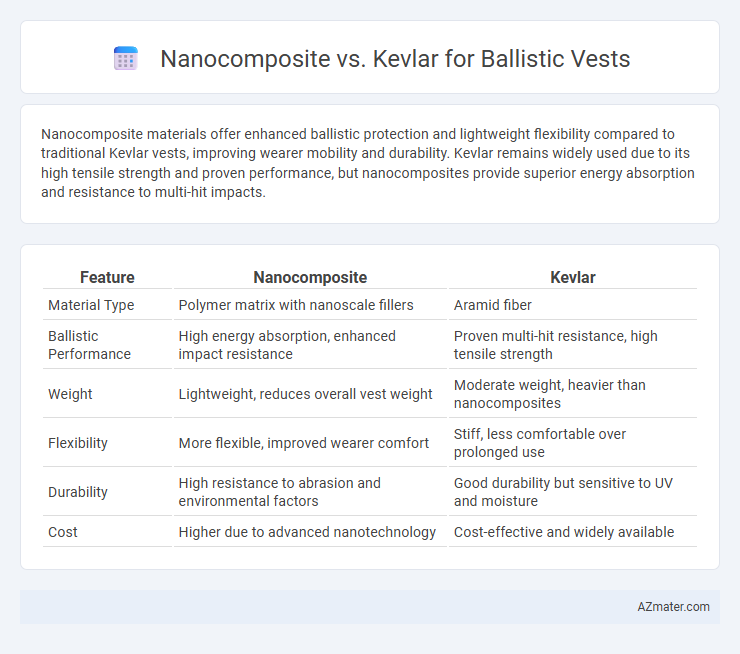
Nanocomposite materials offer enhanced ballistic protection and lightweight flexibility compared to traditional Kevlar vests, improving wearer mobility and durability. Kevlar remains widely used due to its high tensile strength and proven performance, but nanocomposites provide superior energy absorption and resistance to multi-hit impacts.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nanocomposite | Kevlar |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polymer matrix with nanoscale fillers | Aramid fiber |
| Ballistic Performance | High energy absorption, enhanced impact resistance | Proven multi-hit resistance, high tensile strength |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces overall vest weight | Moderate weight, heavier than nanocomposites |
| Flexibility | More flexible, improved wearer comfort | Stiff, less comfortable over prolonged use |
| Durability | High resistance to abrasion and environmental factors | Good durability but sensitive to UV and moisture |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced nanotechnology | Cost-effective and widely available |
Introduction to Ballistic Vests
Ballistic vests employ advanced materials to provide protection against high-velocity projectiles and shrapnel, with nanocomposites and Kevlar being two prominent options. Nanocomposites integrate nanoparticles into polymer matrices, enhancing impact resistance and lightweight properties, while Kevlar is a well-established aramid fiber known for exceptional tensile strength and durability. The choice between nanocomposites and Kevlar influences the vest's flexibility, weight, and ballistic effectiveness, critical factors in personal protective equipment performance.
Understanding Kevlar: Material Properties
Kevlar is a para-aramid synthetic fiber known for its high tensile strength-to-weight ratio, making it exceptionally effective in ballistic vests for stopping projectiles. Its molecular structure consists of long, rigid polymer chains aligned in parallel, providing both flexibility and durability under impact. Compared to nanocomposites, Kevlar offers proven reliability with excellent abrasion resistance and thermal stability, essential for protective body armor performance.
The Rise of Nanocomposite Materials
Nanocomposite materials offer enhanced ballistic protection compared to traditional Kevlar by integrating nanoparticles that improve tensile strength, flexibility, and energy absorption at the molecular level. These advanced composites reduce weight and thickness while maintaining superior impact resistance, making them ideal for next-generation ballistic vests. Research demonstrates that nanocomposites incorporating graphene or carbon nanotubes significantly outperform Kevlar in multi-hit scenarios and durability under extreme conditions.
Ballistic Performance: Nanocomposites vs Kevlar
Nanocomposites exhibit enhanced ballistic performance compared to traditional Kevlar by offering superior energy absorption and improved resistance to penetration due to their nanoscale reinforcement materials such as carbon nanotubes or graphene. Kevlar provides high tensile strength and excellent flexibility, but nanocomposites demonstrate higher impact resistance with reduced weight, leading to improved wearer mobility. The integration of nanomaterials enables ballistic vests to achieve enhanced durability and multi-hit capability beyond the limitations of standard Kevlar fabrics.
Weight and Comfort Comparison
Nanocomposite materials offer significantly lighter weight than Kevlar, reducing overall vest mass and improving wearer mobility during extended use. The enhanced flexibility of nanocomposites allows for better conformability to body contours, which increases comfort compared to the relatively rigid Kevlar fibers. Kevlar remains durable but its heavier composition often results in less breathability and increased fatigue for the user in prolonged wear scenarios.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Nanocomposite materials used in ballistic vests exhibit superior durability due to their enhanced matrix-filler interactions, providing higher resistance to impact and wear compared to Kevlar. Kevlar, while renowned for its high tensile strength and energy absorption, is more susceptible to degradation from UV exposure and moisture, reducing its environmental resistance over time. Nanocomposites offer improved resistance to heat, moisture, and chemical exposure, making them more suitable for long-term use in harsh environmental conditions.
Flexibility and Mobility in Protective Gear
Nanocomposite materials in ballistic vests offer enhanced flexibility and improved mobility compared to traditional Kevlar, due to their lightweight and layered nanoscale structure that conforms more easily to body movements. Kevlar remains a strong and reputable choice for ballistic protection but tends to be heavier and less flexible, potentially limiting wearer comfort and range of motion. The integration of nanocomposites allows for the design of protective gear that maintains high ballistic resistance while significantly increasing flexibility, which is critical for tactical and operational effectiveness.
Cost Analysis: Production and Maintenance
Nanocomposite ballistic vests generally incur higher initial production costs due to advanced materials like carbon nanotubes and complex manufacturing techniques, whereas Kevlar offers more established, cost-effective mass production processes. Maintenance expenses for nanocomposites can be lower as these materials exhibit superior durability and resistance to environmental degradation compared to Kevlar, which may require more frequent replacement or repair. Cost analysis favors Kevlar for budget-conscious applications, but nanocomposites potentially deliver long-term savings through enhanced performance and lifespan in ballistic protection.
Future Developments and Innovations
Nanocomposite materials exhibit enhanced ballistic resistance through improved energy absorption and lightweight properties, positioning them as a promising alternative to traditional Kevlar in vest manufacturing. Innovations such as graphene-reinforced nanocomposites and shear-thickening fluids integrated into textile matrices are driving future developments toward greater flexibility, durability, and multi-threat protection. Research efforts prioritize optimizing nanofiller dispersion and hybridization techniques to maximize performance while reducing weight, addressing the evolving demands of modern ballistic protection.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Ballistic Material
Nanocomposites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced flexibility compared to traditional Kevlar, making them ideal for lightweight, high-performance ballistic vests. Kevlar remains a proven choice with excellent stab and ballistic resistance but tends to be heavier and less adaptable to complex shapes. Selecting the optimal ballistic material depends on balancing protection level, weight constraints, and wearability for specific operational needs.
Infographic: Nanocomposite vs Kevlar for Ballistic vest
 azmater.com
azmater.com