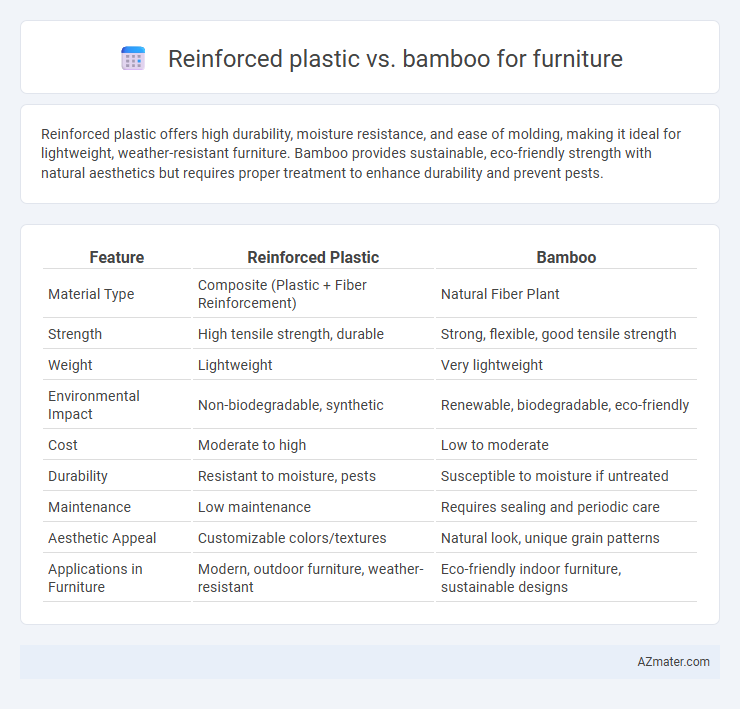
Reinforced plastic offers high durability, moisture resistance, and ease of molding, making it ideal for lightweight, weather-resistant furniture. Bamboo provides sustainable, eco-friendly strength with natural aesthetics but requires proper treatment to enhance durability and prevent pests.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Reinforced Plastic | Bamboo |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Composite (Plastic + Fiber Reinforcement) | Natural Fiber Plant |
| Strength | High tensile strength, durable | Strong, flexible, good tensile strength |
| Weight | Lightweight | Very lightweight |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, synthetic | Renewable, biodegradable, eco-friendly |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Durability | Resistant to moisture, pests | Susceptible to moisture if untreated |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Requires sealing and periodic care |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Customizable colors/textures | Natural look, unique grain patterns |
| Applications in Furniture | Modern, outdoor furniture, weather-resistant | Eco-friendly indoor furniture, sustainable designs |
Introduction to Reinforced Plastic and Bamboo Furniture
Reinforced plastic furniture combines synthetic polymers with materials like glass or carbon fibers, offering high durability, lightweight properties, and resistance to moisture and insects. Bamboo furniture showcases natural strength, rapid renewability, and eco-friendly benefits, making it a popular choice for sustainable, lightweight, and stylish designs. Both materials present unique functional and aesthetic advantages suitable for various furniture applications.
Material Composition and Sustainability
Reinforced plastic furniture is made from synthetic polymers combined with fibrous materials like glass or carbon fibers, offering high durability and resistance to moisture but relying heavily on non-renewable petrochemicals. Bamboo furniture, composed of natural fast-growing bamboo stalks, provides a renewable and biodegradable alternative with a low carbon footprint due to its rapid regrowth and minimal processing requirements. Sustainability in bamboo stems from its natural carbon sequestration and biodegradability, whereas reinforced plastics pose significant environmental challenges related to non-biodegradability and energy-intensive manufacturing.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Reinforced plastic offers high tensile strength and resistance to moisture, making it suitable for long-term outdoor furniture use without significant degradation. Bamboo provides impressive natural strength and flexibility, with excellent durability when properly treated, though it may be prone to insect damage and weathering over time. Both materials excel in strength and durability, but reinforced plastic typically outperforms bamboo in consistent longevity under harsh environmental conditions.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Appeal
Reinforced plastic offers superior design flexibility with its ability to be molded into complex shapes and vibrant colors, enabling innovative and modern furniture designs. Bamboo provides a natural aesthetic appeal with its unique grain patterns and warm tones, ideal for eco-friendly and rustic styles. While reinforced plastic excels in versatility and durability, bamboo stands out for its sustainable charm and organic beauty in furniture design.
Environmental Impact and Eco-Friendliness
Reinforced plastic furniture often involves non-biodegradable materials like fiberglass and resins, resulting in long-term environmental pollution and high carbon emissions during production. Bamboo furniture, sourced from fast-growing bamboo plants, is renewable, biodegradable, and sequesters significant amounts of carbon dioxide, making it a superior eco-friendly alternative. Choosing bamboo reduces landfill waste and promotes sustainable forestry practices, whereas reinforced plastic contributes to microplastic pollution and resource depletion.
Cost and Affordability Analysis
Reinforced plastic furniture typically offers lower upfront costs and greater affordability due to mass production and durability, making it a budget-friendly choice for long-term use. Bamboo furniture, while often more expensive initially due to sustainable harvesting and craftsmanship, provides eco-friendly advantages and potential savings through biodegradability and reduced environmental impact. Cost analysis highlights reinforced plastic's advantage in low-maintenance expenses, whereas bamboo's price reflects investment in sustainable materials and aesthetic value.
Maintenance and Longevity
Reinforced plastic furniture offers superior resistance to moisture, pests, and UV damage, requiring minimal maintenance such as occasional cleaning with mild soap. Bamboo furniture demands regular treatment with oils or sealants to prevent cracking, warping, and insect infestation, especially in humid environments. While reinforced plastic typically outlasts bamboo due to its durability and weather resistance, bamboo provides a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative with moderate longevity when properly maintained.
Health and Safety Considerations
Reinforced plastic furniture offers durability and resistance to moisture, reducing risks of mold and bacterial growth, but may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) affecting indoor air quality. Bamboo furniture is naturally antibacterial, biodegradable, and free from synthetic chemicals, promoting a healthier indoor environment, though it requires proper treatment to avoid pest infestation and fungal decay. Choosing bamboo supports sustainability and reduces exposure to harmful toxins often found in synthetic coatings used on reinforced plastic.
Popular Applications in Modern Furniture
Reinforced plastic is widely used in modern furniture for sleek, durable outdoor pieces and ergonomic office chairs due to its resistance to weather and impact. Bamboo is favored for eco-friendly indoor furniture, including lightweight chairs and tables, valued for its rapid renewability and natural aesthetic. Both materials offer versatility, with reinforced plastic excelling in mass-produced, moldable designs and bamboo thriving in sustainable, handcrafted applications.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Takeaways
Reinforced plastic offers durability, moisture resistance, and low maintenance, making it ideal for outdoor and high-traffic furniture applications. Bamboo stands out for its sustainability, natural aesthetic, and strength, suitable for eco-conscious consumers and indoor use. Selecting between them depends on prioritizing environmental impact versus longevity and maintenance requirements.
Infographic: Reinforced plastic vs Bamboo for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com