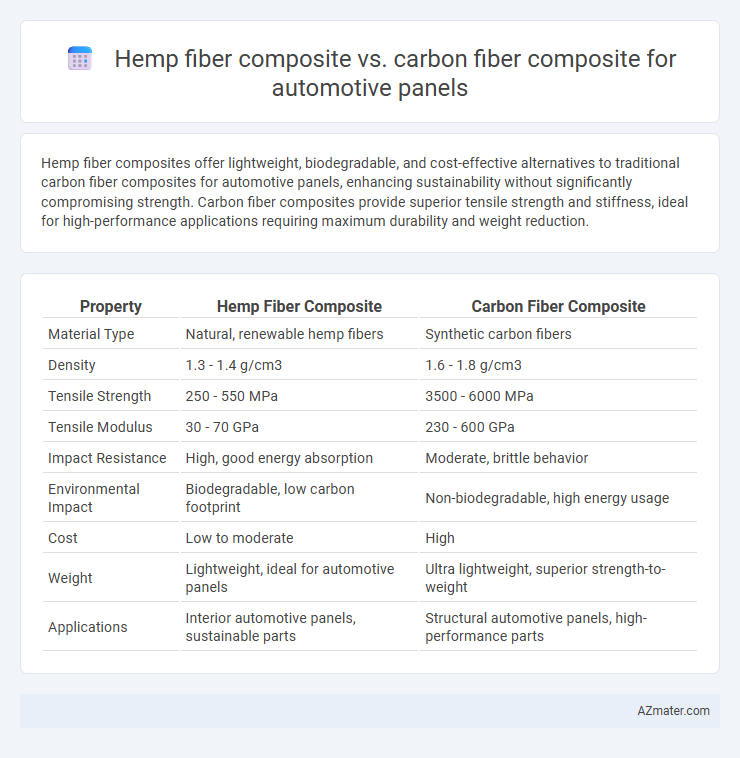
Hemp fiber composites offer lightweight, biodegradable, and cost-effective alternatives to traditional carbon fiber composites for automotive panels, enhancing sustainability without significantly compromising strength. Carbon fiber composites provide superior tensile strength and stiffness, ideal for high-performance applications requiring maximum durability and weight reduction.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Fiber Composite | Carbon Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural, renewable hemp fibers | Synthetic carbon fibers |
| Density | 1.3 - 1.4 g/cm3 | 1.6 - 1.8 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 250 - 550 MPa | 3500 - 6000 MPa |
| Tensile Modulus | 30 - 70 GPa | 230 - 600 GPa |
| Impact Resistance | High, good energy absorption | Moderate, brittle behavior |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, high energy usage |
| Cost | Low to moderate | High |
| Weight | Lightweight, ideal for automotive panels | Ultra lightweight, superior strength-to-weight |
| Applications | Interior automotive panels, sustainable parts | Structural automotive panels, high-performance parts |
Introduction to Automotive Panel Composites
Automotive panel composites combine lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency and durability. Hemp fiber composites offer renewable, biodegradable properties with good impact resistance, making them environmentally friendly alternatives. Carbon fiber composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness, ideal for high-performance vehicle panels requiring maximum structural integrity.
What is Hemp Fiber Composite?
Hemp fiber composite is a sustainable material made by reinforcing a polymer matrix with hemp fibers extracted from the Cannabis sativa plant, offering lightweight and eco-friendly properties. Its natural fibers provide good mechanical strength, vibration damping, and biodegradability, making it suitable for automotive panels where environmental impact and recyclability are prioritized. Compared to carbon fiber composites, hemp fiber composites are less expensive, renewable, and have lower carbon footprints while delivering adequate performance for interior and non-structural automotive components.
What is Carbon Fiber Composite?
