Wood plastic composites offer lightweight durability and resistance to rot, making them ideal for boat hulls. Glass fiber provides superior strength and stiffness, resulting in enhanced structural integrity and impact resistance for marine applications.
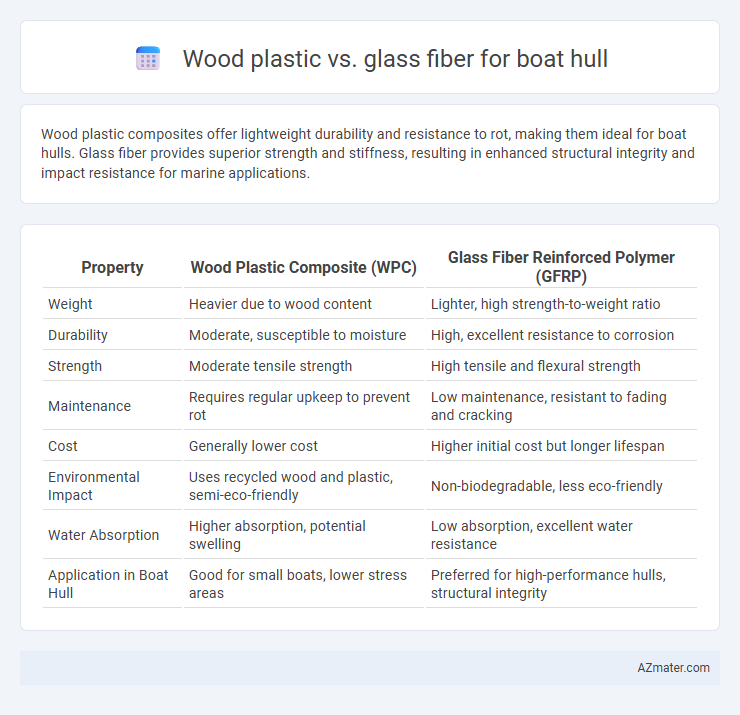
Table of Comparison
| Property | Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) | Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Heavier due to wood content | Lighter, high strength-to-weight ratio |
| Durability | Moderate, susceptible to moisture | High, excellent resistance to corrosion |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile and flexural strength |
| Maintenance | Requires regular upkeep to prevent rot | Low maintenance, resistant to fading and cracking |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher initial cost but longer lifespan |
| Environmental Impact | Uses recycled wood and plastic, semi-eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, less eco-friendly |
| Water Absorption | Higher absorption, potential swelling | Low absorption, excellent water resistance |
| Application in Boat Hull | Good for small boats, lower stress areas | Preferred for high-performance hulls, structural integrity |
Introduction: Comparing Modern Boat Hull Materials
Wood plastic composites offer enhanced rot resistance and lower maintenance compared to traditional wood hulls, making them a durable choice for marine environments. Glass fiber reinforced composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratios and excellent impact resistance, contributing to improved hull performance and longevity. Both materials influence boat hull design by balancing weight, durability, and cost for optimized marine applications.
Overview of Wood Plastic Composites in Boat Construction
Wood plastic composites (WPCs) offer enhanced durability and resistance to moisture, making them a promising material for boat hull construction compared to traditional wood. Their composition, combining wood fibers with thermoplastic polymers, provides improved impact resistance and reduced maintenance needs. WPCs also provide better environmental sustainability and design flexibility, positioning them as a viable alternative to glass fiber-reinforced composites in marine applications.
Advantages of Wood Plastic for Boat Hulls
Wood plastic composites offer superior resistance to rot, moisture, and corrosion compared to glass fiber, ensuring enhanced durability in marine environments. These materials provide excellent impact resistance and flexibility, reducing the risk of cracks and structural damage under stress. Additionally, wood plastic composites require less maintenance and promote sustainability through the utilization of recycled wood fibers.
Understanding Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastics (GFRP)
Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastics (GFRP) are composite materials combining glass fibers with a polymer matrix, providing high strength-to-weight ratios essential for boat hulls. Compared to wood plastic composites, GFRP offers superior durability, corrosion resistance, and low maintenance, making it ideal for marine environments. Its flexibility in shaping and excellent impact resistance contribute to enhanced hull performance and longevity.
Key Benefits of Glass Fiber Boat Hulls
Glass fiber boat hulls offer superior durability and resistance to corrosion compared to wood plastic composites, ensuring longer-lasting performance in marine environments. Their lightweight structure enhances fuel efficiency and maneuverability, while the high strength-to-weight ratio provides excellent impact resistance and structural integrity. Glass fiber materials also require minimal maintenance, reducing long-term repair costs and preserving hull aesthetics over time.
Durability: Wood Plastic vs Glass Fiber
Wood plastic composites offer moderate durability for boat hulls, resisting rot, corrosion, and UV damage better than traditional wood but are generally less impact-resistant than glass fiber. Glass fiber exhibits superior durability due to its high tensile strength, excellent resistance to water absorption, and ability to endure harsh marine environments without significant degradation. The long-term maintenance costs for glass fiber hulls tend to be lower because of their robustness and fewer repair requirements compared to wood plastic.
Weight and Performance Comparison
Wood plastic composites offer a lighter weight alternative to glass fiber, reducing overall boat hull mass and improving fuel efficiency. Glass fiber provides superior strength and stiffness, enhancing hull durability and performance in rough waters. The choice between wood plastic and glass fiber depends on the balance of weight savings and structural requirements for specific marine applications.
Maintenance Requirements: Ease and Cost
Wood plastic composites for boat hulls require minimal maintenance due to their resistance to rot, corrosion, and marine organisms, significantly reducing long-term upkeep costs compared to traditional materials. Glass fiber hulls, although durable and strong, often necessitate regular inspections, repairs to gel coat cracks, and preventative antifouling treatments, leading to higher maintenance efforts and expenses. The ease of cleaning and lower susceptibility to water damage make wood plastic composites a cost-effective choice for boat owners seeking reduced maintenance requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Wood plastic composites (WPC) for boat hulls offer a lower environmental impact due to their use of recycled wood fibers and plastics, reducing landfill waste and conserving natural resources. Glass fiber-reinforced composites typically have higher carbon footprints because of energy-intensive manufacturing processes and challenges in recycling fiberglass materials at end-of-life. WPCs demonstrate enhanced sustainability by providing a biodegradable alternative with potential for circular lifecycle management, whereas glass fiber hulls often contribute to environmental hazards through microplastic pollution and long-term disposal issues.
Choosing the Best Material for Your Boat Hull
Wood plastic composites offer excellent corrosion resistance and reduced maintenance for boat hulls, making them ideal for long-term durability in marine environments. Glass fiber reinforced composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratio and impact resistance, enhancing hull performance and safety. Selecting between wood plastic and glass fiber hinges on balancing factors like weight, durability, maintenance, and environmental exposure to optimize hull longevity and boat efficiency.
Infographic: Wood plastic vs Glass fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com