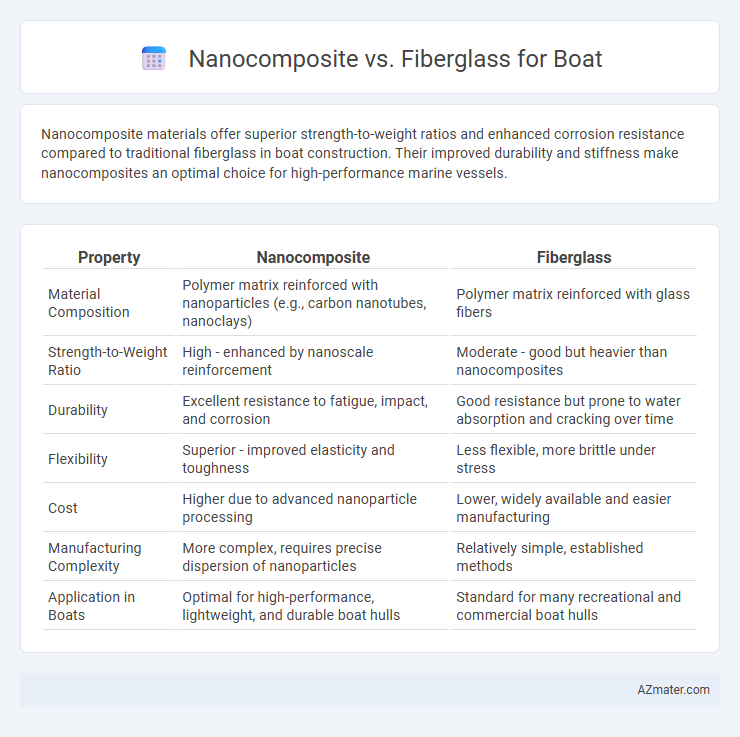
Nanocomposite materials offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced corrosion resistance compared to traditional fiberglass in boat construction. Their improved durability and stiffness make nanocomposites an optimal choice for high-performance marine vessels.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanocomposite | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polymer matrix reinforced with nanoparticles (e.g., carbon nanotubes, nanoclays) | Polymer matrix reinforced with glass fibers |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | High - enhanced by nanoscale reinforcement | Moderate - good but heavier than nanocomposites |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to fatigue, impact, and corrosion | Good resistance but prone to water absorption and cracking over time |
| Flexibility | Superior - improved elasticity and toughness | Less flexible, more brittle under stress |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced nanoparticle processing | Lower, widely available and easier manufacturing |
| Manufacturing Complexity | More complex, requires precise dispersion of nanoparticles | Relatively simple, established methods |
| Application in Boats | Optimal for high-performance, lightweight, and durable boat hulls | Standard for many recreational and commercial boat hulls |
Introduction to Modern Boat Building Materials
Nanocomposite materials, composed of nanoparticles embedded in a polymer matrix, offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced durability compared to traditional fiberglass, making them increasingly popular in modern boat building. Fiberglass, a long-established composite of glass fibers and resin, remains favored for its cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication but tends to be heavier and less impact-resistant than nanocomposites. Innovations in nanotechnology have propelled advancements in boat hulls and structural components, improving performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity in marine applications.
What Are Nanocomposites?
Nanocomposites are advanced materials composed of a polymer matrix embedded with nanoparticles, offering enhanced mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties. Compared to traditional fiberglass used in boats, nanocomposites provide superior strength-to-weight ratios and improved resistance to corrosion and fatigue. These characteristics make nanocomposites an innovative alternative for marine applications, delivering better performance and durability in harsh aquatic environments.
Understanding Fiberglass in Marine Applications
Fiberglass, composed of glass fibers embedded in resin, is extensively used in marine applications due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and affordability. Its durability and ease of repair make it a preferred material for boat hulls, decks, and other structural components exposed to harsh marine environments. While fiberglass offers reliable performance, nanocomposites provide advanced mechanical properties and enhanced water resistance, but typically at higher production costs.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Nanocomposite materials exhibit superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to traditional fiberglass, enhancing boat hull performance under stress. Their nanoscale reinforcement particles significantly improve impact resistance and fatigue durability, resulting in longer lifespan and reduced maintenance. Fiberglass remains cost-effective but falls short in resisting microcracks and environmental degradation compared to nanocomposites.
Weight Considerations: Nanocomposites vs Fiberglass
Nanocomposites offer significant weight reductions compared to traditional fiberglass, enhancing boat fuel efficiency and maneuverability. The enhanced strength-to-weight ratio of nanocomposites allows for thinner, lighter hulls without compromising durability, while fiberglass typically requires thicker laminates to achieve similar structural integrity. Reduced weight in nanocomposite boats directly contributes to improved performance metrics such as acceleration, speed, and overall handling on water.
Corrosion and Environmental Resistance
Nanocomposite materials exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to fiberglass due to their enhanced molecular structure that prevents water absorption and inhibits chemical degradation. Fiberglass, while durable, is more susceptible to environmental factors such as UV radiation and saltwater exposure, leading to potential weakening and surface deterioration over time. The advanced environmental resistance of nanocomposites makes them a preferred choice for boat construction in harsh marine conditions.
Cost Analysis of Nanocomposite and Fiberglass Boats
Nanocomposite boats typically exhibit higher initial production costs due to advanced materials and manufacturing techniques, but offer long-term savings through improved durability and lower maintenance expenses compared to fiberglass boats. Fiberglass boats, while more affordable upfront with widespread availability, often incur additional costs over time for repairs, fading, and structural degradation. Cost analysis reveals that nanocomposite boats provide a better investment value in terms of lifecycle costs despite their premium price point.
Fabrication and Repair Process Differences
Nanocomposite materials offer enhanced mechanical properties and reduced weight compared to fiberglass, resulting in more efficient boat fabrication through advanced molding techniques and faster curing times. Repair processes for nanocomposite boats typically require specialized resins and expertise due to their complex nanostructure, whereas fiberglass repairs are more straightforward with widely available materials like epoxy or polyester resins and standard reinforcement fabrics. The precision and durability of nanocomposites provide long-term performance benefits but involve higher initial repair costs and technical skill compared to the conventional, cost-effective repair approach used for fiberglass boats.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Nanocomposite boat materials offer superior lifespan compared to traditional fiberglass due to enhanced resistance to corrosion, UV damage, and fatigue, extending service life by up to 30%. Maintenance requirements for nanocomposites are significantly lower as their molecular structure reduces water absorption and prevents delamination, minimizing the need for frequent repairs or coatings. Fiberglass, while cost-effective, demands regular inspection and upkeep to address issues like gel coat blistering and structural wear, resulting in higher long-term maintenance costs.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Boat Materials
Nanocomposite materials are rapidly gaining traction in the marine industry due to their superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced corrosion resistance compared to traditional fiberglass. Innovations in nanotechnology enable the integration of carbon nanotubes and graphene into composites, significantly improving mechanical properties and durability for next-generation boats. The future trend points towards hybrid materials combining nanocomposites and advanced polymers to create lighter, more fuel-efficient, and environmentally sustainable vessels.
Infographic: Nanocomposite vs Fiberglass for Boat
 azmater.com
azmater.com