Carbon fiber composite is a lightweight, high-strength material made from carbon fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, commonly used in automotive panels for its superior stiffness, durability, and resistance to corrosion. Compared to hemp fiber composite, carbon fiber composites offer higher tensile strength and better performance in high-stress applications, contributing to improved vehicle fuel efficiency and safety. Their premium cost and energy-intensive production process often limit widespread use to high-performance and luxury automotive sectors.
Mechanical Properties: Hemp vs Carbon Fiber
Hemp fiber composites exhibit lower tensile strength and stiffness compared to carbon fiber composites, typically achieving tensile strengths around 200-400 MPa versus carbon fiber's 3,500-6,000 MPa range. However, hemp fibers offer better impact resistance and higher elongation at break, contributing to improved energy absorption in automotive panels. Carbon fiber composites excel in rigidity and lightweight performance, making them ideal for structural automotive components where mechanical strength is paramount.
Weight and Density Comparison
Hemp fiber composites exhibit a density range of approximately 1.2 to 1.4 g/cm3, significantly lower than traditional carbon fiber composites, which have densities around 1.6 g/cm3. This reduced density translates to lighter automotive panels, improving fuel efficiency and handling without sacrificing structural integrity. Weight savings of up to 15-20% are achievable when substituting hemp fiber composites for carbon fiber in panel applications, enhancing vehicle sustainability and performance.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Hemp fiber composites significantly reduce environmental impact in automotive panels due to their biodegradability and lower carbon footprint compared to carbon fiber composites, which require energy-intensive production and are non-biodegradable. Hemp fibers are renewable and absorb CO2 during growth, enhancing sustainability, while carbon fibers rely heavily on fossil fuels and generate substantial emissions during manufacturing. The use of hemp fiber composites supports circular economy principles by enabling easier recycling and composting, promoting greener automotive design.
Cost Analysis: Hemp Fiber vs Carbon Fiber
Hemp fiber composites offer a significant cost advantage over carbon fiber composites for automotive panels, with raw material costs typically 60-80% lower due to hemp's rapid growth and abundant availability. Manufacturing expenses also decrease as hemp fibers require less energy-intensive processing compared to carbon fibers, reducing overall production costs by approximately 30-50%. While carbon fiber composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratios, hemp fiber composites deliver acceptable mechanical properties for many automotive applications at a fraction of the cost, enhancing affordability in lightweight panel production.
Manufacturing and Processing Differences
Hemp fiber composites offer lower processing temperatures and reduced energy consumption compared to carbon fiber composites, making them more environmentally friendly for automotive panel production. Hemp fibers require less complex machinery and shorter curing times, resulting in cost-effective manufacturing processes, whereas carbon fiber composites demand higher temperatures and longer cycles to achieve optimal strength. The biodegradability and renewability of hemp fibers also contrast sharply with the energy-intensive and less sustainable production of carbon fiber composites.
Performance in Real-World Automotive Applications
Hemp fiber composites offer lightweight, sustainable alternatives with good impact resistance and vibration damping, but generally have lower tensile strength and stiffness compared to carbon fiber composites in automotive panels. Carbon fiber composites provide superior mechanical performance, including high tensile strength, rigidity, and durability, enhancing vehicle structural integrity and crashworthiness under real-world conditions. Automotive manufacturers balance these trade-offs by selecting carbon fiber for high-performance, load-bearing panels, while hemp fiber composites are increasingly adopted for non-structural components to reduce weight and improve environmental sustainability.
Future Trends and Industry Adoption
Hemp fiber composites are gaining traction in the automotive industry due to their sustainability, lightweight properties, and cost-effectiveness compared to carbon fiber composites, which are prized for superior strength and stiffness but come with higher production costs. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach, combining hemp fibers with carbon to optimize performance while reducing environmental impact, accelerating industry adoption for interior and exterior panels. Increasing regulatory pressure for eco-friendly materials and advances in bio-resin technologies further boost the integration of hemp fiber composites in automotive manufacturing.
Infographic: Hemp fiber composite vs Carbon fiber composite for Automotive panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com