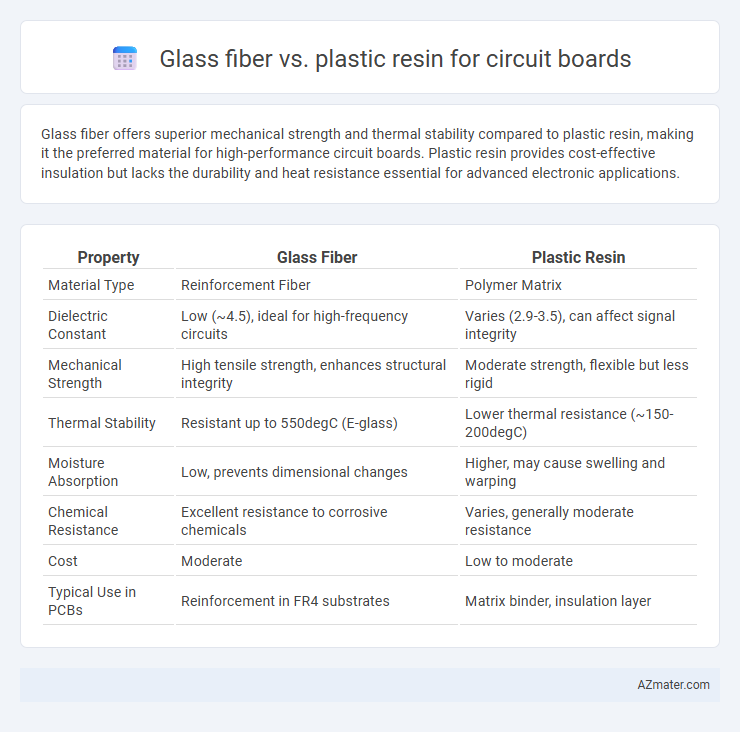
Glass fiber offers superior mechanical strength and thermal stability compared to plastic resin, making it the preferred material for high-performance circuit boards. Plastic resin provides cost-effective insulation but lacks the durability and heat resistance essential for advanced electronic applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber | Plastic Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Reinforcement Fiber | Polymer Matrix |
| Dielectric Constant | Low (~4.5), ideal for high-frequency circuits | Varies (2.9-3.5), can affect signal integrity |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, enhances structural integrity | Moderate strength, flexible but less rigid |
| Thermal Stability | Resistant up to 550degC (E-glass) | Lower thermal resistance (~150-200degC) |
| Moisture Absorption | Low, prevents dimensional changes | Higher, may cause swelling and warping |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to corrosive chemicals | Varies, generally moderate resistance |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Typical Use in PCBs | Reinforcement in FR4 substrates | Matrix binder, insulation layer |
Introduction to Circuit Board Materials
Glass fiber and plastic resin are fundamental materials used in the construction of circuit boards, each contributing unique properties. Glass fiber offers superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and electrical insulation, making it ideal for high-performance printed circuit boards (PCBs). Plastic resin, commonly epoxy-based, acts as a binding matrix providing flexibility, adhesive properties, and dielectric insulation necessary for embedding the glass fibers and forming the laminate structure.
What is Glass Fiber?
Glass fiber is a reinforcing material composed of numerous fine fibers of glass that enhance the mechanical strength and thermal stability of circuit boards. In printed circuit boards (PCBs), glass fiber provides superior rigidity and dimensional stability compared to plastic resin alone, making it essential for high-performance electronics. The use of woven glass fiber mats embedded in resin-based substrates significantly improves resistance to heat, moisture, and electrical insulation properties.
Understanding Plastic Resin in PCBs
Plastic resin in PCBs serves as a crucial insulating material that binds fibers and provides structural integrity, typically made from epoxy, phenolic, or polyimide compounds. Its dielectric properties ensure electrical insulation between conductive layers, while its thermal stability supports reliable performance in varying temperatures. Compared to glass fiber, plastic resin primarily influences flexibility and cost, making it essential in determining the PCB's overall durability and electrical efficiency.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Glass fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and thermal resistance compared to plastic resin, making it ideal for high-performance circuit boards subjected to mechanical stress and elevated temperatures. The composite nature of glass fiber-reinforced materials enhances durability by preventing warping and maintaining structural integrity over extended periods. In contrast, plastic resin alone typically offers less strength and lower resistance to environmental factors, leading to reduced lifespan in demanding electronic applications.
Electrical Performance Differences
Glass fiber-reinforced circuit boards offer superior electrical insulation and higher dielectric strength compared to plastic resin counterparts, reducing signal loss and enhancing high-frequency performance. Plastic resin circuit boards typically exhibit lower thermal stability and higher dielectric constant, which can lead to increased signal attenuation and electromagnetic interference. For applications demanding consistent electrical performance and reliability under varying thermal conditions, glass fiber materials are optimal.
Thermal Resistance and Stability
Glass fiber exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to plastic resin, maintaining structural integrity under higher temperatures typically above 130degC, essential for circuit boards exposed to intense heat during operation. It offers enhanced thermal stability, reducing the risk of deformation, delamination, or material degradation that can compromise circuit reliability and lifespan. Plastic resin, while cost-effective and easier to mold, generally has lower heat tolerance and can experience thermal expansion and mechanical stress under high-temperature conditions, making glass fiber the preferred choice for high-performance circuit boards requiring robust thermal management.
Manufacturing Process and Cost
Glass fiber reinforced circuit boards offer superior mechanical strength and thermal stability due to the woven fiberglass mats used in the manufacturing process, which enhances durability in high-performance applications. Plastic resin boards, typically made from epoxy or phenolic resins without glass reinforcement, present a lower-cost alternative with simpler processing but reduced structural integrity and heat resistance. Manufacturing glass fiber PCBs involves more complex lamination and curing steps, increasing production time and expenses compared to the streamlined, cost-effective molding process of plastic resin boards.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Glass fiber used in circuit boards offers superior durability and thermal stability compared to plastic resin, resulting in longer product lifespans and reduced electronic waste. Plastic resin, often derived from petrochemicals, has a higher carbon footprint and lower recyclability, contributing to environmental pollution. Selecting glass fiber composites enhances sustainability by enabling easier recycling and minimizing hazardous material leaching in electronic manufacturing.
Application Suitability and Use Cases
Glass fiber offers superior mechanical strength and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-performance circuit boards used in aerospace, automotive, and industrial electronics. Plastic resin, such as epoxy or phenolic, provides cost-effective insulation and flexibility, suitable for consumer electronics and low-frequency applications. The choice depends on environmental conditions, electrical requirements, and budget constraints, with glass fiber favored for durability and plastic resin for economical manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Circuit Board
Selecting the right material for your circuit board critically impacts performance, durability, and cost-efficiency. Glass fiber offers superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and electrical insulation, making it ideal for high-frequency and high-power applications, while plastic resin provides flexibility, lower cost, and ease of manufacturing suitable for low-demand or prototype circuits. Evaluating specific requirements such as operating temperature, electrical conductivity, and environmental exposure ensures optimal material choice between glass fiber and plastic resin for reliable circuit board functionality.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Plastic resin for Circuit board
 azmater.com
azmater.com