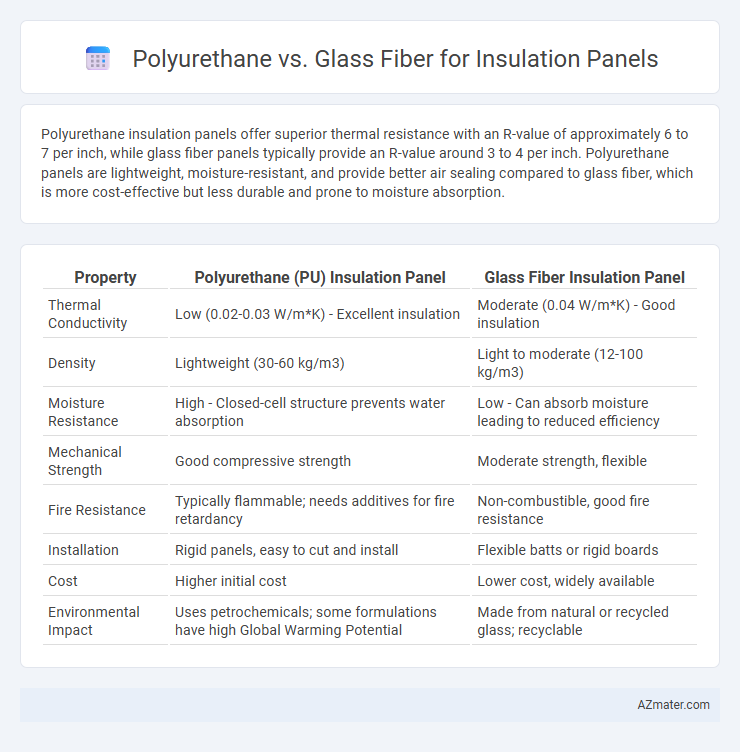
Polyurethane insulation panels offer superior thermal resistance with an R-value of approximately 6 to 7 per inch, while glass fiber panels typically provide an R-value around 3 to 4 per inch. Polyurethane panels are lightweight, moisture-resistant, and provide better air sealing compared to glass fiber, which is more cost-effective but less durable and prone to moisture absorption.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) Insulation Panel | Glass Fiber Insulation Panel |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (0.02-0.03 W/m*K) - Excellent insulation | Moderate (0.04 W/m*K) - Good insulation |
| Density | Lightweight (30-60 kg/m3) | Light to moderate (12-100 kg/m3) |
| Moisture Resistance | High - Closed-cell structure prevents water absorption | Low - Can absorb moisture leading to reduced efficiency |
| Mechanical Strength | Good compressive strength | Moderate strength, flexible |
| Fire Resistance | Typically flammable; needs additives for fire retardancy | Non-combustible, good fire resistance |
| Installation | Rigid panels, easy to cut and install | Flexible batts or rigid boards |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Uses petrochemicals; some formulations have high Global Warming Potential | Made from natural or recycled glass; recyclable |
Introduction: Polyurethane vs Glass Fiber Insulation Panels
Polyurethane insulation panels provide superior thermal resistance with an R-value typically ranging from 6 to 7 per inch, making them highly efficient for energy-saving applications. Glass fiber insulation panels offer a cost-effective solution with an R-value around 2.2 to 3.8 per inch, known for excellent sound absorption and fire resistance. Choosing between polyurethane and glass fiber depends on specific project requirements such as thermal performance, moisture resistance, and budget constraints.
Understanding Polyurethane Insulation
Polyurethane insulation panels offer superior thermal resistance with an R-value typically ranging from 6 to 7 per inch, significantly higher than glass fiber's average of 2.2 to 2.7. The closed-cell structure of polyurethane reduces air and moisture permeability, enhancing energy efficiency and durability in various applications. Polyurethane panels are also lighter and require less thickness than glass fiber, making them ideal for space-constrained insulation projects.
Overview of Glass Fiber Insulation
Glass fiber insulation consists of fine strands of glass woven into a fibrous mat offering excellent thermal resistance with an R-value typically between 2.2 and 2.7 per inch. It is non-combustible, resistant to moisture, and provides effective sound dampening, making it a popular choice for residential and commercial insulation panels. Compared to polyurethane, glass fiber panels generally have lower cost and better fire resistance but may require vapor barriers to prevent moisture accumulation in certain applications.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Polyurethane insulation panels provide superior thermal performance with an average R-value of 6.0 to 7.0 per inch, significantly reducing heat transfer compared to glass fiber panels, which typically offer R-values around 2.2 to 3.8 per inch. The closed-cell structure of polyurethane minimizes thermal bridging and air infiltration, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. In contrast, glass fiber panels rely on trapped air within the fibers and can lose insulating properties if compressed or exposed to moisture.
Moisture Resistance: Which Performs Better?
Polyurethane insulation panels exhibit superior moisture resistance due to their closed-cell structure, which significantly limits water absorption and maintains thermal performance even in humid environments. Glass fiber insulation, while effective for thermal insulation, is more susceptible to moisture retention, leading to reduced R-values and potential mold growth over time. Moisture resistance in polyurethane panels ensures enhanced durability and energy efficiency in applications exposed to damp conditions.
Fire Resistance and Safety Considerations
Polyurethane insulation panels offer higher thermal efficiency but have lower fire resistance compared to glass fiber panels, which inherently resist ignition and reduce smoke toxicity. Glass fiber panels provide superior safety in fire-prone environments due to their non-combustible nature and ability to maintain structural integrity under high heat. Fire-retardant additives in polyurethane can improve safety; however, glass fiber remains the preferred choice for maximizing fire resistance and minimizing health hazards during combustion.
Durability and Longevity of Insulation Panels
Polyurethane insulation panels offer superior durability due to their high resistance to moisture, chemicals, and physical damage, ensuring long-lasting thermal performance. Glass fiber panels, while cost-effective and lightweight, are more susceptible to compression, moisture absorption, and degradation over time, which can reduce their insulating effectiveness. Polyurethane's closed-cell structure provides enhanced longevity by preventing mold growth and maintaining structural integrity in harsh environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane insulation panels typically have a higher environmental impact due to their reliance on petrochemical raw materials and challenges in recyclability, contributing to carbon emissions and landfill waste. Glass fiber panels, made from abundant natural materials like sand and recycled glass, offer better sustainability through lower embodied energy and higher recyclability rates. Choosing glass fiber insulation aligns with eco-friendly building practices by minimizing resource depletion and supporting circular economy principles.
Cost Analysis: Polyurethane vs Glass Fiber
Polyurethane insulation panels typically offer higher initial costs compared to glass fiber due to advanced manufacturing processes and superior thermal performance. Glass fiber panels are more budget-friendly, benefiting from widespread production and lower raw material expenses, making them attractive for large-scale projects. Long-term savings with polyurethane arise from enhanced energy efficiency and durability, potentially offsetting upfront costs over the panel's lifespan.
Choosing the Right Insulation Panel for Your Project
Polyurethane insulation panels offer superior thermal resistance with R-values typically between 6.0 and 7.0 per inch, making them ideal for maximizing energy efficiency in tight spaces. Glass fiber panels provide excellent sound absorption and fire resistance, with R-values ranging from 2.9 to 3.8 per inch, often serving well in applications requiring noise control and cost-effectiveness. Selecting the right insulation panel depends on your project's priorities, such as thermal performance, fire safety standards, moisture resistance, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Glass fiber for Insulation panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com