Glass fiber offers superior strength, water resistance, and durability for boat hulls compared to wood fiber, which is more prone to rot and requires frequent maintenance. Glass fiber composites provide enhanced structural integrity and longer service life in marine environments, making them the preferred choice for modern boat construction.
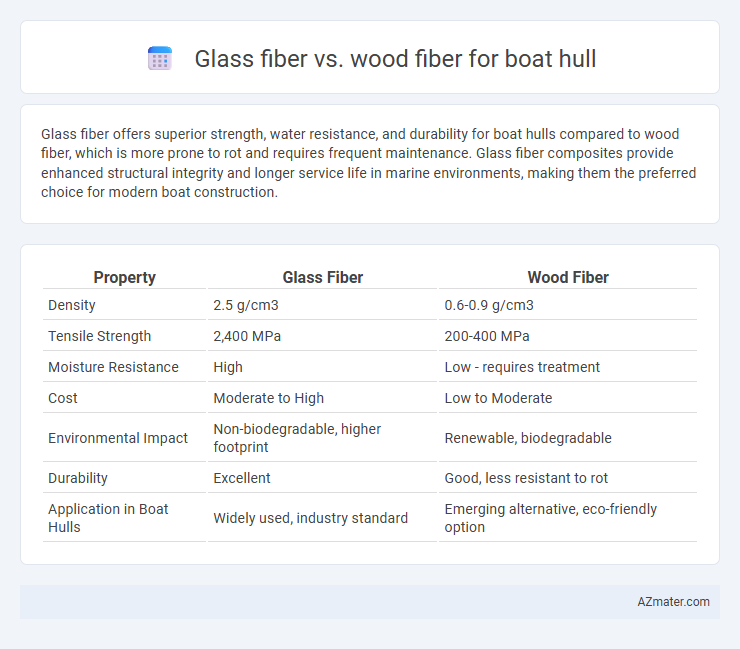
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber | Wood Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 | 0.6-0.9 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 2,400 MPa | 200-400 MPa |
| Moisture Resistance | High | Low - requires treatment |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, higher footprint | Renewable, biodegradable |
| Durability | Excellent | Good, less resistant to rot |
| Application in Boat Hulls | Widely used, industry standard | Emerging alternative, eco-friendly option |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Boat hull materials primarily consist of glass fiber and wood fiber, each offering distinct advantages for marine applications. Glass fiber composites provide superior strength-to-weight ratios, high durability, and excellent resistance to water, making them ideal for modern boat hulls. Wood fiber, while traditional and environmentally friendly, tends to require more maintenance and offers lower resistance to moisture and impact compared to glass fiber.
Overview of Glass Fiber Construction
Glass fiber construction for boat hulls offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced durability compared to wood fiber, making it a preferred material in modern marine applications. The composite structure consists of woven glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, providing excellent resistance to water absorption, corrosion, and impact damage. Its low maintenance requirements and ability to form complex shapes contribute to improved hydrodynamics and long-term performance in harsh marine environments.
Overview of Wood Fiber Construction
Wood fiber construction for boat hulls utilizes natural fibers derived from wood pulp or composites, offering enhanced biodegradability and sustainability compared to synthetic materials. These fibers provide good mechanical strength and impact resistance while maintaining lightweight characteristics essential for hull performance and fuel efficiency. Wood fiber composites often exhibit superior sound-dampening and thermal insulation properties, contributing to improved onboard comfort.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Glass fiber offers superior strength and durability for boat hulls, exhibiting high tensile strength and excellent resistance to impact, fatigue, and water absorption. Wood fiber, while providing a natural aesthetic and some degree of flexibility, generally lacks the structural robustness and long-term resilience of glass fiber, making it more prone to rot, swelling, and degradation in marine environments. The inherent corrosion resistance and low maintenance of glass fiber composites make them the preferred choice for high-performance and long-lasting boat hulls.
Weight and Performance Differences
Glass fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to wood fiber, making boat hulls lighter and more durable under stress. Wood fiber, while heavier and less resistant to water damage, provides natural insulation and vibration dampening but requires more maintenance to prevent rot. The performance advantages of glass fiber include enhanced hydrodynamics due to smoother surfaces and improved longevity, which contribute to faster speeds and reduced fuel consumption.
Maintenance Requirements
Glass fiber boat hulls require less frequent maintenance due to their resistance to rot, corrosion, and marine organisms, making them ideal for long-term durability. Wood fiber hulls demand regular inspections and treatments with sealants or preservatives to prevent water damage, rot, and infestation by marine borers. Effective maintenance of wood fiber involves more labor-intensive upkeep compared to the relatively low-maintenance nature of glass fiber.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Glass fiber, derived from silica sand and other minerals, presents challenges in recyclability and energy-intensive manufacturing processes, leading to higher environmental impact compared to wood fiber. Wood fiber, sourced from sustainably managed forests, offers biodegradability and carbon sequestration benefits, making it a more sustainable material for boat hulls. Choosing wood fiber reduces carbon footprint and supports circular economy principles in marine construction.
Cost Analysis: Glass Fiber vs. Wood Fiber
Glass fiber boat hulls typically incur higher initial material costs, averaging $5 to $8 per pound, compared to wood fiber, which can cost between $2 to $4 per pound depending on the species and treatment. Maintenance expenses for glass fiber tend to be lower over time due to its resistance to rot and corrosion, while wood fiber requires regular sealing and repairs, increasing lifecycle costs. Factoring in both upfront and ongoing expenses, glass fiber often presents a more cost-effective solution despite the higher initial investment, especially for long-term durability and reduced labor costs.
Suitability for Different Boat Types
Glass fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to water absorption, making it ideal for high-performance speedboats, yachts, and commercial vessels requiring durability and low maintenance. Wood fiber provides excellent natural insulation and vibration damping, suitable for traditional wooden boats, small recreational crafts, and applications where aesthetics and repairability are priorities. The choice between glass fiber and wood fiber depends on boat type, with glass fiber favored for structural integrity in demanding marine environments and wood fiber preferred for classic design and comfort.
Final Considerations and Recommendations
Glass fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced durability for boat hulls compared to wood fiber, reducing maintenance needs and increasing longevity. Wood fiber provides natural aesthetics and environmental benefits but requires more frequent upkeep and is susceptible to rot and swelling in marine conditions. For long-term performance and resilience, glass fiber remains the preferred choice in modern boat hull construction.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Wood fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com