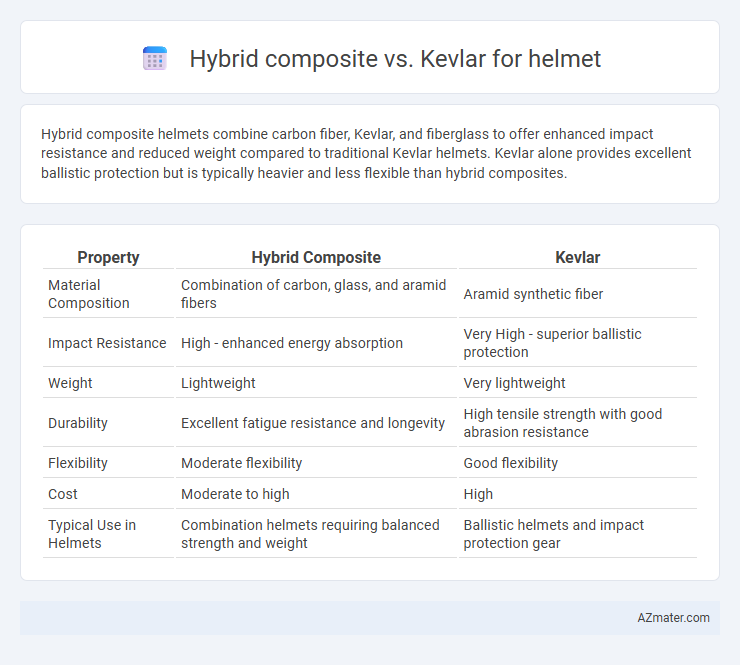
Hybrid composite helmets combine carbon fiber, Kevlar, and fiberglass to offer enhanced impact resistance and reduced weight compared to traditional Kevlar helmets. Kevlar alone provides excellent ballistic protection but is typically heavier and less flexible than hybrid composites.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hybrid Composite | Kevlar |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Combination of carbon, glass, and aramid fibers | Aramid synthetic fiber |
| Impact Resistance | High - enhanced energy absorption | Very High - superior ballistic protection |
| Weight | Lightweight | Very lightweight |
| Durability | Excellent fatigue resistance and longevity | High tensile strength with good abrasion resistance |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | Good flexibility |
| Cost | Moderate to high | High |
| Typical Use in Helmets | Combination helmets requiring balanced strength and weight | Ballistic helmets and impact protection gear |
Introduction to Helmet Materials
Helmet materials such as hybrid composites and Kevlar offer distinct advantages in impact resistance and weight reduction. Hybrid composites combine fibers like carbon, glass, and aramid to optimize strength, stiffness, and energy absorption, enhancing overall helmet performance. Kevlar, a para-aramid synthetic fiber known for its high tensile strength and thermal stability, provides excellent ballistic protection while maintaining lightness and flexibility for comfortable wear.
What is Hybrid Composite?
Hybrid composite materials in helmets combine fibers such as carbon, fiberglass, and Kevlar to optimize strength, impact resistance, and weight reduction. Kevlar, a high-strength synthetic fiber known for exceptional ballistic and puncture resistance, is often integrated within these composites to enhance helmet durability and safety performance. The hybrid composite structure leverages the unique properties of each fiber type to provide superior protection and comfort compared to helmets made solely from Kevlar.
Understanding Kevlar: Properties and Uses
Kevlar is a high-strength synthetic fiber known for its exceptional tensile strength, lightweight nature, and outstanding resistance to impact and abrasion, making it a preferred material in helmet manufacturing. Its use in ballistic helmets is prominent due to its ability to absorb and disperse energy from impacts, providing superior protection against shrapnel and ballistic threats. Kevlar's thermal stability and resistance to chemicals further enhance its durability and reliability in demanding protective gear applications.
Weight Comparison: Hybrid Composite vs Kevlar
Hybrid composite helmets generally weigh less than Kevlar helmets due to the use of advanced materials like carbon fiber combined with resin matrices, which provide high strength-to-weight ratios. Kevlar helmets, while offering excellent ballistic protection, tend to be heavier because of the dense woven aramid fibers used in their construction. The weight difference impacts comfort and extended wearability, making hybrid composite helmets preferable for users prioritizing lightweight gear without compromising protection.
Impact Resistance and Protection Levels
Hybrid composite helmets combine materials like carbon fiber, fiberglass, and Kevlar to deliver enhanced impact resistance by distributing force more effectively across the shell. Kevlar helmets offer excellent puncture resistance and high tensile strength, making them reliable for absorbing sharp impacts, but may be heavier compared to hybrid composites. Studies show hybrid composites provide superior protection levels by optimizing energy absorption and reducing helmet deformation under high-impact conditions.
Comfort and Ergonomics
Hybrid composite helmets offer superior comfort and ergonomics compared to Kevlar helmets due to their lightweight materials and better impact absorption properties. The combination of carbon fiber, fiberglass, and Kevlar in hybrid composites reduces overall helmet weight, minimizing neck strain during extended use. Enhanced ventilation and customizable padding systems in hybrid composite helmets improve airflow and fit, providing a more ergonomic experience for users.
Durability and Longevity
Hybrid composite helmets combine materials like carbon fiber and fiberglass, offering enhanced impact resistance and superior energy absorption compared to pure Kevlar helmets. Kevlar provides excellent tensile strength and cut resistance but is less effective in resisting repeated impacts over time, potentially leading to reduced durability. Research indicates hybrid composites maintain structural integrity longer under stress, resulting in helmets with greater longevity and sustained protective performance.
Cost-Effectiveness: Which Is More Affordable?
Hybrid composite helmets typically offer greater cost-effectiveness compared to Kevlar helmets due to the use of a blend of materials like fiberglass and carbon fiber, which reduce manufacturing expenses while maintaining high impact resistance. Kevlar helmets, known for their excellent ballistic protection and durability, generally come at a higher price point because of the specialized aramid fibers and complex weaving processes required. For budget-conscious consumers seeking reliable safety, hybrid composites present a more affordable option without significant compromise in helmet performance.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Hybrid composite helmets combine materials like carbon fiber and fiberglass to optimize strength-to-weight ratio, offering superior impact resistance and durability in military and law enforcement scenarios compared to standard Kevlar helmets. Case studies reveal hybrid composites reduce overall helmet weight by up to 20%, enhancing soldier mobility while maintaining certified ballistic protection under NIJ Level IIIA standards. Real-world applications in combat zones demonstrate hybrid composite helmets' effectiveness in mitigating blast trauma and penetrating injuries, contributing to increased wearer survivability over traditional Kevlar alternatives.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Helmet
Choosing the right material for your helmet involves comparing hybrid composites and Kevlar, both known for their excellent impact resistance and lightweight properties. Hybrid composites combine multiple fibers like carbon and fiberglass, offering enhanced strength-to-weight ratios and improved durability, while Kevlar excels in tensile strength and ballistic protection, making it ideal for high-impact scenarios. Prioritize hybrid composites for versatile performance and abrasion resistance, whereas Kevlar is preferred for superior penetration resistance and long-term reliability in rugged conditions.
Infographic: Hybrid composite vs Kevlar for Helmet
 azmater.com
azmater.com