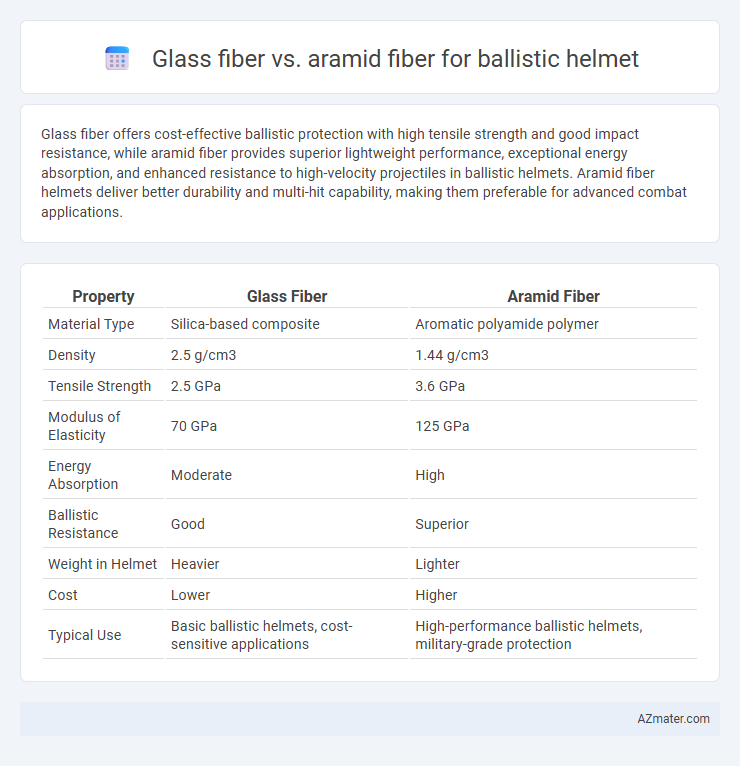
Glass fiber offers cost-effective ballistic protection with high tensile strength and good impact resistance, while aramid fiber provides superior lightweight performance, exceptional energy absorption, and enhanced resistance to high-velocity projectiles in ballistic helmets. Aramid fiber helmets deliver better durability and multi-hit capability, making them preferable for advanced combat applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Silica-based composite | Aromatic polyamide polymer |
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 2.5 GPa | 3.6 GPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 70 GPa | 125 GPa |
| Energy Absorption | Moderate | High |
| Ballistic Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Weight in Helmet | Heavier | Lighter |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Use | Basic ballistic helmets, cost-sensitive applications | High-performance ballistic helmets, military-grade protection |
Introduction to Ballistic Helmet Materials
Ballistic helmets typically utilize advanced materials like glass fiber and aramid fiber to provide protection against ballistic threats and blunt impacts. Glass fiber offers high tensile strength and excellent resistance to abrasion and impact, making it a cost-effective choice for helmet shells. Aramid fiber, known for its superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced ballistic resistance, delivers better multi-hit performance and durability in ballistic helmet applications.
Overview of Glass Fiber in Protective Gear
Glass fiber in ballistic helmets offers a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it an effective material for impact resistance while maintaining comfort. Its excellent stiffness and durability contribute to reliable protection against shrapnel and low-velocity projectiles. Cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication further enhance glass fiber's popularity in manufacturing protective gear.
Aramid Fiber: Properties and Applications
Aramid fiber offers exceptional tensile strength, impact resistance, and thermal stability, making it a preferred material for ballistic helmets. Its lightweight nature combined with superior energy absorption enhances protection against high-velocity projectiles and shrapnel. Widely used in military and law enforcement helmets, aramid fiber improves durability and comfort without compromising safety.
Comparative Ballistic Performance
Aramid fiber provides superior ballistic performance for helmets due to its high tensile strength and energy absorption capabilities compared to glass fiber, which tends to be more brittle under impact. The tensile strength of aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, typically ranges from 2,500 to 3,000 MPa, significantly outperforming glass fibers that average around 2,000 MPa. Aramid's ability to dissipate kinetic energy effectively reduces penetration risk and enhances multi-hit resistance, making it the preferred choice for advanced ballistic helmet applications.
Weight and Comfort Considerations
Glass fiber ballistic helmets offer a lighter weight alternative compared to aramid fiber helmets, enhancing wearer comfort during extended use. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide superior impact resistance and durability but typically result in heavier helmets, potentially causing increased fatigue. The balance between weight and protection is crucial; selecting glass fiber can improve mobility and reduce strain, whereas aramid fiber helmets prioritize higher ballistic resistance with a marginal weight increase.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Glass fiber offers excellent durability with high tensile strength and resistance to abrasion, making it a reliable choice for ballistic helmets in various impact scenarios. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, surpasses glass fiber in environmental resistance, maintaining structural integrity under extreme temperatures, moisture, and UV exposure. The superior chemical stability and fatigue resistance of aramid fibers contribute to enhanced helmet longevity in harsh operating conditions compared to glass fiber.
Cost Analysis: Glass Fiber vs Aramid Fiber
Glass fiber ballistic helmets typically cost 30-50% less than aramid fiber helmets due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses. While aramid fibers like Kevlar offer superior impact resistance and lighter weight, their complex production process results in higher price points. Cost-sensitive procurement often favors glass fiber helmets, balancing adequate protection with budget constraints.
Manufacturing and Design Flexibility
Glass fiber offers cost-effective manufacturing with ease of molding into complex shapes, making it suitable for mass production of ballistic helmets with consistent quality. Aramid fiber, known for higher tensile strength and impact resistance, demands more precise fabrication techniques, resulting in a more labor-intensive process but enabling helmets with superior protection and tailored design flexibility. The combination of aramid fibers with advanced resin systems allows for lightweight, ergonomic helmets that can be customized for enhanced comfort and mission-specific requirements.
Real-World Use Cases and Testing
Glass fiber ballistic helmets offer a balance of lightweight protection and affordability, making them common in law enforcement and military training environments where moderate threat levels are expected. Aramid fiber helmets, such as those made from Kevlar, provide superior impact resistance and higher ballistic protection, frequently deployed in combat zones and special operations where enhanced durability against higher-velocity projectiles is critical. Real-world testing reveals that aramid helmets outperform glass fiber variants in multi-hit scenarios and extreme conditions, although glass fiber remains popular due to cost-effectiveness and ease of production for widespread use.
Future Trends in Ballistic Helmet Materials
Advancements in ballistic helmet materials are increasingly focusing on hybrid composites combining glass fiber and aramid fiber to optimize strength, weight, and energy absorption. Emerging research highlights the potential of nano-enhanced aramid fibers for superior ballistic resistance and durability compared to traditional glass fiber composites. Future trends anticipate the integration of smart materials and bio-inspired designs to further improve impact mitigation and user comfort in ballistic helmets.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Aramid fiber for Ballistic helmet
 azmater.com
azmater.com