded to a substrate, offering authentic wood aesthetics with enhanced durability and moisture resistance. Compared to fiber reinforced polymer (FRP), which provides high strength and weather resistance, wood veneer laminate excels in delivering a warm, natural appearance ideal for indoor furniture applications. Understanding this material helps in selecting the right laminate that balances visual appeal and functional performance for furniture surfaces.
Durability Comparison: FRP vs Wood Veneer
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) exhibits superior durability compared to wood veneer in furniture laminate applications due to its high resistance to impact, moisture, and abrasion. FRP's composite structure prevents warping, cracking, and delamination that commonly affect wood veneer under fluctuating environmental conditions. In contrast, wood veneer, while aesthetically pleasing, is more susceptible to damage from scratches, moisture infiltration, and UV exposure, reducing its long-term performance and lifespan.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) laminates offer superior design flexibility compared to wood veneer, enabling intricate patterns, vibrant colors, and custom textures that enhance modern furniture aesthetics. FRP materials provide consistent surface finishes resistant to warping, making them ideal for contemporary, high-design applications where durability and sleek appearance are critical. Wood veneer maintains a natural, warm look with unique grain patterns, appealing to classic and upscale designs, but it offers limited customization and can be more prone to damage over time.
Maintenance and Longevity
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) laminates offer superior maintenance benefits compared to wood veneer due to their resistance to moisture, scratches, and chemical damage, reducing the need for frequent repairs or refinishing. The longevity of FRP is significantly higher, with enhanced durability under various environmental conditions, making it ideal for high-traffic or humid areas. Wood veneer, while aesthetically pleasing, requires regular sealing and careful maintenance to prevent warping, fading, and delamination over time, limiting its lifespan relative to FRP laminates.
Cost Analysis of FRP and Wood Veneer
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) typically incurs higher initial costs than wood veneer due to advanced manufacturing processes and material composition. Wood veneer offers a cost-effective solution with lower material expenses and simpler application techniques, making it suitable for budget-conscious furniture production. Long-term durability and maintenance savings often make FRP a competitive investment despite upfront price differences.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) laminates offer durability and resistance to moisture but rely heavily on non-renewable petrochemical resources, leading to higher environmental footprints and challenges in recycling. Wood veneer laminates derive from renewable timber sources, often supporting sustainable forest management and carbon sequestration, though their environmental benefits depend on responsible sourcing and treatment. Choosing wood veneer typically promotes biodegradability and lower embodied energy, making it a more sustainable option in furniture laminates when sourced from certified forests.
Application Suitability: Residential vs Commercial Use
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) laminates offer superior durability, moisture resistance, and impact strength, making them highly suitable for high-traffic commercial furniture applications where long-term performance and easy maintenance are critical. Wood veneer laminates provide a natural aesthetic and warmth ideal for residential furniture, emphasizing visual appeal and comfort over extreme durability. In commercial settings such as offices and hospitality, FRP laminates endure heavy use and cleaning better than wood veneer, which excels in low-traffic, decorative residential environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Laminate for Your Furniture
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) laminates offer superior durability, moisture resistance, and impact strength compared to traditional wood veneer, making them ideal for high-traffic or moisture-prone environments. Wood veneer provides a natural, warm aesthetic with authentic grain patterns, preferred for luxury or classic furniture designs but requires more maintenance and is less resistant to wear. Selecting the right laminate depends on balancing durability needs, aesthetic preferences, and maintenance capabilities to ensure long-lasting, visually appealing furniture surfaces.
Infographic: Fiber reinforced polymer vs Wood veneer for Furniture laminate
 azmater.com
azmater.com