Bio-based composites offer enhanced sustainability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional fiberglass, making them ideal for eco-friendly boat manufacturing. These composites provide competitive strength and durability while significantly lowering carbon footprints in marine applications.
Table of Comparison
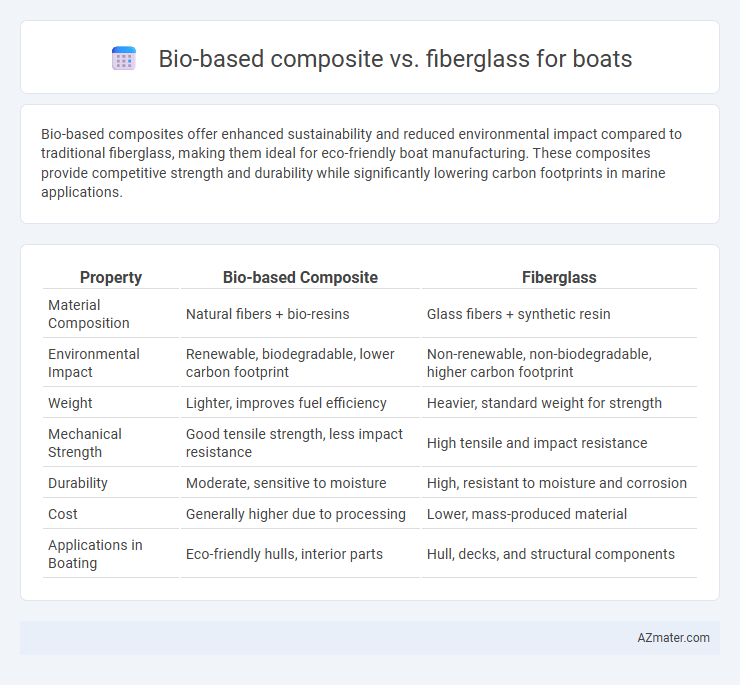
| Property | Bio-based Composite | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers + bio-resins | Glass fibers + synthetic resin |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, biodegradable, lower carbon footprint | Non-renewable, non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Weight | Lighter, improves fuel efficiency | Heavier, standard weight for strength |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength, less impact resistance | High tensile and impact resistance |
| Durability | Moderate, sensitive to moisture | High, resistant to moisture and corrosion |
| Cost | Generally higher due to processing | Lower, mass-produced material |
| Applications in Boating | Eco-friendly hulls, interior parts | Hull, decks, and structural components |
Introduction to Boat Building Materials
Bio-based composites offer sustainable alternatives to traditional fiberglass in boat building, utilizing renewable natural fibers such as flax, hemp, or jute combined with bio-resins. These materials provide comparable strength-to-weight ratios and improved environmental impact through reduced carbon footprint and biodegradability. Fiberglass remains popular for its durability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness, but bio-based composites are gaining traction for eco-conscious marine applications.
What Are Bio-based Composites?
Bio-based composites are materials made from natural fibers such as flax, hemp, or jute combined with bio-resins derived from renewable resources, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional fiberglass composites. These composites provide comparable strength and durability while reducing environmental impact and improving biodegradability. Bio-based composites also enhance boat performance by lowering weight and improving vibration dampening compared to conventional fiberglass materials.
Understanding Fiberglass Composites
Fiberglass composites, composed of glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent durability, making them a preferred material for boat hull construction. These composites provide resistance to corrosion, water absorption, and UV degradation, ensuring longevity and structural integrity in marine environments. Understanding the properties of fiberglass composites helps in evaluating their performance compared to bio-based composites, which emphasize sustainability but may have different mechanical and environmental resistance characteristics.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Bio-based composites for boats significantly reduce carbon emissions and reliance on non-renewable fossil fuels compared to traditional fiberglass, which primarily uses petroleum-based resins and glass fibers. These sustainable materials offer better end-of-life options, including biodegradability and recyclability, whereas fiberglass composites contribute to long-term environmental pollution due to their non-biodegradable and difficult-to-recycle nature. Life cycle assessments consistently show bio-based composites lower environmental footprints in energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and waste generation throughout production, use, and disposal phases.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Bio-based composites offer comparable tensile strength to fiberglass but excel in impact resistance due to their natural fiber matrix, making them a sustainable alternative for boat construction. Fiberglass remains superior in consistent durability under marine conditions, exhibiting higher resistance to water absorption and UV degradation. Strength and durability analysis reveals bio-based composites require advanced resin formulations to match fiberglass's long-term performance, especially in saltwater environments.
Weight and Performance Differences
Bio-based composites offer a significant weight reduction compared to traditional fiberglass, often achieving up to 20-30% lighter structures while maintaining comparable strength. This weight advantage enhances boat performance by improving fuel efficiency and increasing speed due to reduced drag and mass. Fiberglass remains favored for its proven durability and cost-effectiveness but generally results in heavier vessels that may compromise agility and handling.
Cost Comparison: Bio-based vs. Fiberglass
Bio-based composites typically have higher upfront material costs compared to traditional fiberglass due to renewable raw material sourcing and novel processing technologies. Fiberglass remains more cost-effective for large-scale boat production because of its established supply chain and lower raw material expenses. Long-term cost considerations for bio-based composites include potential savings from reduced environmental impact and improved lifecycle sustainability, which may offset initial price differences.
Manufacturing Processes and Scalability
Bio-based composites in boat manufacturing leverage renewable fibers like flax or hemp combined with bio-resins, enabling eco-friendly production processes that often require lower energy inputs and reduce reliance on petrochemical-based materials. Fiberglass boat production involves well-established processes including hand lay-up, spray-up, and vacuum infusion, offering high scalability due to mature supply chains and consistent material performance. The scalability of bio-based composites remains limited by material availability and processing variability, whereas fiberglass benefits from decades of industrial optimization, making it more suitable for large-scale marine applications.
Long-term Maintenance and Lifespan
Bio-based composites exhibit superior resistance to moisture absorption and UV degradation compared to traditional fiberglass, resulting in reduced long-term maintenance needs for boat hulls. Their natural fiber reinforcement offers enhanced impact resistance and prevents delamination issues common with fiberglass over extended use. As a result, bio-based composites can provide a longer lifespan with lower repair frequency, making them increasingly preferred in sustainable marine applications.
Future Trends in Sustainable Boat Construction
Bio-based composites are rapidly gaining traction in sustainable boat construction due to their renewable raw materials, reduced carbon footprint, and biodegradability compared to traditional fiberglass. Innovations in resin chemistry and natural fiber reinforcements enhance mechanical performance and durability, making bio-based composites increasingly viable for high-stress marine applications. Future trends emphasize hybrid materials combining bio-based composites with advanced fiberglass layers to optimize strength, weight reduction, and environmental impact in next-generation watercraft.
Infographic: Bio-based composite vs Fiberglass for Boat
 azmater.com
azmater.com