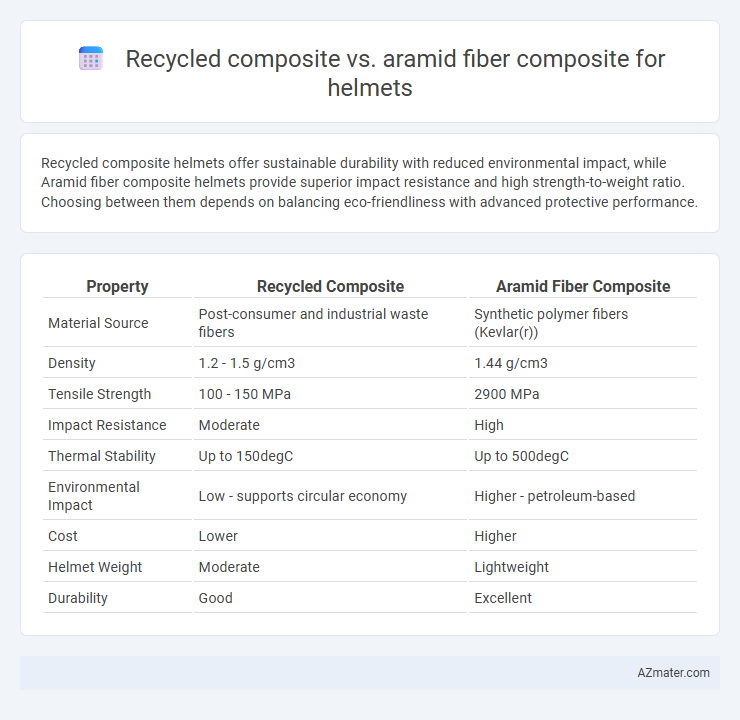
Recycled composite helmets offer sustainable durability with reduced environmental impact, while Aramid fiber composite helmets provide superior impact resistance and high strength-to-weight ratio. Choosing between them depends on balancing eco-friendliness with advanced protective performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Composite | Aramid Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-consumer and industrial waste fibers | Synthetic polymer fibers (Kevlar(r)) |
| Density | 1.2 - 1.5 g/cm3 | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 100 - 150 MPa | 2900 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 150degC | Up to 500degC |
| Environmental Impact | Low - supports circular economy | Higher - petroleum-based |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Helmet Weight | Moderate | Lightweight |
| Durability | Good | Excellent |
Introduction to Helmet Composite Materials
Helmet composite materials are engineered for impact resistance, durability, and lightweight performance, with recycled composites and aramid fiber composites being prominent choices. Recycled composites utilize reused fibers and resins to enhance sustainability while maintaining structural integrity, whereas aramid fiber composites, such as Kevlar, offer superior tensile strength and energy absorption crucial for helmet safety. Selecting between recycled and aramid composites involves balancing eco-friendly credentials with optimal protective performance in helmet applications.
Overview of Recycled Composite Materials
Recycled composite materials for helmets typically consist of reprocessed plastics or fibers combined with resins to create lightweight, durable protective gear. These composites offer environmental benefits by reducing landfill waste and lowering the carbon footprint compared to virgin materials used in traditional aramid fiber composites such as Kevlar. Despite having lower impact resistance and tensile strength, recycled composites continue to improve through advanced fabrication techniques, making them a sustainable alternative in helmet manufacturing.
Understanding Aramid Fiber Composites
Aramid fiber composites, renowned for their extraordinary strength-to-weight ratio and impact resistance, are extensively used in helmet manufacturing to enhance protection and durability. These fibers exhibit excellent energy absorption and thermal stability, making them ideal for high-performance safety equipment. Compared to recycled composites, aramid fiber composites offer superior tensile strength and toughness, ensuring optimal safety for users in critical impact scenarios.
Environmental Impact: Recycled vs Aramid Composites
Recycled composites used in helmets significantly reduce landfill waste and lower carbon emissions by reusing materials such as fiberglass and plastic waste, promoting circular economy principles. Aramid fiber composites, while offering superior strength and impact resistance, rely on energy-intensive production processes and non-renewable petrochemical resources, resulting in higher environmental footprints. Choosing recycled composites enhances helmet sustainability by minimizing resource extraction and facilitating end-of-life material recovery compared to aramid fiber composites.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Recycled composite materials in helmet manufacturing offer moderate mechanical strength and durability but generally fall short compared to Aramid fiber composites, which provide superior impact resistance and tensile strength due to their molecular structure. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, enhance helmet durability by effectively absorbing and redistributing impact forces, leading to improved resistance against wear and fatigue over time. The enhanced mechanical performance of Aramid fiber composites makes them a preferred choice for high-performance protective helmets requiring long-lasting durability and robust safety features.
Weight and Comfort in Helmet Design
Recycled composite helmets offer significant weight reduction compared to traditional Aramid fiber composites, enhancing overall comfort during extended wear. The lower density of recycled materials contributes to better shock absorption and reduced fatigue, which is crucial for helmet safety and user endurance. Aramid fiber composites, while highly durable, typically result in heavier helmets that may compromise comfort, especially in high-performance or long-duration applications.
Cost Analysis: Production and Market Value
Recycled composite helmets typically offer a lower production cost due to the use of repurposed materials and simplified manufacturing processes, making them an economical choice for budget-conscious markets. Aramid fiber composites, such as those using Kevlar, have higher production expenses driven by raw material costs and advanced fabrication techniques, which justify their premium pricing through superior impact resistance and durability. Market value reflects these differences, with aramid fiber helmets positioned as high-end protective gear, while recycled composite helmets target cost-sensitive consumers seeking sustainable yet effective protection.
Safety Standards and Performance Testing
Recycled composite helmets demonstrate compliance with key safety standards such as DOT and ECE, offering sustainable protection without compromising impact resistance and energy absorption capabilities. Aramid fiber composites, known for high tensile strength and excellent durability, consistently exceed stringent performance tests including SHARP and Snell certification, enhancing helmet impact resistance and penetration protection. Performance testing reveals aramid composites provide superior fatigue resistance and thermal stability, while recycled composites offer competitive environmental benefits alongside reliable safety metrics.
Future Trends in Helmet Materials
Recycled composites are gaining momentum in helmet manufacturing due to their environmental benefits and lower carbon footprint compared to traditional materials. Aramid fiber composites, such as Kevlar, continue to dominate for impact resistance and lightweight protection but face challenges in cost and sustainability. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach combining recycled composites with aramid fibers to optimize durability, sustainability, and performance in advanced helmet designs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Composite for Helmets
Recycled composites offer sustainability benefits and cost-effectiveness for helmet manufacturing, while aramid fiber composites provide superior impact resistance and durability critical for safety. Selecting the right composite depends on balancing environmental impact with performance requirements, where aramid fibers excel in high-stress protection applications and recycled materials suit less demanding contexts. Helmet designers prioritizing optimal safety often favor aramid fiber composites despite higher costs due to their proven mechanical strength and energy absorption properties.
Infographic: Recycled composite vs Aramid fiber composite for Helmet
 azmater.com
azmater.com